【C++】快速入门list的使用
@[toc]
一、引入
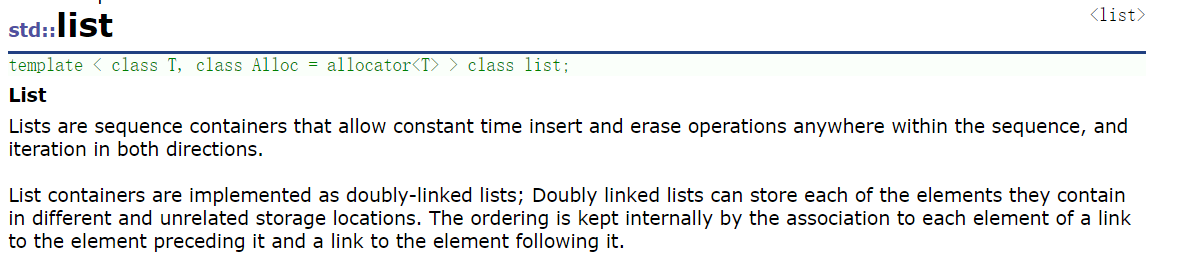
list的本质是带头双向循环链表,对于带头双向循环链表我们可是比较熟悉的了。本文只对list的一些常用接口进行说明,对于其他一些接口可自行查看文档。
二、构造
void Test()
{
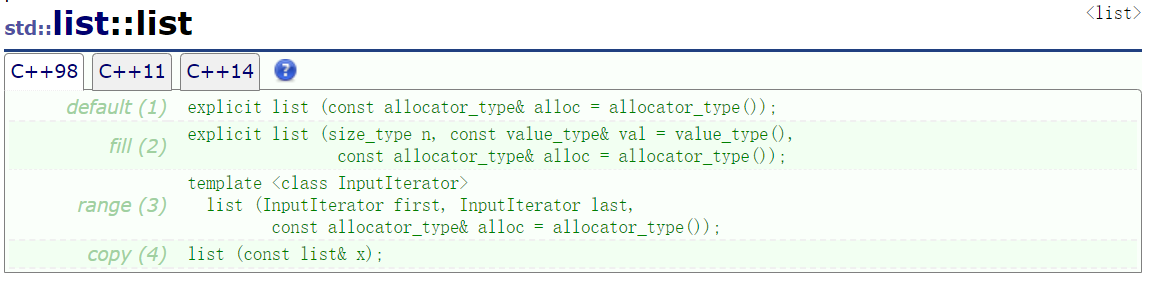
list<int> lt;//无参构造
list<int> lt1(5, 1);//n个val构造
list<int> lt2(lt1);//拷贝构造
string s("hello world");
list<char> lt3(s.begin(), s.end());//迭代器区间构造
}
三、迭代器
//正向迭代器
int main()
{
list<int> lt(5, 10);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

//反向迭代器
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = lt.rbegin();
while (rit != lt.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

四、增删查
1.头插头删
push_front和pop_front
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_front(10);
lt.push_front(20);
lt.push_front(30);
lt.push_front(40);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.pop_front();
lt.pop_front();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
return 0;
}

2.尾插尾删
push_back和pop_back
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.pop_back();
lt.pop_back();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

3.查找和插入
find和insert
find和insert可以相互配合使用。find是算法库里面的,在添加头文件#include <algorithm>
对于list的插入insert:

1.通过find找到位置插入
2.找到位置后插入n个val的值
3.找到位置后插入迭代器的区间
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
//1.插入一个值
auto pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 3);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
//对于链表的insert,迭代器不会失效
lt.insert(pos, 30);
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << *pos << endl;
//2.插入n个val的值
pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 3);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
lt.insert(pos, 4, 100);
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//3.插入迭代器区间
list<int> tmp(3, 8);
pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 100);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
lt.insert(pos, tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

注意:对于list的insert的pos位置不会失效,在这个地方,只是在pos位置前增加节点,改变链接,pos位置并不会变成野指针。
4.删除
erase

int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(5);
auto pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 3);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
lt.erase(pos);
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 4);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
lt.erase(pos, lt.end());
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}

注意:对于list的erase的pos位置是会失效的,删除之后,如果直接进行访问会直接报错,此时的pos已经是野指针了。
五、其他操作
排序和去重
1.sort和unique
对于sort:算法库里面已经有一个sort了,而对于list自己也提供了一个sort:
算法库里的sort对于list并不适用,算法库里的sort对于物理空间是连续的,只有vector和string能够使用,而对于list来说,物理空间并不是连续的,并不适用,所以list自己提供了一个sort进行排序,此外,链表的排序是归并排序。
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(0);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.sort();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

对于unique:用来删除链表中连续的重复元素,但是注意:一定是要先排完序在进行删除,如果没有进行排序:而直接进行去重的话,会导致去重去不完全
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(0);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.sort();
lt.unique();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

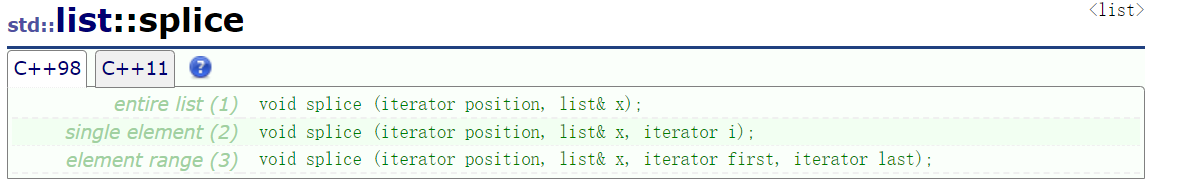
2.splice和remove
slice进行转移:
int main()
{
//转移到某个位置
list<int> lt1(5,10);
list<int> lt2(4,7);
lt1.splice(lt1.begin(), lt2);
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//从某个位置转移
list<int> lt3(4,10);
list<int> lt4(4, 5);
lt3.splice(lt3.begin(), lt4, lt4.begin());
for (auto e : lt3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器区间转移
list<int>lt5(3,10);
list<int>lt6(3,20);
lt5.splice(lt5.begin(), lt6, lt6.begin(), lt6.end());
for (auto e : lt5)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

remove可以直接删除list中指定的数据:
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(5);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.remove(5);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

3.resize

感觉resize放在list这里并不太常用把,简单测试一下代码:
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.resize(5, 1);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt2;
lt2.push_back(1);
lt2.push_back(2);
lt2.push_back(3);
lt2.push_back(4);
lt2.push_back(5);
lt2.push_back(6);
lt2.resize(4);
for (auto e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)