SpringCloud Bus消息总线
@[toc](SpringCloud Bus消息总线)
这篇主要是为了配合上一篇SpringCloudConfig分布式配置中心实现配置的动态刷新功能。
衔接这一篇文章:SpringCloud Config分布式配置中心
仓库地址:Gitee仓库地址
1、SpringCloud Bus概述
1.1 什么是SpringCloud Bus?
Spring Cloud Bus是用来将分布式系统的节点与轻量级消息系统链接起来的框架,它整合了Java的事件处理机制和消息中间件的功能。Spring Clud Bus目前支持RabbitMQ和Kafka。
Spring Cloud Bus 配合 Spring Cloud Config 使用可以实现配置的动态刷新。

1.2 Bus能做什么?
Spring Cloud Bus能管理和传播分布式系统间的消息,就像一个分布式执行器,可用于广播状态更改、事件推送等,也可以当作微服务间的通信通道。
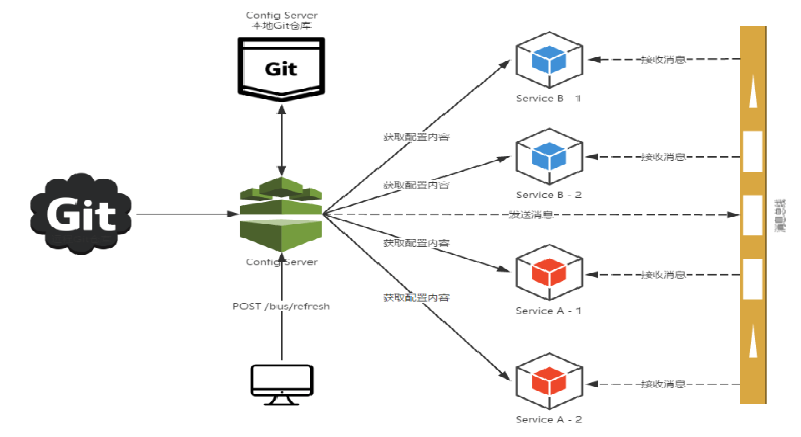
1.3 为什么被称为总线?
1.3.1 什么是总线?
在微服务架构的系统中,通常会使用轻量级的消息代理来构建一个共用的消息主题,并让系统中所有微服务实例都连接上来。由于该主题中产生的消息会被所有实例监听和消费,所以称它为消息总线。在总线上的各个实例,都可以方便地广播一些需要让其他连接在该主题上的实例都知道的消息。
1.3.2 基本原理
ConfigClient实例都监听MQ中同一个topic(默认是springCloudBus)。当一个服务刷新数据的时候,它会把这个信息放入到Topic中,这样其它监听同一Topic的服务就能得到通知,然后去更新自身的配置。
有关RabbitMQ的安装我就不赘述了。
2、SpringCloud Bus动态刷新全局广播
这里假定你已经配置好了RabbitMQ的环境
2.1 新建cloud-config-client-3366,演示广播效果
pom.xml:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
bootstrap.yml:
server:
port: 3366
spring:
application:
name: config-client
cloud:
#Config客户端配置
config:
label: master #分支名称
name: config #配置文件名称
profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml
uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址
#服务注册到eureka地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
# 暴露监控端点
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
主启动类:
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigClientMain3366
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientMain3366.class,args);
}
}
Controller:
@RestController
@RefreshScope
public class ConfigClientController
{
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@Value("${config.info}")
private String configInfo;
@GetMapping("/configInfo")
public String configInfo()
{
return "serverPort: "+serverPort+"\t\n\n configInfo: "+configInfo;
}
}
2.2 设计思想
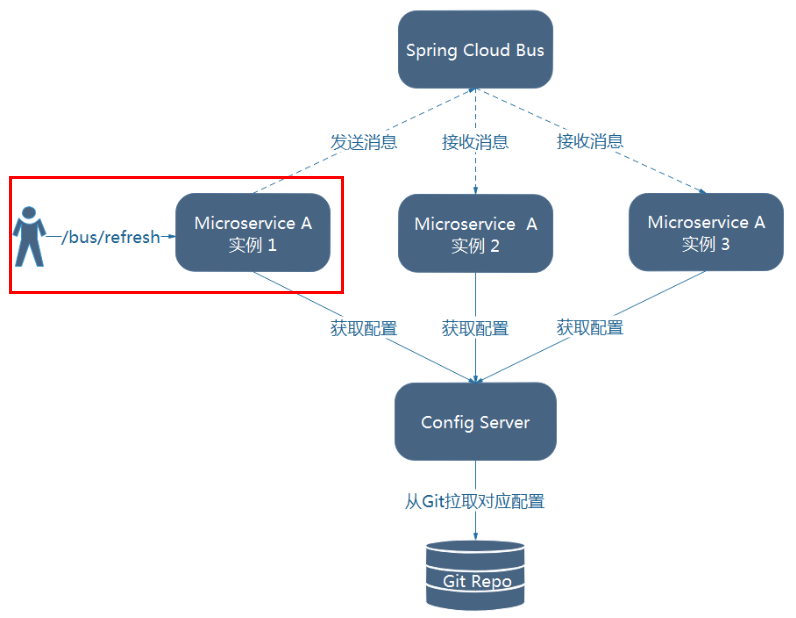
- 1)利用消息总线触发一个客户端/bus/refresh,而刷新所有客户端的配置
- 2)利用消息总线触发一个服务端ConfigServer的/bus/refresh端点,而刷新所有客户端的配置
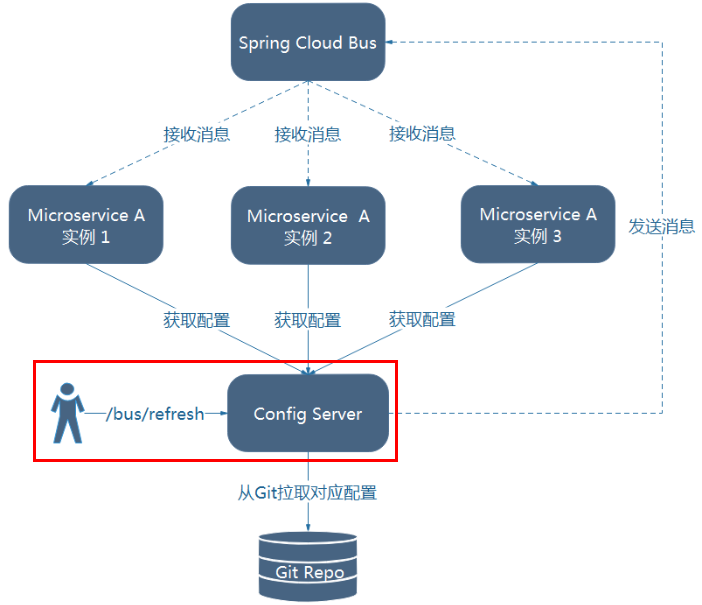
第二种架构方式显然更适合,第一种不适合的原因如下:
- 打破了微服务的职责单一性,因为微服务本身是业务模块,它本不应该承担配置刷新的职责。
- 破坏了微服务各节点的对等性。
- 有一定的局限性。例如,微服务在迁移时,它的网络地址常常会发生变化,此时如果想要做到自动刷新,那就会增加更多的修改
2.3 给cloud-config-center-3344配置中心服务端添加消息总线支持
pom:
<!--添加消息总线RabbitMQ支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml:
server:
port: 3344
spring:
application:
name: cloud-config-center #注册进Eureka服务器的微服务名
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: git@gitee.com:interface_xiongtete/springcloud-config.git #Gitee上面的git仓库名字
####搜索目录
search-paths:
- springcloud-config
####读取分支
label: master
#rabbitmq相关配置
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#服务注册到eureka地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
##rabbitmq相关配置,暴露bus刷新配置的端点
management:
endpoints: #暴露bus刷新配置的端点
web:
exposure:
include: 'bus-refresh'
2.4 给cloud-config-client-3355客户端添加消息总线支持
pom.xml
<!--添加消息总线RabbitMQ支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
bootstrap.yml
server:
port: 3355
spring:
application:
name: config-client
cloud:
#Config客户端配置
config:
label: master #分支名称
name: config #配置文件名称
profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml
uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址k
#rabbitmq相关配置 15672是Web管理界面的端口;5672是MQ访问的端口
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#服务注册到eureka地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
# 暴露监控端点
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
2.5 给cloud-config-client-3366客户端添加消息总线支持
pom.xml
<!--添加消息总线RabbitMQ支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
bootstrap.yml
server:
port: 3366
spring:
application:
name: config-client
cloud:
#Config客户端配置
config:
label: master #分支名称
name: config #配置文件名称
profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml
uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址
#rabbitmq相关配置 15672是Web管理界面的端口;5672是MQ访问的端口
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#服务注册到eureka地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
# 暴露监控端点
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
2.6 测试
我们先启动配置后者你敢信和两个客户端
访问配置中心:http://config-3344.com:3344/config-dev.yml
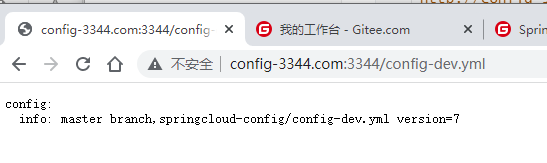
访问客户端:http://localhost:3355/configInfo
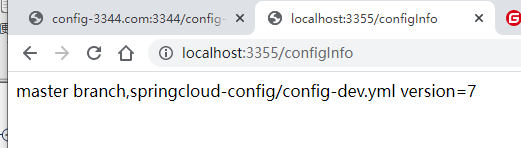
http://localhost:3366/configInfo
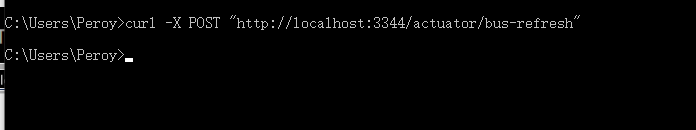
此时修改远端仓库中的文件版本号,将version改为8
使用curl发送请求:curl -X POST “http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh”
一次发送,处处生效
此时再查看配置中心:http://config-3344.com:3344/config-dev.yml
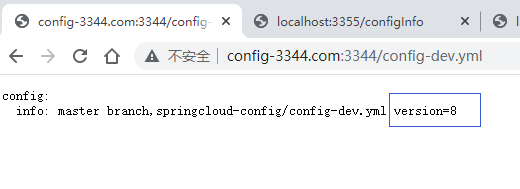
查看两个客户端的配置是否都已经更新:
http://localhost:3355/configInfo
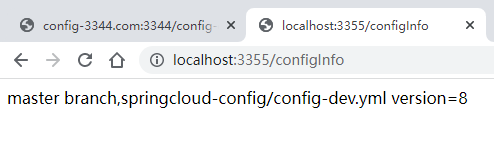
http://localhost:3366/configInfo
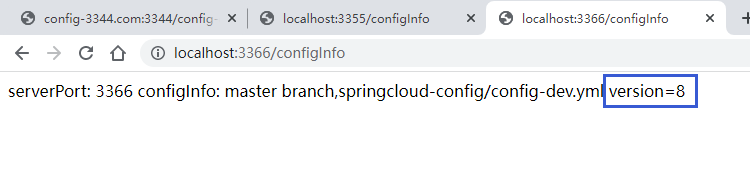
可以看到,配置都已经刷新成功了。有关RabbitMQ的知识在此不做过多介绍,去查看我消息队列的专栏。
这种方式是触发服务端端点实现所有客户端配置刷新,那能不能指定某个服务刷新呢,当然可以。
3、SpringCloud Bus动态刷新定点通知
3.1 需求
我们现在的需求是配置更新以后,不想全部通知,只通知3355,不通知3366
其实就是指定具体某一个实例生效而不是全部。
公式:http://localhost:配置中心的端口号/actuator/bus-refresh/{destination}
/bus/refresh请求不再发送到具体的服务实例上,而是发给config server并通过destination参数类指定需要更新配置的服务或实例
3.2 案例演示
我们这里以刷新运行在3355端口上的config-client为例,只通知3355,不通知3366
现在修改远程仓库中的配置,将version由8改成9
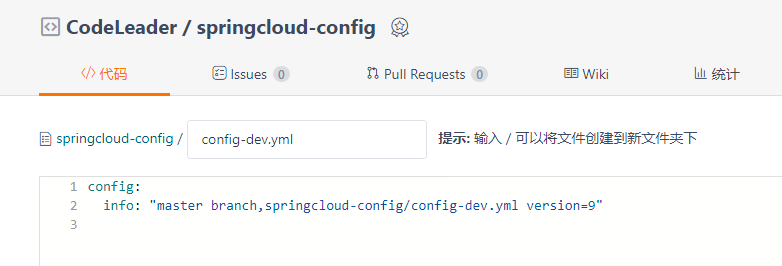
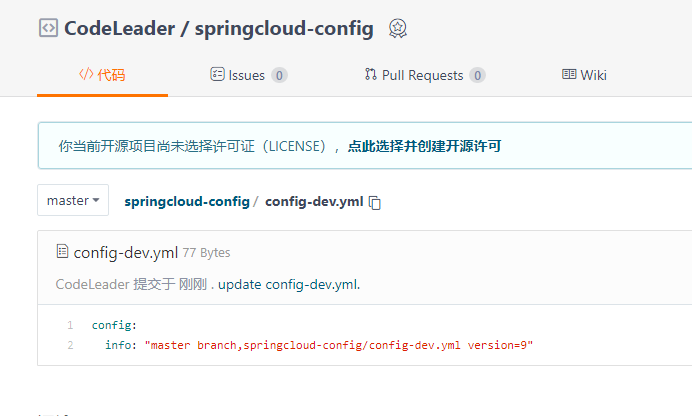
只通知3355:curl -X POST "http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh/config-client:3355"
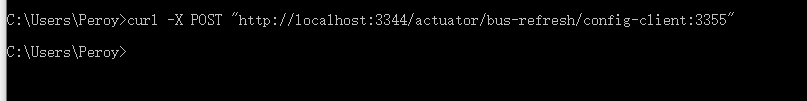
访问配置中心:http://config-3344.com:3344/config-dev.yml
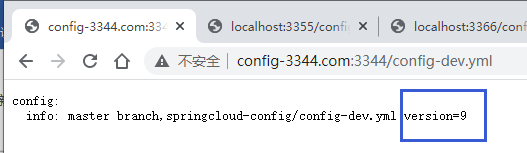
访问客户端
3355:http://localhost:3355/configInfo
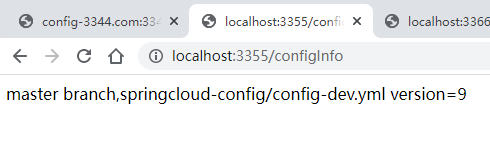
3355端口的微服务已经更新了version。
3366:http://localhost:3366/configInfo
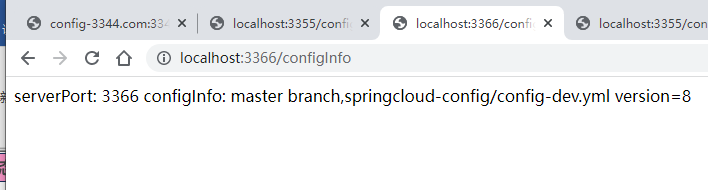
发现3366微服务的端口号并没有更新,还是version=8,并没有和远程仓库中version=9保持一致。说明我们定点通知的配置是正确的。
3.3 流程图
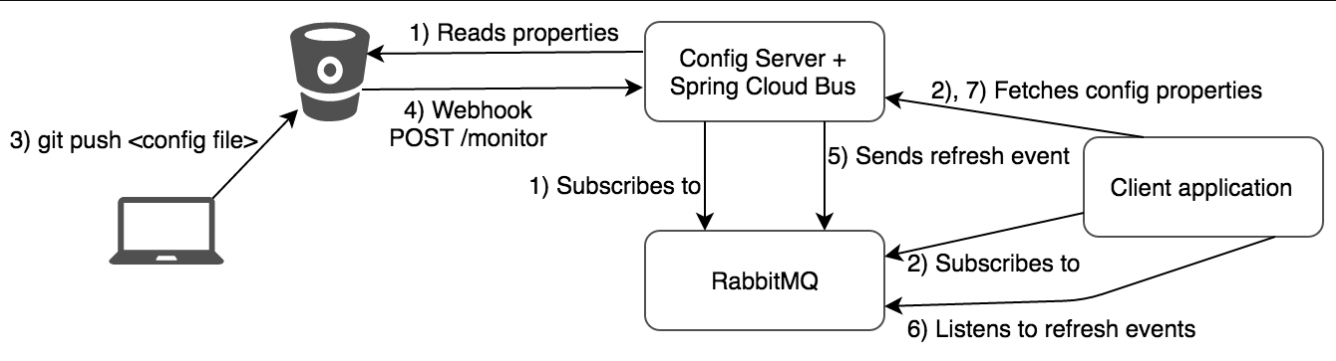
到此,我们SpringCloud Bus配合SpringCloud Config实现配置动态刷新就介绍完了,这里只是讲了点皮毛,更高级的东西需要我们在开发过程中去挖掘和提炼。就比如消息队列这块,RabbitMQ和Kafka这都已经是前置知识了。微服务中间件这么多,技术也一直在更新迭代,学起来很容易,但技术是学不完的。如何进行技术选型?项目如何落地实现等等都是我们要深入思考的东西。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)