AcWing 蓝桥杯AB组辅导课 06、双指针、BFS与图论
@[toc]
前言
目前正在马不停蹄学习中…,等待更新

例题:
- AcWing 1238. 双指针-例题 日志统计 Java题解 滑动窗口(中等,蓝桥杯)
- AcWing 1101. BFS-例题 献给阿尔吉侬的花束 Java题解
- AcWing 1113. DFS-例题 红与黑 Java题解
- AcWing 1224. 图论—例题 交换瓶子 Java题解(蓝桥杯)
所有博客文件目录索引:博客目录索引(持续更新)
一、双指针
知识点
例题
例题1:1238. 日志统计(中等,蓝桥杯)
题目链接:1238. 日志统计
标签:双指针、滑动窗口
分析:
首先是输入大小范围分析:
K:赞数 n:日志的长度(输入的数量) 100000
ts:时刻、id:帖子id 100000
D:时间长度 10000
数据量是10万,O(n^2^)平方的话肯定直接超时,基本就是O(n)或者O(nlogn)。
原本自己的暴力思路就是遍历1-10万的所有的时刻,每一个时刻去比对每个订单,那这个复杂度就是上面所说的O(n^2^),这个思路就肯定pass了。
接着通过看题解,才发现这道题O(nlogn)的巧妙之处,我们转换一下思路,并不是遍历所有时刻,而是遍历所有根据时刻排好序的订单,由于时刻是排好序的,随着从前往后推移,以时间长度作为窗口,虽说每次遍历到的是不同的订单,但是同样窗口之间的时间范围是确定的,这一点是我一开始没有想得到的。
巧妙点:多订单根据点赞的时刻先来进行排序,接着以两个订单之间的时刻作为窗口大小来进行不断滑动,达到遍历所有订单时仅有O(n)的时间复杂度。
题解:
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n.logn)【sort的时间的复杂度,下面的for循环O(n)】;空间复杂度O(n)
//K:赞数 n:日志的长度(输入的数量) 100000
//ts:时刻、id:帖子id 100000
//D:时间长度 10000
//条件为[T, T + D)中满足 >= K个赞 即表示是热帖,该ID就需要被记录
//输出所有的帖子ID
//遍历所有的帖子数,每个帖子的时刻
//尝试:90000 x 100000
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
//帖子
class Log implements Comparable<Log>{
int ts;
int id;
public Log(int ts, int id) {
this.ts = ts;
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Log l) {
return this.ts - l.ts;
}
}
class Main {
static final BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static final PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
static int N = 100010;
static int K, n, D;
//记录所有的日志(时刻、帖子)
static Log[] logs = new Log[N];
//记录指定帖子的点赞数
static int[] cnt = new int[N];
//记录帖子是否是热帖(使用数组,直接就是排序效果)
static int[] hotPosts = new int[N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String[] s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);//日志数量
D = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);//时间长度
K = Integer.parseInt(s[2]);//点赞数
//记录所有的帖子
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
int ts = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int id = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
logs[i] = new Log(ts, id);
}
//根据时刻来进行排序
Arrays.sort(logs, 0, n);
//遍历所有的日志,进行双指针滑动窗口操作
//l指针仅仅只是记录窗口左侧的帖子时刻(l与r主要就是维护一个时间窗口,与帖子几并不相关)
for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < n; r++) {
Log cur = logs[r];
//给当前帖子进行点赞
cnt[cur.id]++;
//滑动窗口判断当前帖子时间与l位置的帖子时间区间是否>=D
while (l < r && cur.ts - logs[l].ts >= D) {
//满足条件时:窗口向右移动,点赞数-1
cnt[logs[l].id]--;
l++;
}
//当前是在时间段里 && 满足点赞数
if (cnt[cur.id] >= K) {
hotPosts[cur.id] = 1;
}
}
//遍历一遍所有的帖子(题目说要从前往后)
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (hotPosts[i] > 0) System.out.println(i);
}
}
}

习题
二、BFS
知识点
例题
例题1:1101. 献给阿尔吉侬的花束【中等,信息学奥赛一本通】
题目链接:1101. 献给阿尔吉侬的花束
分析:
首先看下数据范围,宽高范围最大是200,每个已访问过的格子只会被访问一次,那么时间复杂度就是O(n^2^)。
又题目说是要找最短路径,此时我们就可以使用bfs,那么直接模板套,我们只需要关注一些边界条件。
广搜-二维矩阵模板:
class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class Solution {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Point(1,2));//出发点
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//取出Point结点进行操作
Point point = queue.poll();
//进行操作
//放置四个方向的节点
for (int d = 0; d < dicts.length; d++) {
int x = point.x + dicts[d][0];
int y = point.y + dicts[d][1];
queue.offer(new Point(x, y))
}
}
}
}
}
思路:
思路1:BFS,广搜
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n^2^);空间复杂度O(n^2^)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Point{
int x;
int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class Main {
static final BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static final PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
static int N = 210;
static char[][] arr = new char[N][N];
//四个方向
static final int[][] dicts = {
{-1, 0},
{0, -1},
{1, 0},
{0, 1}
};
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
int c = Integer.parseInt(cin.readLine());
while (c -- != 0) {
String[] s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
//确定S的位置
int x = 0, y = 0;
//初始化数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = cin.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = str.charAt(j);
//找到出发点
if (arr[i][j] == 'S') {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
bfs(arr, n, m, x, y);
}
}
public static void bfs(char[][] arr, int n, int m, int x, int y) {
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
queue.offer(new Point(x, y));
boolean isFind = false;
int res = -1;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && !isFind) {
int size = queue.size();
res++;
//遍历当前圈中的所有节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Point p = queue.poll();
x = p.x;
y = p.y;
//若是越界停止访问
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= n || y >= m) continue;
//若是碰到栏杆或者已访问过就停止继续访问
if (arr[x][y] == '#' || visited[x][y]) continue;
//找到目标点
if (arr[x][y] == 'E') {
isFind = true;
break;
}
visited[x][y] = true;
//每个节点都有四个方向
for (int d = 0; d < dicts.length; d++) {
queue.offer(new Point(x + dicts[d][0], y + dicts[d][1]));
}
}
}
if (isFind) {
System.out.println(res);
}else {
System.out.println("oop!");
}
}
}

习题
三、DFS
例题
1113. 红与黑【中等,信息学奥赛一本通】
题目链接:1113. 红与黑
分析:
看看数据范围20,是真的小,并且每个格子只会被访问一次。
又题目说总共能够到达多少块黑色的瓷砖,也就是最大值,我们这里就可以使用dfs,我直接拿dfs模板套。
dfs-二维矩阵模板:
int f[4][2]={{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}; //用于判断下一步怎么走向几个方向走就是几个数据
void dfs(int x,int y){ //进入点的坐标
if(/*跳出循环的条件*/){
/*作出相应操作*/
return; //不要忘了return
}
for(int i=0;i</*f的长度*/;i++){
int x0=x+f[i][0];
/*此处是更新点的坐标,注意是直接让原来的点加上这个数据,不是直接等于*/
int y0=y+f[i][1];
if(/*用新坐标x0,y0判断是否符合条件*/){
dfs(x0,y0); //用新的坐标进行递归
}
}
}
题解:
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n^2^);空间复杂度O(n^2^)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static final BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int N = 30;
static char[][] arr = new char[N][N];
static int[][] dicts = {
{-1, 0},
{0, -1},
{1, 0},
{0, 1}
};
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
while (true) {
String[] s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
//停止读入
if (n == 0 && m == 0) break;
//初始化空间
int x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = cin.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = str.charAt(j);
if (arr[i][j] == '@') {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
System.out.println(dfs(n, m, x, y, new boolean[n][m]));
}
}
public static int dfs(int n, int m, int i, int j, boolean[][] visited) {
//越界情况
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= n || j >= m) {
return 0;
}
//遇到红色瓷砖停止
if (arr[i][j] == '#' || visited[i][j]) return 0;
int res = 1;
visited[i][j] = true;
//四个方向
for (int d = 0; d < dicts.length; d++) {
int x = i + dicts[d][0];
int y = j + dicts[d][1];
res += dfs(n, m, x, y, visited);
}
return res;
}
}

四、图论
知识点
例题
例题1:1224. 交换瓶子(中等,蓝桥杯)
题目链接:1224. 交换瓶子
分析:
首先看下数据量的范围,长度为10000,符合1s的时间复杂度有O(n^2^),O(nlogn),O(n),其中O(n^2^)时间特别紧,若是代码量比较少是刚好能够卡过的。本道题的话可以使用暴力解法(选择排序)以及一个图论解法。
①暴力解法:选择排序
选择排序的过程我不再过多阐述,就是每一轮找到[i + 1, n]部分 < arr[i]的元素,若是有的话满足了符合交换的条件,那么对于符合条件的进行计数+1,最后排序下来之后,我们也就可以得到结果了。
②图论解法:
本道题实际上与前面树状数组的1215. 小朋友排队比较类似,不过还是有一些区别,小朋友排队是求逆序对,并且交换的必须是临近的两个数,在这道题中实际上并没有临近的数才能够进行交换的限制,所以这里可以借助图论来进行解决。
举例:5个数为2 3 1 5 4
初始位置:1 2 3 4 5
实际位置:2 3 1 5 4
从实际位置这行来看,2应当是在3这个位置上,3应该是在1位置上,1应该是在2位置上;5应该是在4位置上,4应该是在5位置上。
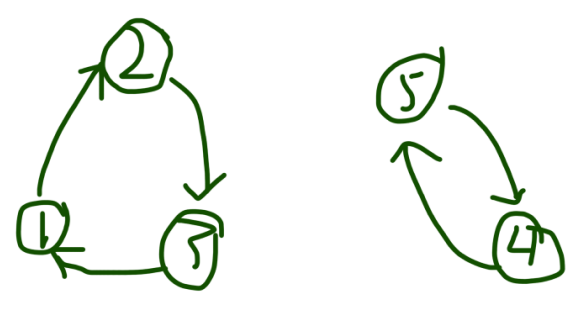
对于单个环中的两个元素去交换与两个环中的单个元素去交换会产生两种情况:
情况①:单个环中的两个元素去交换,例如我们去交换第一个环里的2与3
此时位置为:
初始位置:1 2 3 4 5
实际位置:3 2 1 5 4
结论:单个环内两个元素交换,此时一个环就会变为两个环。
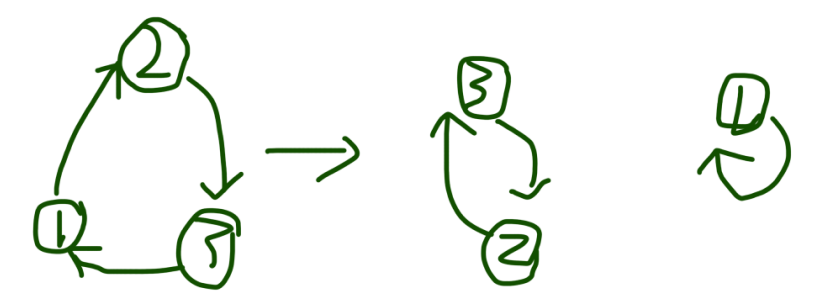
情况2:两个环中的单个元素去交换,例如我们去交换第一个环中的2与第二个环中的5
此时位置为:
初始位置:1 2 3 4 5
实际位置:5 3 1 2 4
结论:两个环中的单个元素去交换,此时两个环会变为1个环。
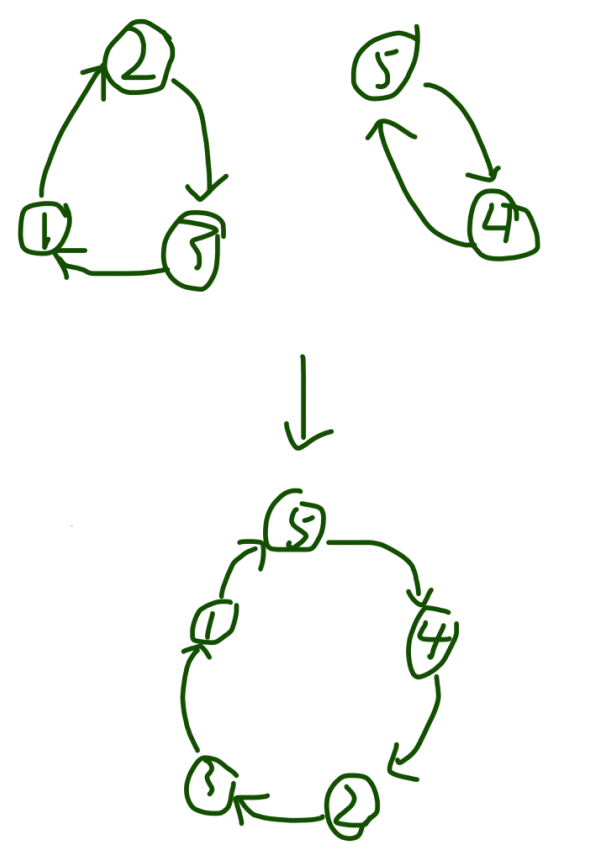
知道了这两个结论后,我们对于解这道题有什么帮助?我们本道题实际上最终的效果想要达到的效果如下:

实际上只需要运用结论1即可,若是我们5个数,形成了两个环,那么如何将两个环拆为五个环内,那么就是使用结论1我们交换1次环内两个元素,一个环就会变为两个环,实际上交换的次数就是 = 数字数量 - 环数
那么由此我们只需要得到构成环数的数量也就知道需要交换的次数了,我们可以借助一个boolean辅助数组来进行标识环的数量,看代码推一遍即可!
拿arr数组[2 3 1 5 4]来举例,visited = [false, false, false, false, false],下标从1开始
cnt = 0; //表示成环的数量
i = 1
visited[1] false成立,表示以1作为成环的开始,cnt++
以visited[1]开始 条件为!visited[j] j = arr[j],这个过程就是成环的过程,一旦回到1时,此时visited[1]=true结束
最终:visited = [true, true, true, false, false]
i = 2 x
i = 3 x
i = 4
visited[4] false成立,表示4作为环的开始:cnt++
同样以visted[4]开始 同上过程,回到4即可截止
最终:visited = [true, true, true, true, true]
i = 5 x
//可以看到该例子上面进行了两次成环,cnt加了两次,最终就是表示2个环
交换的次数 = 5 - 2 = 3
思路有了,直接可以code了!
代码:
思路1:暴力(选择排序)
复杂度分析:
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n^2^);空间复杂度O(n)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static final BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int N = 10010;
static int[] arr = new int[N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
int n = Integer.parseInt(cin.readLine());
String[] s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[i - 1]);
}
//选择排序
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
//找到[i + 1, n]中比arr[i]小的数
int min = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min]) {
min = j;
}
}
//若是索引不同,说明有需要交换的数,那么次数就+1,并且两个数字进行交换
if (min != i) {
cnt++;
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[min];
arr[min] = tmp;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}

思路2:图论解法
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n);空间复杂度O(n)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static final BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int N = 10010;
static int[] arr = new int[N];
static boolean[] visited = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
int n = Integer.parseInt(cin.readLine());
String[] s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[i - 1]);
}
//取出有多少能够进行成环的
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
//成环的数量+1
cnt++;
//给当前能够进行成环的visited数组进行下标设置true
for (int j = i; !visited[j]; j = arr[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
//最后交换的次数就是所有小朋友的数量 - 环数
System.out.println(n - cnt);
}
}

习题
习题—单链表
单链表:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static final BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int N = 100010;
static int n;
//存放第idx位数据
static int[] e = new int[N];
//存放第idk位数据的下一个结点索引
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int head = -1;//头节点,存的是数据的索引
static int idx;//最新的下标
public static void addToHead(int x) {
e[idx] = x;//赋值
ne[idx] = head;//更新当前的新添加的结点next的索引
head = idx;//更新头节点
idx++;//索引更新
}
public static void insert(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;//赋值
ne[idx] = ne[k];//当前next索引更新为第k个位置的next索引
ne[k] = idx;//更新第k个next索引为当前值索引
idx++;//索引更新
}
public static void remove(int k) {
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];//获取当前第k个next索引值的next索引,即可表示删除
}
public static void print() {
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
System.out.printf("%d ", e[i]);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)throws Exception {
n = Integer.parseInt(cin.readLine());
//初始化链表
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
while (n -- != 0) {
String[] s = cin.readLine().split(" ");
String oper = s[0];
int k = 0, x = 0;
//插入数
switch(oper) {
case "I":
k = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
x = Integer.parseInt(s[2]);
insert(k - 1, x);
break;
case "D":
k = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
//若是k=0,直接更新头节点位置
if (k == 0) {
head = ne[head];
}else {
remove(k - 1);
}
break;
case "H":
x = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
addToHead(x);
break;
}
}
//遍历所有值
print();
}
}

- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)