LSTM应用于MNIST数据集分类
【摘要】 @toc 1、概述 LSTM网络是序列模型,一般比较适合处理序列问题。这里把它用于手写数字图片的分类,其实就相当于把图片看作序列。 一张MNIST数据集的图片是28×2828\times 2828×28的大小,我们可以把每一行看作是一个序列输入,那么一张图片就是28行,序列长度为28;每一行有28个数据,每个序列输入28个值。 这里我们可以将LSTM和CNN的代码结果进行对比。 2、L...
@toc
1、概述
LSTM网络是序列模型,一般比较适合处理序列问题。这里把它用于手写数字图片的分类,其实就相当于把图片看作序列。
一张MNIST数据集的图片是 的大小,我们可以把每一行看作是一个序列输入,那么一张图片就是28行,序列长度为28;每一行有28个数据,每个序列输入28个值。
这里我们可以将LSTM和CNN的代码结果进行对比。
2、LSTM实现
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM,Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2.1 载入数据集
# 载入数据集
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
# 载入数据,数据载入的时候就已经划分好训练集和测试集
# 训练集数据x_train的数据形状为(60000,28,28)
# 训练集标签y_train的数据形状为(60000)
# 测试集数据x_test的数据形状为(10000,28,28)
# 测试集标签y_test的数据形状为(10000)
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 对训练集和测试集的数据进行归一化处理,有助于提升模型训练速度
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# 把训练集和测试集的标签转为独热编码
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train,num_classes=10)
y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test,num_classes=10)
# 数据大小-一行有28个像素
input_size = 28
# 序列长度-一共有28行
time_steps = 28
# 隐藏层memory block个数
cell_size = 50
2.2 创建模型
# 创建模型
# 循环神经网络的数据输入必须是3维数据
# 数据格式为(数据数量,序列长度,数据大小)
# 载入的mnist数据的格式刚好符合要求
# 注意这里的input_shape设置模型数据输入时不需要设置数据的数量
model = Sequential([
LSTM(units=cell_size,input_shape=(time_steps,input_size),return_sequences=True),
Dropout(0.2),
LSTM(cell_size),
Dropout(0.2),
# 50个memory block输出的50个值跟输出层10个神经元全连接
Dense(10,activation=tf.keras.activations.softmax)
])
2.3 定义优化器
adam = Adam(lr=1e-3)
2.4 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer=adam,loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
2.5 训练模型
history=model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=64,epochs=10,validation_data=(x_test,y_test))
2.6 打印模型摘要
model.summary()

2.7 绘制acc和loss曲线
loss=history.history['loss']
val_loss=history.history['val_loss']
accuracy=history.history['accuracy']
val_accuracy=history.history['val_accuracy']
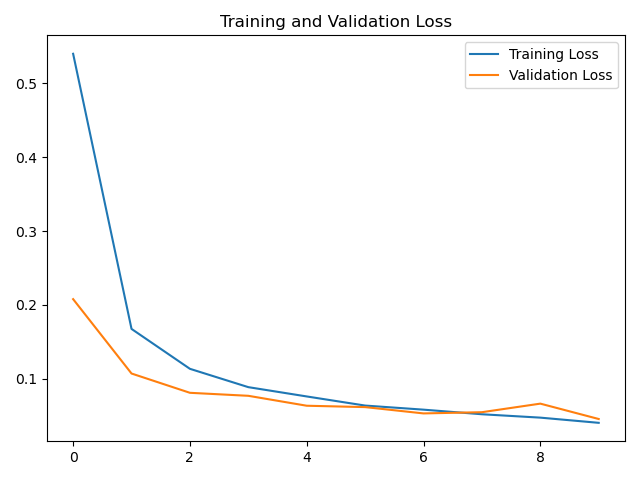
# 绘制loss曲线
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 绘制acc曲线
plt.plot(accuracy, label='Training accuracy')
plt.plot(val_accuracy, label='Validation accuracy')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
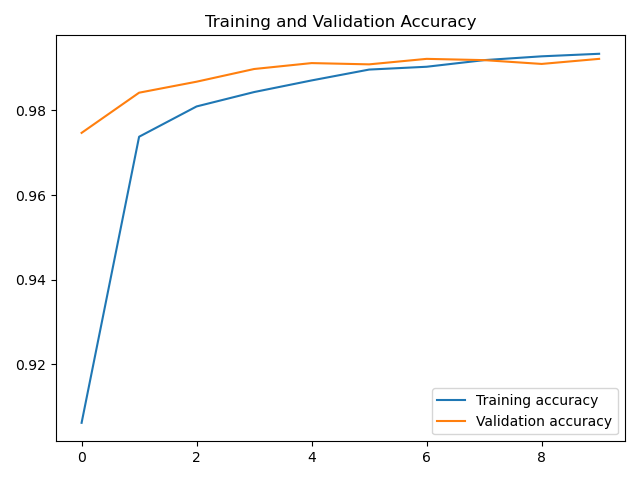

LSTM应用于MNIST数据识别也可以得到不错的结果,但当然没有卷积神经网络得到的结果好。
3、CNN实现
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,Dropout,Convolution2D,MaxPooling2D,Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 载入数据
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
# 载入数据,数据载入的时候就已经划分好训练集和测试集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 这里要注意,在tensorflow中,在做卷积的时候需要把数据变成4维的格式
# 这4个维度是(数据数量,图片高度,图片宽度,图片通道数)
# 所以这里把数据reshape变成4维数据,黑白图片的通道数是1,彩色图片通道数是3
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1,28,28,1)/255.0
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1,28,28,1)/255.0
# 把训练集和测试集的标签转为独热编码
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train,num_classes=10)
y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test,num_classes=10)
# 定义顺序模型
model = Sequential()
# 第一个卷积层
# input_shape 输入数据
# filters 滤波器个数32,生成32张特征图
# kernel_size 卷积窗口大小5*5
# strides 步长1
# padding padding方式 same/valid
# activation 激活函数
model.add(Convolution2D(
input_shape = (28,28,1),
filters = 32,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = 1,
padding = 'same',
activation = 'relu'
))
# 第一个池化层
# pool_size 池化窗口大小2*2
# strides 步长2
# padding padding方式 same/valid
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size = 2,strides = 2,padding = 'same'))
# 第二个卷积层
# filters 滤波器个数64,生成64张特征图
# kernel_size 卷积窗口大小5*5
# strides 步长1
# padding padding方式 same/valid
# activation 激活函数
model.add(Convolution2D(64,5,strides=1,padding='same',activation='relu'))
# 第二个池化层
# pool_size 池化窗口大小2*2
# strides 步长2
# padding padding方式 same/valid
model.add(MaxPooling2D(2,2,'same'))
# 把第二个池化层的输出进行数据扁平化
# 相当于把(64,7,7,64)数据->(64,7*7*64)
model.add(Flatten())
# 第一个全连接层
model.add(Dense(1024,activation = 'relu'))
# Dropout
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
# 第二个全连接层
model.add(Dense(10,activation='softmax'))
# 定义优化器
adam = Adam(lr=1e-4)
# 定义优化器,loss function,训练过程中计算准确率
model.compile(optimizer=adam,loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
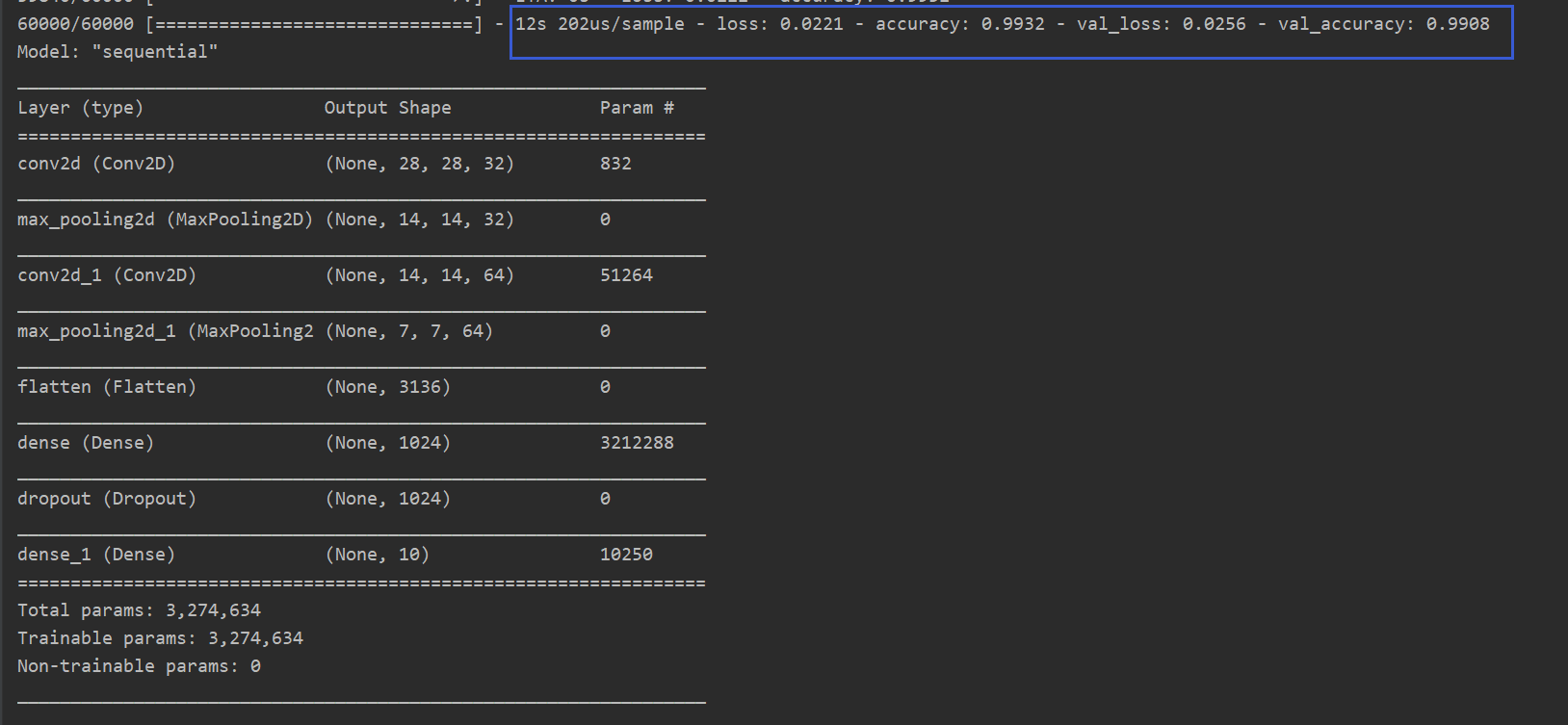
history=model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=64,epochs=10,validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
# 保存模型
model.save('mnist_cnn.h5')
#打印模型摘要
model.summary()
loss=history.history['loss']
val_loss=history.history['val_loss']
accuracy=history.history['accuracy']
val_accuracy=history.history['val_accuracy']
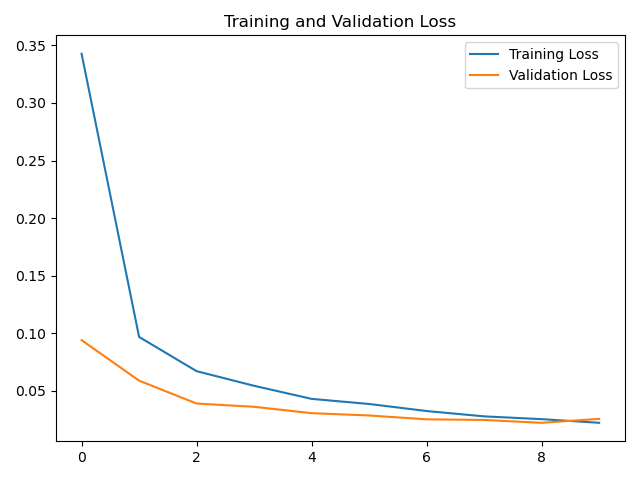
# 绘制loss曲线
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 绘制acc曲线
plt.plot(accuracy, label='Training accuracy')
plt.plot(val_accuracy, label='Validation accuracy')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
模型摘要
loss曲线
acc曲线

从结果来看,CNN确实比LSTM更适合MNIST数据集的分类。
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)