【java高性能编程基础】 - 线程池的应用及实现原理
@[TOC]
为什么要用线程池?
线程池是一种多线程处理形式,处理过程中将任务添加到队列,然后在创建线程后自动启动这些任务。线程池线程都是后台线程。每个线程都使用默认的堆栈大小,以默认的优先级运行,并处于多线程单元中。如果某个线程在托管代码中空闲(如正在等待某个事件),则线程池将插入另一个辅助线程来使所有处理器保持繁忙。如果所有线程池线程都始终保持繁忙,但队列中包含挂起的工作,则线程池将在一段时间后创建另一个辅助线程但线程的数目永远不会超过最大值。超过最大值的线程可以排队,但他们要等到其他线程完成后才启动。
线程的数量是不是越多越好呢?
- 线程在java中是一个对象,更是操作系统的资源,线程的创建和销毁都需要时间。如果(创建时间+销毁时间)> (执行任务的时间),就很不合算。
- java对象占用堆内存,操作系统线程占用系统的内存,根据JVM规范:一个线程默认最大栈空间大小为1M,这个栈空间是需要从系统内存中分配的。所以线程过多,会消耗很多的内存。
- 在线程执行任务时,操作系统需要频繁的切换线程上下文,线程过多会影响性能。
==线程池的退出,就是为了方便的控制线程数量。==
线程池的原理
1、线程池管理器:
用于创建并管理线程池,包括创建线程池、销毁线程池、添加新任务。
2、工作线程:
线程池的中的线程,在没有任务时处于等待状态,每个线程都可以循环的执行任务。
3、任务接口:
每个任务必须实现的接口,以供工作线程调度任务的执行;
它主要规定了任务的入口、任务执行完后的收尾工作、任务的执行状态等。
4、任务队列:
用于存放没有处理的任务。提供一种缓冲机制。
线程池的接口定义和实现类API
java中操作线程池的api位于java.util.concurrent;包中。
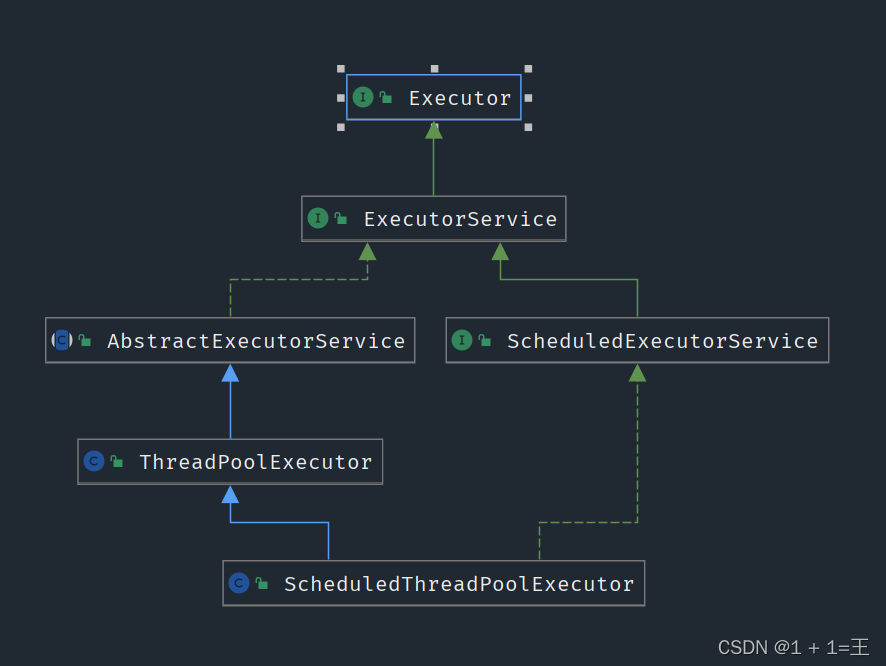
Executor接口
最上层的接口,定义了执行任务的execute()方法。

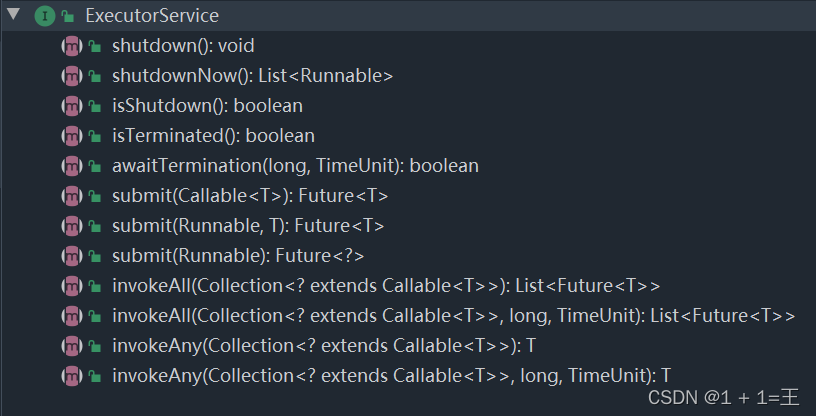
ExecutorService接口
继承了Executor接口,扩展了Callable、Future、关闭方法。
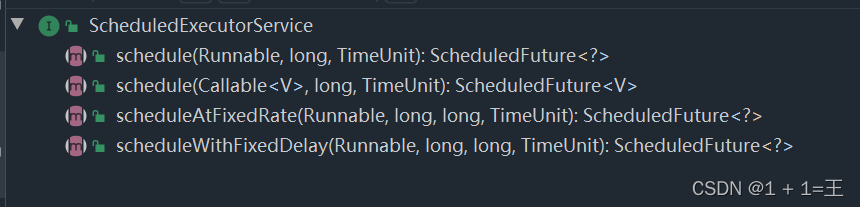
ScheduledExecutorService接口
继承了ExecutorService接口,增加了定时任务相关的方法。
 ThreadPoolExecutor实现类
ThreadPoolExecutor实现类
基础、标准的线程池实现。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor实现类
继承了ThreadPoolExecutor,实现了ScheduledExecutorService中定时任务相关的方法。
 ==后续将补充关于上述接口与实现类的源码分析。。。==
==后续将补充关于上述接口与实现类的源码分析。。。==
Executors工具类
Executors类中提供了一系列工厂方法用于创建线程池,返回的线程池都实现了ExecutorService接口。
- newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
创建一个固定大小、任务队列容量无界的线程池。核心线程数=最大线程数。 - newCachedThreadPool()
- 创建的是一个大小无界的缓冲线程池。它的任务队列是一个同步队列。任务加入到池中,如果池中有空闲线程,则用空闲线程执行,如无则创建新线程执行。池中的线程空闲超过60秒,将被销毁释放。线程数随任务的多少变化。适用于执行耗时较小的异步任务。池的核心线程数=0,最大线程数= Integer.MAX_VALUE
- newSingleThreadExecutor()
只有一个线程来执行无界任务队列的单一线程池。该线程池确保任务按加入的顺序一个一个依次执行。当唯一的线程因任务异常中止时,将创建一个新的线程来继续执行后续的任务。与newFixedThreadPool(1)的区别在于,单一线程池的池大小在newSingleThreadExecutor方法中硬编码,不能再改变的。 - newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)能定时执行任务的线程池。该池的核心线程数由参数指定,最大线程数= lnteger.MAX_VALUE。
线程池应用示例
通过ThreadPoolExecutor实例创建。
1. 创建一个任务,交给线程池执行
/**
* 测试: 提交15个执行时间需要3秒的任务,看线程池的状况
*
* @param threadPoolExecutor 传入不同的线程池,看不同的结果
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testCommand(ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor) throws Exception{
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
int n = i;
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println("开始执行" + n);
Thread.sleep(3000L);
System.out.println("执行结束" + n);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
System.out.println("任务提交成功:" + i);
}
Thread.sleep(500L);
System.out.println("当前线程池线程数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("当前线程池等待的数量为: " + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(15000L);
System.out.println("当前线程池线程数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("当前线程池等待的数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
}
2. 创建线程池执行上面的任务
/**
* 核心线程个数:5个
* 最大线程个数:10个
* 超出核心线程个数的线程存活时间:5S
* 队列大小:无界队列
* @throws Exception
*/
public void pool1() throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
testCommand(threadPoolExecutor);
}
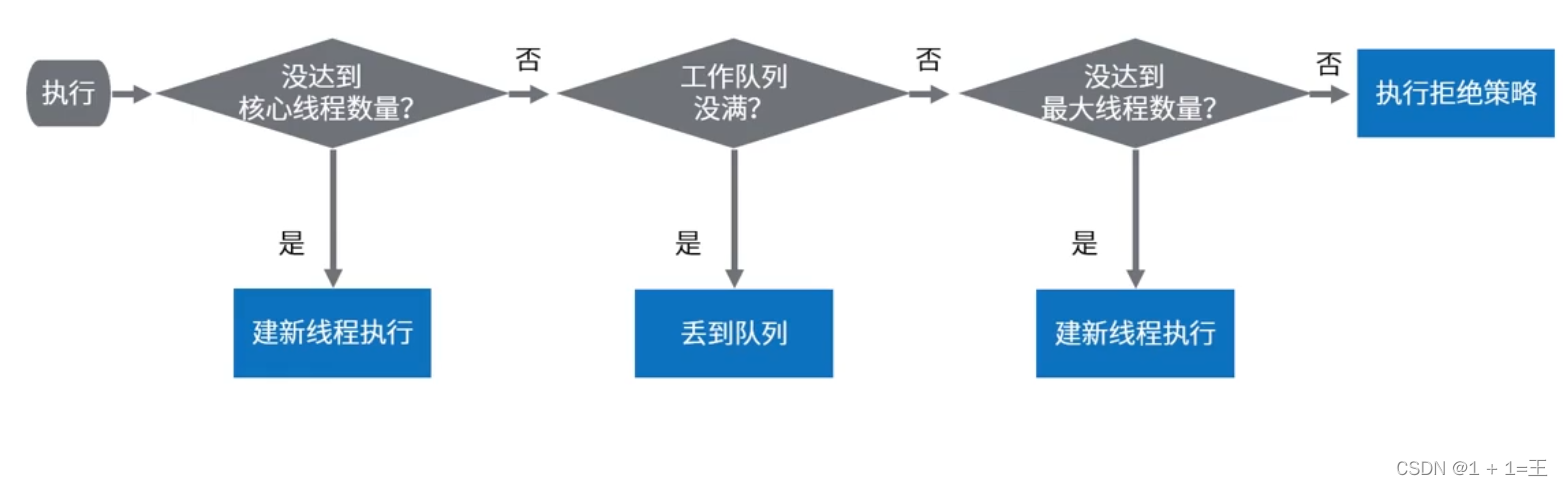
任务execute过程
- 是否达到核心线程数量?没达到,创建一个工作线程来执行任务。
- 工作队列是否已满?没满,则将新提交的任务存储在工作队列里。
- 是否达到线程池最大数量?没达到,则创建一个新的工作线程来执行任务。
- 最后,执行拒绝策略来处理这个任务。
各种线程池的使用
/** 线程池的使用 */
public class Demo9 {
/**
* 测试: 提交15个执行时间需要3秒的任务,看线程池的状况
*
* @param threadPoolExecutor 传入不同的线程池,看不同的结果
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testCommon(ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor) throws Exception {
// 测试: 提交15个执行时间需要3秒的任务,看超过大小的2个,对应的处理情况
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
int n = i;
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("开始执行:" + n);
Thread.sleep(3000L);
System.err.println("执行结束:" + n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
System.out.println("任务提交成功 :" + i);
}
// 查看线程数量,查看队列等待数量
Thread.sleep(500L);
System.out.println("当前线程池线程数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("当前线程池等待的数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
// 等待15秒,查看线程数量和队列数量(理论上,会被超出核心线程数量的线程自动销毁)
Thread.sleep(15000L);
System.out.println("当前线程池线程数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("当前线程池等待的数量为:" + threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());
}
/**
* 1、线程池信息: 核心线程数量5,最大数量10,无界队列,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:5秒, 指定拒绝策略的
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest1() throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
testCommon(threadPoolExecutor);
// 预计结果:线程池线程数量为:5,超出数量的任务,其他的进入队列中等待被执行
}
/**
* 2、 线程池信息: 核心线程数量5,最大数量10,队列大小3,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:5秒, 指定拒绝策略的
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest2() throws Exception {
// 创建一个 核心线程数量为5,最大数量为10,等待队列最大是3 的线程池,也就是最大容纳13个任务。
// 默认的策略是抛出RejectedExecutionException异常,java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.err.println("有任务被拒绝执行了");
}
});
testCommon(threadPoolExecutor);
// 预计结果:
// 1、 5个任务直接分配线程开始执行
// 2、 3个任务进入等待队列
// 3、 队列不够用,临时加开5个线程来执行任务(5秒没活干就销毁)
// 4、 队列和线程池都满了,剩下2个任务,没资源了,被拒绝执行。
// 5、 任务执行,5秒后,如果无任务可执行,销毁临时创建的5个线程
}
/**
* 3、 线程池信息: 核心线程数量5,最大数量5,无界队列,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:5秒
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest3() throws Exception {
// 和Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)一样的
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 5, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
testCommon(threadPoolExecutor);
// 预计结:线程池线程数量为:5,超出数量的任务,其他的进入队列中等待被执行
}
/**
* 4、 线程池信息:
* 核心线程数量0,最大数量Integer.MAX_VALUE,SynchronousQueue队列,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:60秒
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest4() throws Exception {
// SynchronousQueue,实际上它不是一个真正的队列,因为它不会为队列中元素维护存储空间。与其他队列不同的是,它维护一组线程,这些线程在等待着把元素加入或移出队列。
// 在使用SynchronousQueue作为工作队列的前提下,客户端代码向线程池提交任务时,
// 而线程池中又没有空闲的线程能够从SynchronousQueue队列实例中取一个任务,
// 那么相应的offer方法调用就会失败(即任务没有被存入工作队列)。
// 此时,ThreadPoolExecutor会新建一个新的工作者线程用于对这个入队列失败的任务进行处理(假设此时线程池的大小还未达到其最大线程池大小maximumPoolSize)。
// 和Executors.newCachedThreadPool()一样的
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
testCommon(threadPoolExecutor);
// 预计结果:
// 1、 线程池线程数量为:15,超出数量的任务,其他的进入队列中等待被执行
// 2、 所有任务执行结束,60秒后,如果无任务可执行,所有线程全部被销毁,池的大小恢复为0
Thread.sleep(60000L);
System.out.println("60秒后,再看线程池中的数量:" + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
}
/**
* 5、 定时执行线程池信息:3秒后执行,一次性任务,到点就执行 <br/>
* 核心线程数量5,最大数量Integer.MAX_VALUE,DelayedWorkQueue延时队列,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:0秒
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest5() throws Exception {
// 和Executors.newScheduledThreadPool()一样的
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(5);
threadPoolExecutor.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务被执行,现在时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, 3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(
"定时任务,提交成功,时间是:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ", 当前线程池中线程数量:" + threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize());
// 预计结果:任务在3秒后被执行一次
}
/**
* 6、 定时执行线程池信息:线程固定数量5 ,<br/>
* 核心线程数量5,最大数量Integer.MAX_VALUE,DelayedWorkQueue延时队列,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:0秒
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest6() throws Exception {
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(5);
// 周期性执行某一个任务,线程池提供了两种调度方式,这里单独演示一下。测试场景一样。
// 测试场景:提交的任务需要3秒才能执行完毕。看两种不同调度方式的区别
// 效果1: 提交后,2秒后开始第一次执行,之后每间隔1秒,固定执行一次(如果发现上次执行还未完毕,则等待完毕,完毕后立刻执行)。
// 也就是说这个代码中是,3秒钟执行一次(计算方式:每次执行三秒,间隔时间1秒,执行结束后马上开始下一次执行,无需等待)
threadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务-1 被执行,现在时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, 2000, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 效果2:提交后,2秒后开始第一次执行,之后每间隔1秒,固定执行一次(如果发现上次执行还未完毕,则等待完毕,等上一次执行完毕后再开始计时,等待1秒)。
// 也就是说这个代码钟的效果看到的是:4秒执行一次。 (计算方式:每次执行3秒,间隔时间1秒,执行完以后再等待1秒,所以是 3+1)
threadPoolExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务-2 被执行,现在时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, 2000, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 7、 终止线程:线程池信息: 核心线程数量5,最大数量10,队列大小3,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:5秒, 指定拒绝策略的
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest7() throws Exception {
// 创建一个 核心线程数量为5,最大数量为10,等待队列最大是3 的线程池,也就是最大容纳13个任务。
// 默认的策略是抛出RejectedExecutionException异常,java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.err.println("有任务被拒绝执行了");
}
});
// 测试: 提交15个执行时间需要3秒的任务,看超过大小的2个,对应的处理情况
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
int n = i;
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("开始执行:" + n);
Thread.sleep(3000L);
System.err.println("执行结束:" + n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
});
System.out.println("任务提交成功 :" + i);
}
// 1秒后终止线程池
Thread.sleep(1000L);
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
// 再次提交提示失败
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("追加一个任务");
}
});
// 结果分析
// 1、 10个任务被执行,3个任务进入队列等待,2个任务被拒绝执行
// 2、调用shutdown后,不接收新的任务,等待13任务执行结束
// 3、 追加的任务在线程池关闭后,无法再提交,会被拒绝执行
}
/**
* 8、 立刻终止线程:线程池信息: 核心线程数量5,最大数量10,队列大小3,超出核心线程数量的线程存活时间:5秒, 指定拒绝策略的
*
* @throws Exception
*/
private void threadPoolExecutorTest8() throws Exception {
// 创建一个 核心线程数量为5,最大数量为10,等待队列最大是3 的线程池,也就是最大容纳13个任务。
// 默认的策略是抛出RejectedExecutionException异常,java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.err.println("有任务被拒绝执行了");
}
});
// 测试: 提交15个执行时间需要3秒的任务,看超过大小的2个,对应的处理情况
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
int n = i;
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("开始执行:" + n);
Thread.sleep(3000L);
System.err.println("执行结束:" + n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
});
System.out.println("任务提交成功 :" + i);
}
// 1秒后终止线程池
Thread.sleep(1000L);
List<Runnable> shutdownNow = threadPoolExecutor.shutdownNow();
// 再次提交提示失败
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("追加一个任务");
}
});
System.out.println("未结束的任务有:" + shutdownNow.size());
// 结果分析
// 1、 10个任务被执行,3个任务进入队列等待,2个任务被拒绝执行
// 2、调用shutdownnow后,队列中的3个线程不再执行,10个线程被终止
// 3、 追加的任务在线程池关闭后,无法再提交,会被拒绝执行
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest1();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest2();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest3();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest4();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest5();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest6();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest7();
// new Demo9().threadPoolExecutorTest8();
}
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)