01、Netty学习笔记—(三大组件、bytebuffer、文件编程)(下)
2.4、ByteBuffer分散读写
分散集中读、写好处:能够减少ByteBuffer之间的拷贝,减少数据的复制次数,变相的提高了效率。下面是读写的示例:
Scattering Reads(分散读)
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import static com.changlu.utils.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @ClassName ScatteringReads
* @Author ChangLu
* @Date 2021/12/17 17:32
* @Description 分散读取文件内容至ByteBuffer
*/
public class ScatteringReads {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(7);
ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("data1.txt", "r").getChannel()) {
//直接读取内容到各个ByteBuffer对象中
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{b1,b2,b3});
debugAll(b1);
debugAll(b2);
debugAll(b3);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
//data1.txt文件内容
changluliner123
效果:
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [7], limit: [7]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 63 68 61 6e 67 6c 75 |changlu |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 6c 69 6e 65 72 |liner |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [3], limit: [3]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 31 32 33 |123 |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
分散写
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @ClassName GatheringWrites
* @Author ChangLu
* @Date 2021/12/17 17:37
* @Description 分散写:将多个ByteBuffer中内容依次写入到一个文件中
*/
public class GatheringWrites {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer b1 = CharsetUtil.UTF_8.encode("changlu");
ByteBuffer b2 = CharsetUtil.UTF_8.encode("hennuli");
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("data3.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
//将多个ByteBuffer中存储的内容依次写入到文件中
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1,b2});
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
效果:
//data3.txt
changluhennuli
2.5、网络黏包、半包案例(重要)
案例分析
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔
但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条为
- Hello,world\n
- I’m zhangsan\n
- How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)
- Hello,world\nI’m zhangsan\nHo
- w are you?\n
若是两个消息和在一起就是粘包,若是消息被截断到下一条消息里就是半包!
黏包出现原因:由于效率原因(多个打包比一个一个打包发出去肯定高),其也就会出现黏包的原因。
半包出现原因:由于服务器的缓冲大小限制决定的,例如ByteBuffer不可能无限大,那么一次发送过来的内容ByteBuffer只能接收其所能接收的部分,那么剩余的一部分只能下一次接收,此时就产生半包现象。
现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
代码编写
现在我们直接向Buffer中输入指定黏包、半包情况,接着对ByteBuffer中的内容进行解析读取:
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static com.changlu.utils.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @ClassName ByteBufferExam
* @Author ChangLu
* @Date 2021/12/17 17:58
* @Description 黏包、半包解析(底层实现)
*/
public class ByteBufferExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(256);
//黏包情况:
buffer.put("I am changlu!\nhello,xiaoli\nha".getBytes());
handle(buffer);
//半包情况:
buffer.put(",are you ok?\n".getBytes());
handle(buffer);
}
/**
* 处理黏包、半包情况:每次能够将\n结尾的内容读取到一个ByteBuffer,并测该ByteBuffer对象
* @param buffer
*/
private static void handle(ByteBuffer buffer) {
buffer.flip();//切换到读状态
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.limit(); i++) {
if (buffer.get(i) == '\n') {
int readLen = i - buffer.position() + 1;
ByteBuffer temp = ByteBuffer.allocate(20);
for (int j = 0; j < readLen; j++) {
temp.put(buffer.get());
}
debugAll(temp);
}
}
buffer.compact();//切换写状态(压缩):保留未读取的内容
}
}
效果展示:可以看到三条信息都被单独读取并处理!
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [14], limit: [20]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 49 20 61 6d 20 63 68 61 6e 67 6c 75 21 0a 00 00 |I am changlu!...|
|00000010| 00 00 00 00 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [20]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f 2c 78 69 61 6f 6c 69 0a 00 00 00 |hello,xiaoli....|
|00000010| 00 00 00 00 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [15], limit: [20]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 61 2c 61 72 65 20 79 6f 75 20 6f 6b 3f 0a 00 |ha,are you ok?..|
|00000010| 00 00 00 00 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
三、文件编程
3.1、FileChannel
FileChannel:只能工作在阻塞模式下。
获取
不能直接打开 FileChannel,必须通过 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 来获取 FileChannel,它们都有 getChannel 方法
- 通过 FileInputStream 获取的 channel 只能读
- 通过 FileOutputStream 获取的 channel 只能写
- 通过 RandomAccessFile 是否能读写根据构造 RandomAccessFile 时的读写模式决定
读取
会从 channel 读取数据填充 ByteBuffer,返回值表示读到了多少字节,-1 表示到达了文件的末尾
int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);
写入
写入的正确姿势如下, SocketChannel
ByteBuffer buffer = ...;
buffer.put(...); // 存入数据
buffer.flip(); // 切换读模式
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
在 while 中调用 channel.write 是因为 write 方法并不能保证一次将 buffer 中的内容全部写入 channel
关闭
channel 必须关闭,不过调用了 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 的 close 方法会间接地调用 channel 的 close 方法
位置
获取当前位置
long pos = channel.position();
设置当前位置
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos);
设置当前位置时,如果设置为文件的末尾
- 这时读取会返回 -1
- 这时写入,会追加内容,但要注意如果 position 超过了文件末尾,再写入时在新内容和原末尾之间会有空洞(00)
大小
使用 size 方法获取文件的大小
强制写入
操作系统出于性能的考虑,会将数据缓存,不是立刻写入磁盘。可以调用 force(true) 方法将文件内容和元数据(文件的权限等信息)立刻写入磁盘
注意:只有当channel关闭的时候才会同步到磁盘上去,也可以通过编程式直接写入,不过对性能会有影响!
3.2、两个Channel传输数据(transferTo())
目的:进行文件的复制拷贝。
底层:使用操作系统的零拷贝。
方式:使用Channel的transferTo()方法,需要注意的是每次方法调用只能拷贝2GB容量,所以对于大于2G大小的需要多次重复调用。
代码说明:两个demo复制拷贝方法,一个是>2G的,另一个是<=2G。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @ClassName TestTransferTo
* @Author ChangLu
* @Date 2021/12/17 19:26
* @Description 测试FileChannel的transferTo方法:底层为零拷贝
*/
public class TestTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String FILE_FROM = "C:\\Users\\93997\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\这个杀手不太冷1994.mp4";
String FILE_TO = "C:\\Users\\93997\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\新建文件夹\\这个杀手不太冷1994.mp4";
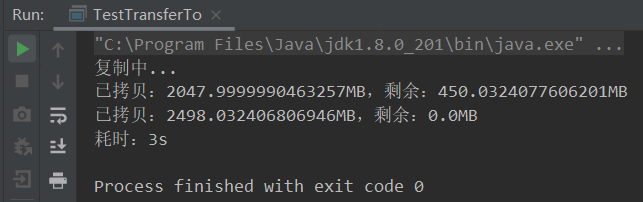
final long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制中...");
//传输<=2G
// transferTo_2G(FILE_FROM, FILE_TO);
//>2G
transferTo_t2G(FILE_FROM, FILE_TO);
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin) / 1000 + "s");
}
/**
* 传输超过<=2G容量大小,默认transferTo传输一次上限为2G容量
*/
public static void transferTo_2G(String FILE_FROM, String FILE_TO){
try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream(FILE_FROM).getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream(FILE_TO).getChannel();
) {
final long size = from.size();
//注意:传输默认上限最大为2G
from.transferTo(0, size, to);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 传输超过2G容量大小
*/
public static void transferTo_t2G(String FILE_FROM, String FILE_TO){
try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream(FILE_FROM).getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream(FILE_TO).getChannel();
) {
//通过传输容量与原始容量比对来解决一次传输>2G文件的情况
long leftSize = from.size();
while (true) {
leftSize -= from.transferTo(from.size() - leftSize, leftSize, to);
System.out.println("已拷贝:" + (from.size() - leftSize)/1024.0/1024.0 + "MB,剩余:" + leftSize/1024.0/1024.0 + "MB");
if (leftSize < 2 * 1024 * 1024){
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.3、Path类、Paths工具类
jdk7 引入了 Path 和 Paths 类
- Path 用来表示文件路径
- Paths 是工具类,用来获取 Path 实例
基本的Paths.get()路径设置:
//基本的Path.get()格式
public static void test01(){
// 相对路径 使用 user.dir 环境变量来定位 1.txt
Path path1 = Paths.get("1.txt");
System.out.println(path1);//1.txt
// 绝对路径 代表了 d:\1.txt
Path path2 = Paths.get("E:\\资源\\电影资源\\1.txt");
System.out.println(path2);//E:\资源\电影资源\1.txt
// 绝对路径 同样代表了 d:\1.txt
Path path3 = Paths.get("d:/1.txt");
System.out.println(path3);
// 代表了 d:\data\projects
Path path4 = Paths.get("d:\\data", "changlu.txt");
System.out.println(path4);
}
较特殊的路径格式:可转义…
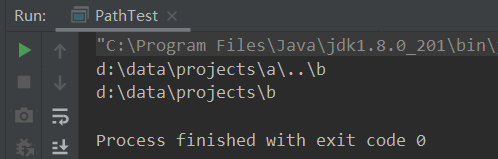
//调用normalize()可对路径进行转义:..表示上级
public static void test02(){
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\data\\projects\\a\\..\\b");
System.out.println(path);
System.out.println(path.normalize());
}
3.4、Files工具类(自带传输方法copy)
3.4.1、基本API使用
检查文件是否存在
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
System.out.println(Files.exists(path));
创建目录
创建一级目录:
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.createDirectory(path);
- 如果目录已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
- 不能一次创建多级目录,否则会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
创建多级目录:
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1/d2");
Files.createDirectories(path);
拷贝文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.copy(source, target);//底层使用的操作系统的拷贝,性能也很好!与transferTo相似。
- 如果文件已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
如果希望用 source 覆盖掉 target,需要用 StandardCopyOption 来控制
Files.copy(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
移动文件
移动文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Files.move(source, target, StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE);
- StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE 保证文件移动的原子性
删除
删除文件:
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.delete(target);
- 如果文件不存在,会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
删除目录:
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.delete(target);
- 如果目录还有内容,会抛异常 DirectoryNotEmptyException
3.4.2、walk、walkFileTree(递归遍历文件目录工具方法)
方法介绍
//递归遍历文件目录,返回的是一个文件Path Stream流
public static Stream<Path> walk(Path start, FileVisitOption... options) throws IOException {
return walk(start, Integer.MAX_VALUE, options);
}
//递归遍历文件目录,访问者模式,重写接口方法
public static Path walkFileTree(Path start, FileVisitor<? super Path> visitor)
throws IOException
{
return walkFileTree(start,
EnumSet.noneOf(FileVisitOption.class),
Integer.MAX_VALUE,
visitor);
}
//访问接口
public interface FileVisitor<T> {
//访问文件目录前
FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(T dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException;
//访问文件时
FileVisitResult visitFile(T file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException;
//访问文件失败
FileVisitResult visitFileFailed(T file, IOException exc)
throws IOException;
//访问文件目录后
FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(T dir, IOException exc)
throws IOException;
}
使用场景:
walk():返回的是stream流,流中包含所有的文件Path对象,可以进行过滤、统计、复制一系列操作。walkFileTree():在递归过程中,可以通过接口重写的方式在不同的文件或目录访问时刻进行一些操作。
功能1:遍历目录文件
/**
* 单独功能点1:遍历目录文件,打印出文件夹数量、文件数。
* 说明:这里将root文件也算入文件夹的数量中,所以内部文件夹数量应该-1
*/
private static void testViewAllFiles() throws IOException {
final Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_201");
//由于匿名实现类中重写方法不能直接对局部变量进行改变值操作所以使用AtomicInteger
AtomicInteger dirCount = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
//递归遍历文件夹
Files.walkFileTree(path,new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>() {
//进入目录前
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println("进入文件目录=》" + dir);
dirCount.getAndIncrement();
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
//访问当前文件
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println(" =》" + file);
fileCount.getAndIncrement();
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println("文件夹数量:" + dirCount);
System.out.println("文件数量:" + fileCount);
}
功能2:统计JDK8目录中jar包的个数
/**
* 单独功能点2:统计JDK8目录中jar包的个数
*/
private static void testJarFileCount() throws IOException {
final Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_201");
AtomicInteger jarCount = new AtomicInteger();
//递归遍历文件夹
Files.walkFileTree(path,new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>() {
//访问当前文件
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
//注意:file.getFileName()返回值是Path
if (file.toFile().getName().endsWith(".jar")){
System.out.println(file.getFileName());
jarCount.getAndIncrement();
}
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println("jar包数量:" + jarCount);
}
功能3:删除多级目录(不走回收站,谨慎删除)
/**
* 单独功能点3:删除多级目录(不走回收站,谨慎删除)
*/
private static void testFileMultDirs() throws IOException {
final Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\93997\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\工作室网站");
//注意点:删除多级目录时,首先需要先将某个文件夹中的文件内容删除,之后才可以删除文件目录
Files.walkFileTree(path,new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>() {
//1、先删除文件
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
Files.delete(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
//2、后删除目录(后置文件访问器)
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc) throws IOException {
Files.delete(dir);
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
});
}
####功能4、拷贝文件夹到指定目录
/**
* 单独功能点4、拷贝文件夹到指定目录
*/
private static void testCopyMultDir() throws IOException {
String COPY_ORIGIN = "C:\\Users\\93997\\Desktop\\工作室网站";
//复制到的文件目录为:指定路径\\工作室网站1
String COPY_TARGET = "C:\\Users\\93997\\Desktop\\新建文件夹\\工作室网站1";
//递归返回所有的文件Path集合stream流
Files.walk(Paths.get(COPY_ORIGIN)).forEach(path->{
final String copyFileName = path.toFile().getAbsolutePath().replace(COPY_ORIGIN, COPY_TARGET);
System.out.println(copyFileName);
//若是文件先创建文件
try {
if (Files.isDirectory(path)){
Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(copyFileName));
} else {
Files.copy(path, Paths.get(copyFileName));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)