卷积神经网络模型之——GoogLeNet网络结构与代码实现
@[TOC]
GoogLeNet网络简介
GoogLeNet原文地址:Going Deeper with Convolutions:https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Szegedy_Going_Deeper_With_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf

GoogLeNet在2014年由Christian Szegedy提出,它是一种全新的深度学习结构。
GoogLeNet网络的主要创新点在于:
-
提出Inception结构在多个尺寸上同时进行卷积再聚合;

-
使用1X1的卷积进行降维以及映射处理;
-
添加两个辅助分类器帮助训练;
辅助分类器是将中间某一层的输出用作分类,并按一个较小的权重加到最终分类结果中。 -
使用平均池化层代替全连接层,大大减少了参数量。
GoogLeNet网络结构
GoogLeNet的完整网络结构如下所示:

下面我们将其逐层拆分讲解并结合代码分析
Inception之前的几层结构
在进入Inception结构之前,GoogLeNet网络先堆叠了两个卷积(实则3个,有一个1X1的卷积)和两个最大池化层。
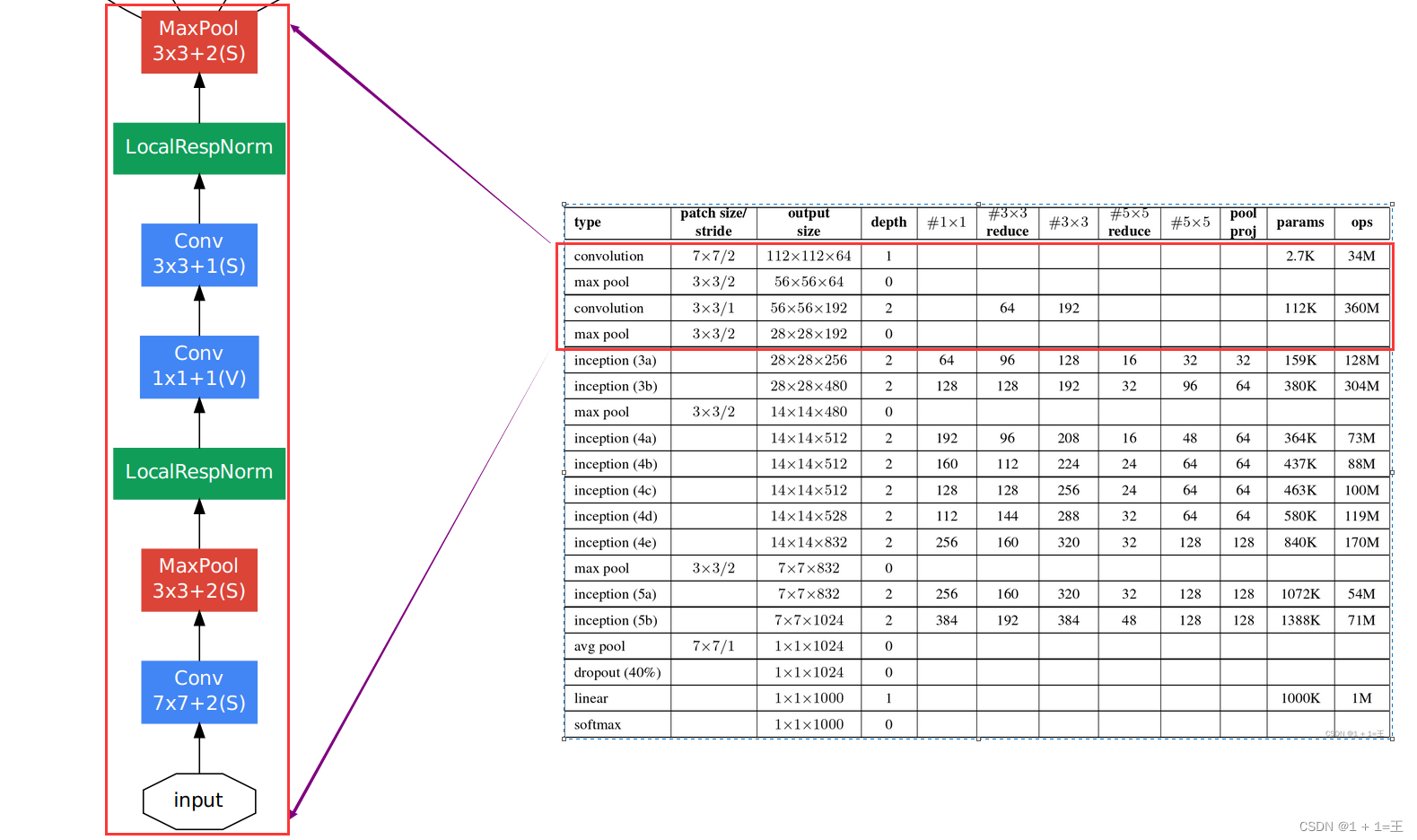
# input(3,224,224)
self.front = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3), # output(64,112,112)
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2,ceil_mode=True), # output(64,56,56)
nn.Conv2d(64,64,kernel_size=1),
nn.Conv2d(64,192,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), # output(192,56,56)
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2,ceil_mode=True), # output(192,28,28)
)
Inception结构
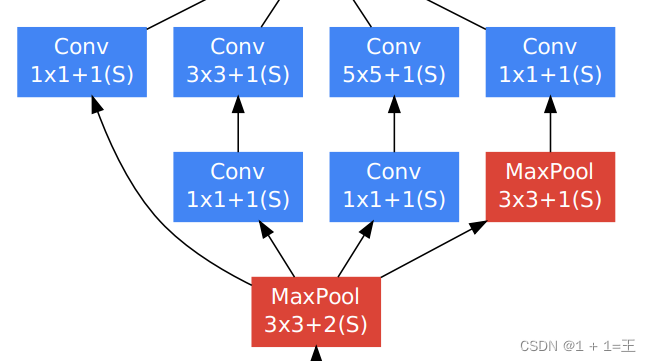
==Inception模块只会改变特征图的通道数,而不会改变尺寸大小。==
Inception结构相对复杂,我们重新创建一个类来构建此结构,并通过参数不同的参数来控制各层的通道数。
class Inception(nn.Module):
'''
in_channels: 输入通道数
out1x1:分支1输出通道数
in3x3:分支2的3x3卷积的输入通道数
out3x3:分支2的3x3卷积的输出通道数
in5x5:分支3的5x5卷积的输入通道数
out5x5:分支3的5x5卷积的输出通道数
pool_proj:分支4的最大池化层输出通道数
'''
def __init__(self,in_channels,out1x1,in3x3,out3x3,in5x5,out5x5,pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out1x1, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in3x3,kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in3x3,out3x3,kernel_size=3,padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in5x5, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in5x5, out5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,pool_proj,kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self,x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1,branch2,branch3,branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs,1) # 按通道数叠加
Inception3a模块
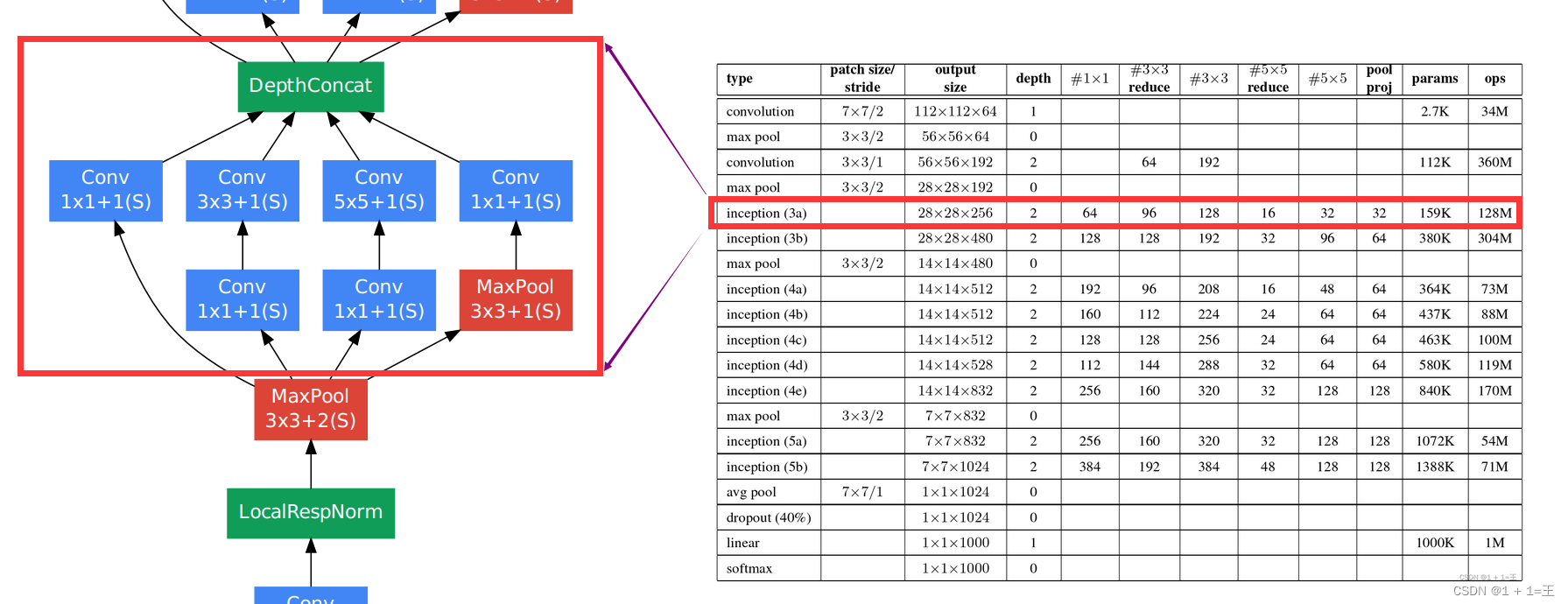
# input(192,28,28)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32) # output(256,28,28)
Inception3b + MaxPool

# input(256,28,28)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64) # output(480,28,28)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # output(480,14,14)
Inception4a
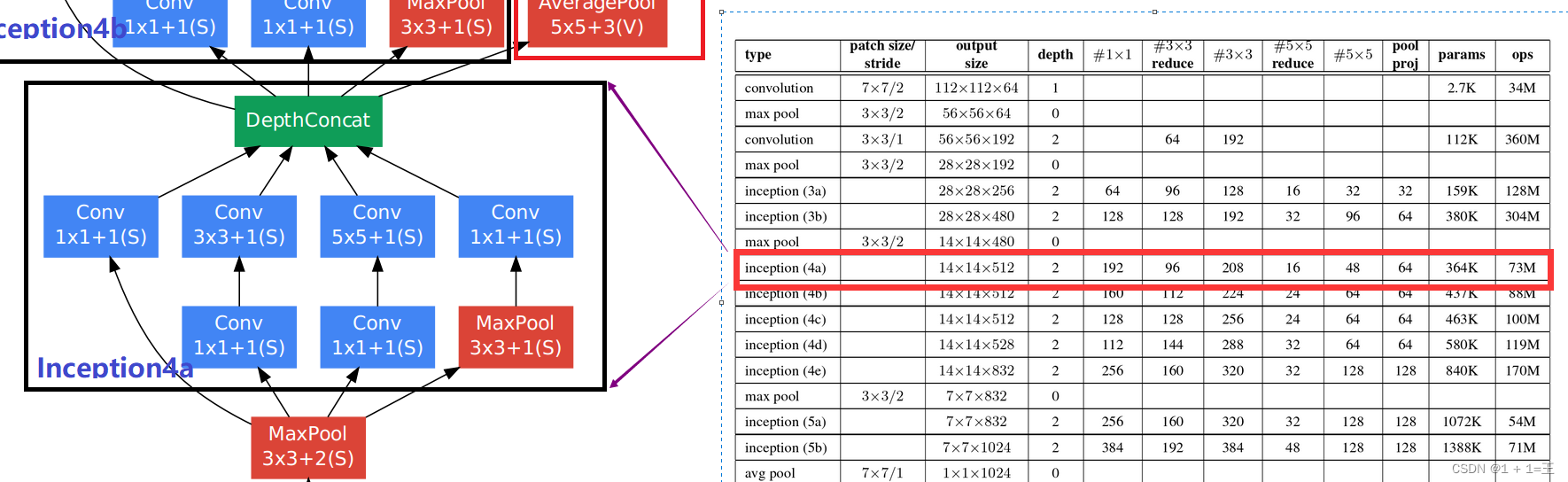
# input(480,14,14)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64) # output(512,14,14)
Inception4b
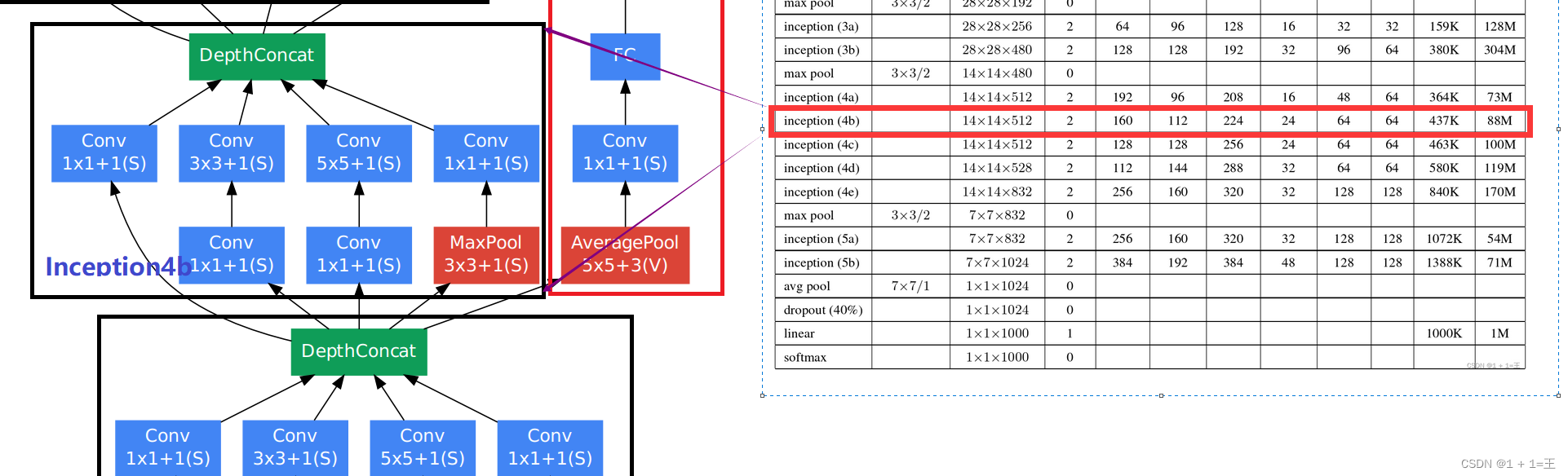
# input(512,14,14)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64) # output(512,14,14)
Inception4c

# input(512,14,14)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64) # output(512,14,14)
Inception4d
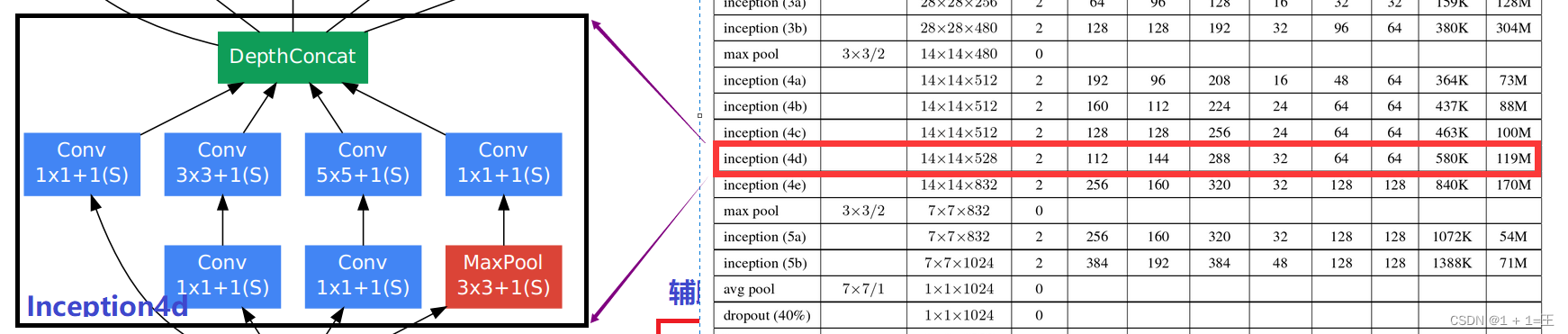
# input(512,14,14)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64) # output(528,14,14)
Inception4e+MaxPool
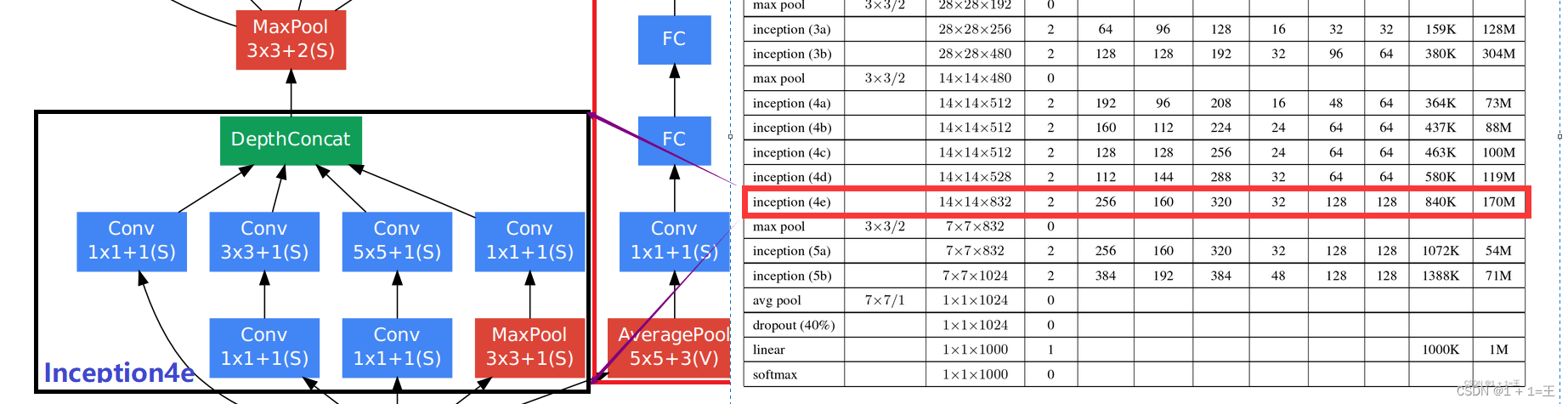
# input(528,14,14)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128) # output(832,14,14)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # output(832,7,7)
Inception5a
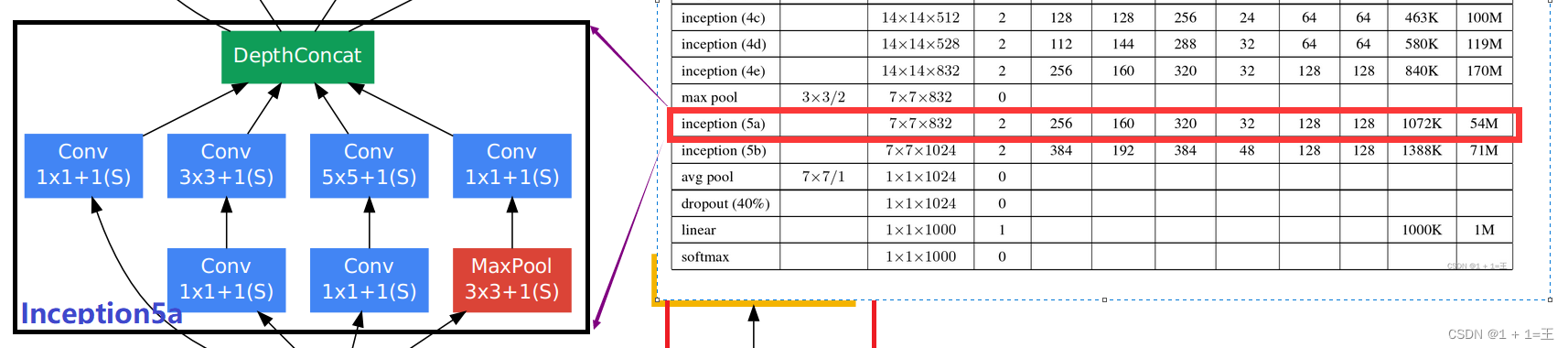
# input(832,7,7)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128) # output(832,7,7)
Inception5b

# input(832,7,7)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128) # output(1024,7,7)
Inception之后的几层结构
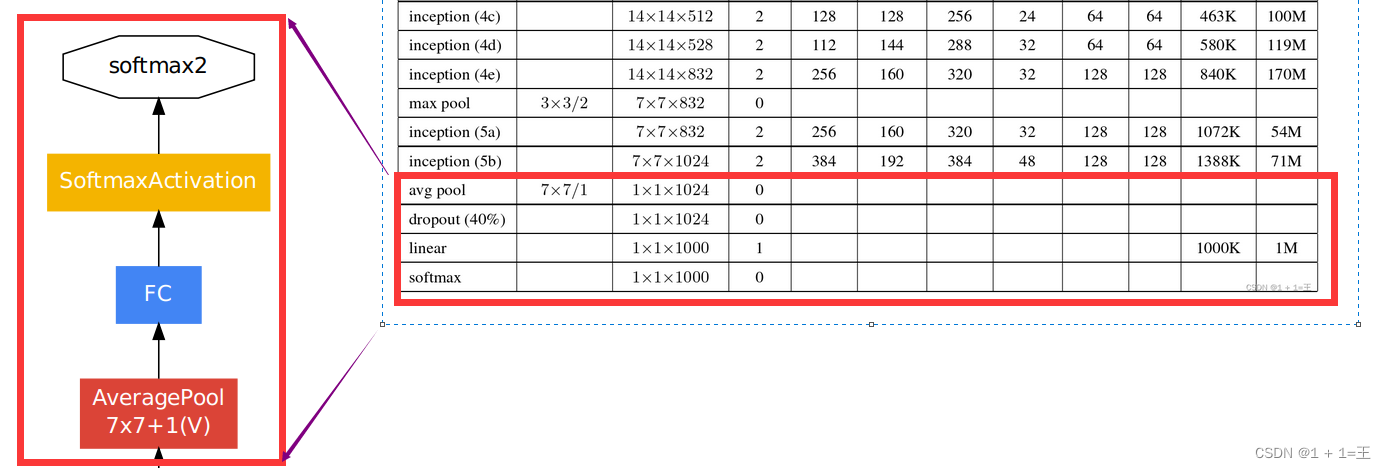
辅助分类模块
除了以上主干网络结构以外,GoogLeNet还提供了两个辅助分类模块,用于将中间某一层的输出用作分类,并按一个较小的权重(0.3)加到最终分类结果。
与Inception模块一样,我们也重新创建一个类来搭建辅助分类模块结构。
class AccClassify(nn.Module):
# in_channels: 输入通道
# num_classes: 分类数
def __init__(self,in_channels,num_classes):
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv = nn.MaxPool2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output[batch, 128, 4, 4]
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
辅助分类模块1
第一个中间层输出位于Inception4a之后,将Inception4a的输出经过平均池化,1X1卷积和全连接后等到分类结果。

self.acc_classify1 = AccClassify(512,num_classes)
辅助分类模块2

self.acc_classify2 = AccClassify(528,num_classes)
整体网络结构
pytorch搭建完整代码
"""
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
# @author: wangyu a beginner programmer, striving to be the strongest.
# @date: 2022/7/5 18:37
"""
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,num_classes=1000,aux_logits=True):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
# input(3,224,224)
self.front = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3), # output(64,112,112)
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2,ceil_mode=True), # output(64,56,56)
nn.Conv2d(64,64,kernel_size=1),
nn.Conv2d(64,192,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), # output(192,56,56)
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2,ceil_mode=True), # output(192,28,28)
)
# input(192,28,28)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32) # output(64+128+32+32=256,28,28)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64) # output(480,28,28)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # output(480,14,14)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64) # output(512,14,14)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64) # output(512,14,14)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64) # output(512,14,14)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64) # output(528,14,14)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128) # output(832,14,14)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # output(832,7,7)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128) # output(832,7,7)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128) # output(1024,7,7)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
self.acc_classify1 = AccClassify(512,num_classes)
self.acc_classify2 = AccClassify(528,num_classes)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)) # output(1024,1,1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024,num_classes)
def forward(self,x):
# input(3,224,224)
x = self.front(x) # output(192,28,28)
x= self.inception3a(x) # output(256,28,28)
x = self.inception3b(x)
x = self.maxpool3(x)
x = self.inception4a(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
classify1 = self.acc_classify1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x)
x = self.inception4c(x)
x = self.inception4d(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
classify2 = self.acc_classify2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x)
x = self.maxpool4(x)
x = self.inception5a(x)
x = self.inception5b(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x,dims=1)
x = self.dropout(x)
x= self.fc(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
return x,classify1,classify2
return x
class Inception(nn.Module):
'''
in_channels: 输入通道数
out1x1:分支1输出通道数
in3x3:分支2的3x3卷积的输入通道数
out3x3:分支2的3x3卷积的输出通道数
in5x5:分支3的5x5卷积的输入通道数
out5x5:分支3的5x5卷积的输出通道数
pool_proj:分支4的最大池化层输出通道数
'''
def __init__(self,in_channels,out1x1,in3x3,out3x3,in5x5,out5x5,pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
# input(192,28,28)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out1x1, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in3x3,kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in3x3,out3x3,kernel_size=3,padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in5x5, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in5x5, out5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,pool_proj,kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self,x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1,branch2,branch3,branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs,1)
class AccClassify(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels,num_classes):
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv = nn.MaxPool2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output[batch, 128, 4, 4]
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
# print(GoogLeNet())
结构图

- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)