01数据结构与算法刷题之【链表】篇
@[toc]
前言
除了去年11月份以及今年近几月的算法刷题之外,只有在当时20年蓝桥杯准备的时候才刷过一些题,在当时就有接触到一些动归、递归回溯、贪心等等,不过那会也还是一知半解,做的题目也特别少,因为考虑到之后面试有算法题以及数据结构算法对于一个程序员十分重要,我也开始了刷题之路。
我目前的学习数据结构与算法及刷题路径:
1、学习数据结构的原理以及一些常见算法。
2、代码随想录:跟着这个github算法刷题项目进行分类刷,在刷题前可以学习一下对应类别的知识点,而且这里面每道题都讲的很详细。
3、牛客网高频面试101题:牛客网—面试必刷101题,在刷的过程中可以在leetcode同步刷一下。
4、接下来就是力扣上的专栏《剑指offer II》、《程序员面试金典(第 6 版)》…有对应的精选题单来对着刷即可。
5、大部分的高频面试、算法题刷完后,就可以指定力扣分类专栏进行一下刷题了。
刚开始刷的时候真的是很痛苦的,想到去年一道题可能就需要好几小时,真的就很难受的,不过熬过来一切都会好起来,随着题量的增多,很多题目你看到就会知道使用什么数据结构或者算法来去求解,并且思考对应的时间空间复杂度,并寻求最优解,我们一起加油!
我的刷题历程
截止2022.8.18:
1、牛客网101题(其中1题是平台案例有问题):
2、剑指offerII:
力扣总记录数: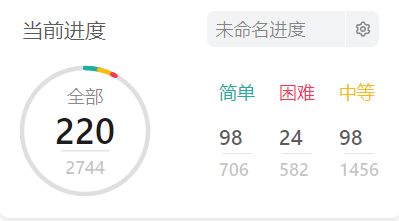
加油加油!
基本概念
链表节点
//链表节点定义
class ListNode{
private int val;
private ListNode listNode;
ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
删除操作时间复杂度O(1)
查找某个节点的时间复杂度O(n)
数组与链表:
- 数组:插入、删除时间复杂度为O(n),查询O(1),适用于频繁查询。数组长度一般为固定。
- 链表:插入、删除时间复杂度为O(1),查询O(n),适用于频繁增删。链表长度一般不固定。
剑指offer
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表【简单】
题目内容:输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
解法:
1、反转链表+遍历
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),实际上是2n
- 空间复杂度:O(n),集合n+数组n,也是2n
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
//反转链表
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
//遍历一遍链表
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
while (pre != null) {
res.add(pre.val);
pre = pre.next;
}
int[] resArr = new int[res.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resArr.length; i++) {
resArr[i] = res.get(i);
}
return resArr;
}
}
2、双遍历:对比1中在空间复杂度上作了优化
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
int n = 0;
while (cur != null) {
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
//开启数组
int[] res = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res[i] = head.val;
head = head.next;
}
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点【简单】
题目链接:剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
题目内容:给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。返回删除后的链表的头节点。
思路:
1、定义虚拟结点,来进行指定删除。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1);
temp.next = head;
ListNode pre = temp;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = pre.next;
break;
}else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return temp.next;
}
}
牛客
简单
判断表中是否有环【简单】
题目地址:BM6 判断链表中是否有环
题目:判断给定的链表中是否有环。如果有环则返回true,否则返回false。
思路1:哈希表
-
存储到一个hash表中来不断进行判断是否有环。(牛客网中提交报语法错误,不理解)
-
set的添加方法是add。
时间复杂度O(N):其中 N 为链表中节点的数目。遍历整个链表的结点
空间复杂度O(N):其中 N 为链表中节点的数目。我们需要将链表中的每个节点都保存在哈希表当中。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos = head;
// 哈希表记录访问过的结点
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (pos != null) {
// 判断结点是否被访问
if (visited.contains(pos)) {
return true;
} else {
// 结点记录添加到哈希表中
visited.add(pos);
}
// 遍历
pos = pos.next;
}
return false;
}
思路2:双指针(推荐)。
- 定义一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,若是快指针过程中碰到null了那么就表示没有环,在移动的过程中一旦快慢指针相等,那么就表示链表成环。
时间复杂度O(N):其中 N 为链表中节点的数目。在最初判断快慢指针是否相遇时,slow 指针走过的距离不会超过链表的总长度
空间复杂度O(1):额外使用的指针占用常数空间
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
链表中倒数最后k个结点【简单】
题目地址:链表中倒数最后k个结点
题目描绘:输入一个长度为 n 的链表,设链表中的元素的值为 ai ,返回该链表中倒数第k个节点。如果该链表长度小于k,请返回一个长度为 0 的链表。
思路1(推荐):返回为0,则表示返回null。我们使用快慢指针来进行移动,快的先移动k个,之后双方同时向后移动。
时间复杂度O(N):N为链表长度,遍历整个链表
空间复杂度O(1):使用额外常数大小空间
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
//双指针
ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1);
temp.next = pHead;
ListNode slow = temp;
ListNode fast = temp;
//先让快指针移动
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
//边界问题:若是倒数k个数超过范围了,返回null
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
//同时向后移动
while (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
思路2:通过栈数据结构,先入栈,后出栈k个。
时间复杂度O(N):N为链表长度,遍历整个链表
空间复杂度O(N):使用额外常数大小空间
两个链表的第一个公共结点【简单】
题目地址:两个链表的第一个公共结点
题目描述:输入两个无环的单向链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点,如果没有公共节点则返回空。(注意因为传入数据是链表,所以错误测试数据的提示是用其他方式显示的,保证传入数据是正确的)
思路1:利用哈希表来定位公共结点
时间复杂度O(N):N为链表长度,遍历整个链表
空间复杂度O(N):使用额外常数大小空间
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//思路:利用哈希表来解决
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>();
//遍历headA添加结点到set中
while (headA != null) {
visited.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headB != null) {
if (visited.contains(headB)) {
return headB;
}
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
思路2:念念不忘,必有回想,通过从另一个他路径上不断寻找
时间复杂度O(N):N为链表长度,遍历整个链表
空间复杂度O(1):使用额外常数大小空间
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB ==null ) {
return null;
}
//定义两个结点
ListNode n1 = headA;
ListNode n2 = headB;
while (n1 != n2) {
n1 = n1 == null ? headB : n1.next;
n2 = n2 == null ? headA : n2.next;
}
return n1;
}
判断一个链表是否为回文结构【简单】
题目链接:判断一个链表是否为回文结构
题目内容:给定一个链表,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。
思路1:双指针+反转链表
- 后半部分反转,以后半部分为null作为结束比对条件。
时间复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类 the head
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean isPail (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
//定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//奇数情况
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
//后半部分链表进行反转
ListNode right = reverse(slow);
//回文比较
while (right != null) {
if (right.val != head.val) {
return false;
}
right = right.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = dummy;
dummy = head;
head = temp;
}
return dummy;
}
}
删除有序链表中重复的元素-I【简单】
题目链接:删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
题目内容:删除给出链表中的重复元素(链表中元素从小到大有序),使链表中的所有元素都只出现一次。
思路1:使用Set容器来进行判重操作。
时间复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
Set<Integer> sets = new HashSet<>();
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
//判断是否在容器中出现
if (!sets.contains(cur.val)) {
sets.add(cur.val);
pre = cur;
}else {
//删除节点动作
pre.next = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}
思路2:遍历删除
- 注意题目是有序,那么我们无需考虑乱序的一个情况。
时间复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
//遍历到不相等的元素
while (temp != null && temp.val == cur.val) temp = temp.next;
cur.next = temp;
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}
中等
链表内指定区间反转【中等】
题目地址:BM2 链表内指定区间反转
题目描述:将一个节点数为 size 链表 m 位置到 n 位置之间的区间反转,要求时间复杂度 O(n)O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)O(1)。
思路:
/**
* 思路:起始位定位,翻转指定区间链表,需要临时保存的结点有:初始定位前置结点以及初始结点,方便反转后进行连接。
*/
public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) {
//到达要反转的链表节点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode reverseHeadPre = null;//反转前头结点的前置结点
ListNode reverseTail = null;//反转后链表的末尾结点
ListNode cur = dummy;//反转后的头结点
n = n - m + 1;
while (m != 0) {
if (m == 1) {
reverseHeadPre = cur;//保存前置结点
}
cur = cur.next;
m--;
}
//进行反转链表
reverseTail = cur;//临时保存下链表反转后的末尾结点
ListNode pre = null;
while (n != 0) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
n--;
}
reverseTail.next = cur;
reverseHeadPre.next = pre;
return dummy.next;
}
删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点(【中等】,牛客/第3题的升级版)
题目地址: 删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点
题目描述:给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
思路1:首先定位到对应的倒数第k个结点,接着再此基础上加上一个前缀结点,用于之后进行删除操作,即可AC。
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1);
temp.next = head;
//定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = temp;
ListNode fast = temp;
ListNode pre = null;
//快指针先走
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
//同时走
while (fast != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
pre.next = slow.next;
return temp.next;
}
}
链表中的两数相加【中等】
题目链接:链表中的两数相加
题目内容:假设链表中每一个节点的值都在 0 - 9 之间,那么链表整体就可以代表一个整数。给定两个这种链表,请生成代表两个整数相加值的结果链表。
思路1:使用两个栈来进行操作,依次相加并最终组成链表返回。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head1 ListNode类
* @param head2 ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode addInList (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
// 937
// 63
//1000
//筛选情况
if (head1 == null) {
return head2;
}
if (head2 == null) {
return head1;
}
//链表转为栈
Stack<ListNode> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<ListNode> s2 = new Stack<>();
while (head1 != null) {
s1.push(head1);
head1 = head1.next;
}
while (head2 != null) {
s2.push(head2);
head2 = head2.next;
}
//处理进位情况
int tmp = 0;
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode nHead = head.next;
//只要任意一个栈有元素即可
while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty()) {
//求得一个相加值
int val = tmp;
if (!s1.isEmpty()) {
val += s1.pop().val;
}
if (!s2.isEmpty()) {
val += s2.pop().val;
}
tmp = val / 10;
ListNode node = new ListNode(val % 10);
node.next = nHead;
nHead = node;
}
//处理tmp>0最终情况
if (tmp > 0) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(tmp);
node.next = nHead;
nHead = node;
}
return nHead;
}
}
单链表的排序【中等,三种方案包含哨兵、归并排序,只有归并排序在leetcode不超时】
题目链接:单链表的排序
题目内容:给定一个节点数为n的无序单链表,对其按升序排序。
思路1:对链表进行选择排序,仅仅只是交换结点的值(超时)
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类 the head node
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
//选择排序:交换结点中的值
ListNode move = head;
while (move != null) {
ListNode temp = move.next;
while (temp != null) {
if (move.val > temp.val) {
int tmp = move.val;
move.val = temp.val;
temp.val = tmp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
move = move.next;
}
return head;
}
}
思路2:交换结点。【leetcode超时】
- 1.建立哨兵节点
- 2.每次从未排序的链表节点中找出最小的节点接到已排序链表的后面
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
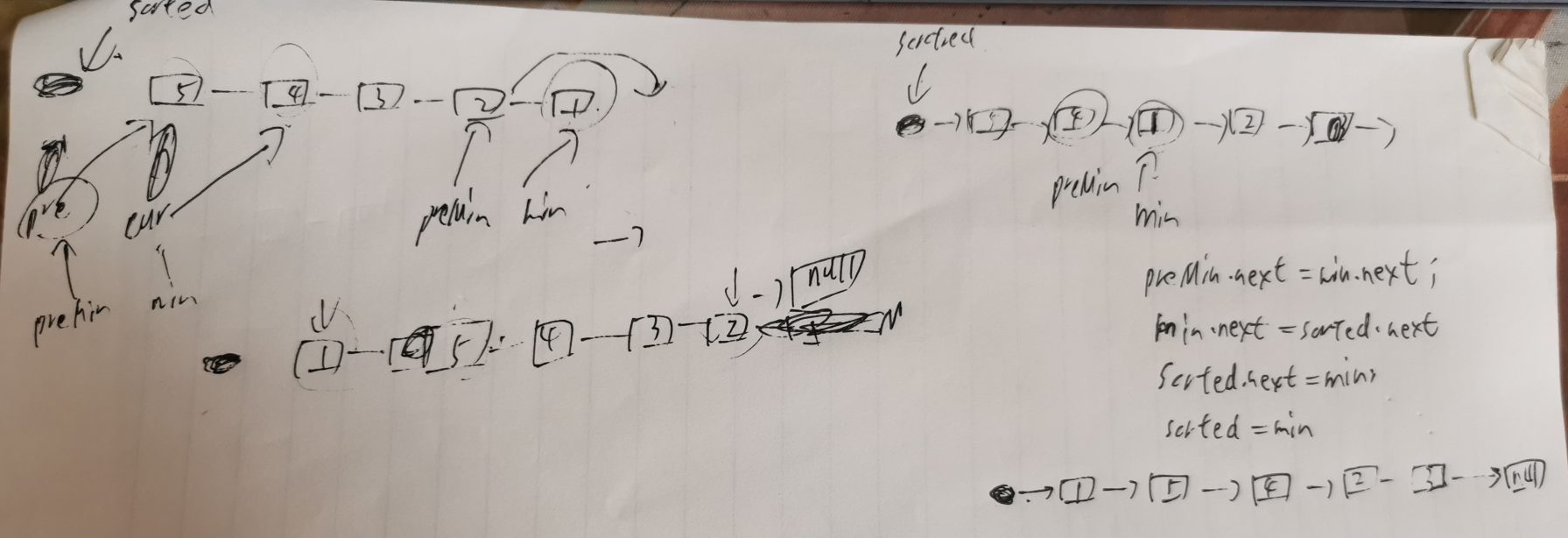
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类 the head node
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
//定义一个虚拟结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
//定义一个哨兵结点
ListNode sentryNode = dummy;
//若是哨兵的下一个结点为null,那么不继续往下执行
while (sentryNode.next != null) {
ListNode pre = sentryNode;
ListNode cur = sentryNode.next;
ListNode minPre = null;
ListNode min = null;
//来找出最小结点
while (cur != null) {
//比较取得最小值
if (min == null || min.val > cur.val) {
min = cur;
minPre = pre;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
//此时已经找到最小结点,来依靠哨兵结点进行交接对换
minPre.next = min.next;
min.next = sentryNode.next;
sentryNode.next = min;
sentryNode = min;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
思路3:归并排序
时间复杂度O(nlogn)
空间复杂度O(1)
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类 the head node
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
//若是当前只有一个结点,那么直接返回该结点即可
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
//找到中间点,定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;//若是fast结点不设置为head.next那么就会进入到死循环中
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode tmp = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
//递归左右两边来进行比较操作
ListNode left = sortInList(head);
ListNode right = sortInList(tmp);
//开始进行合并操作
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode dummy = res;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
dummy.next = left;
left = left.next;
}else {
dummy.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
dummy = dummy.next;
}
dummy.next = left != null ? left : right;
return res.next;
}
}
问题:为什么fast=head.next,设置为fast=head就会出现栈溢出?
核心就是出现了无限递归调用的情况了,这里举个例子就明白了:
例如:5->4->null
head为5结点
接着fast、slow一轮下来之后,slow为结点4,此时调用sortInList(head),此时head依旧是5结点
那么下一次同样也是5->4->null,此时就会出现无限递归调用了!
链表中环的入口结点【中等】
题目链接:链表中环的入口结点
题目内容:给一个长度为n链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,返回null。
思路1:①判断是否为环形。②若是环形,从相遇点以及链表初始点同时出发n个位置相等时的结点即为入口结点。
时间复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode hasCircular(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) {
return null;
}
//定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = pHead;
ListNode fast = pHead;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
//判断是否有环
ListNode node = hasCircular(pHead);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
//若是不为null,表示有环,从环中点与起点同时出发相遇的点即可入口结点
ListNode node2 = pHead;
while (node2 != node) {
node2 = node2.next;
node = node.next;
}
return node2;
}
}
删除有序链表中重复的元素-II【中等】
题目链接:删除有序链表中重复的元素-II
题目内容:给出一个升序排序的链表,删除链表中的所有重复出现的元素,只保留原链表中只出现一次的元素。
思路1:通过一个计数器来判断重复
时间复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode h = dummy;
//基准比较结点
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null) {
//重复检测动作
fast = fast.next;
int num = 0;
while (fast != null && fast.val == slow.val) {
num++;
fast = fast.next;
}
//表示出现了重复情况
if (num > 0) {
if (fast == null)
break;
slow = fast;
fast = fast;
continue;
}
//添加到新的结点
h.next = new ListNode(slow.val);
h = h.next;
if (slow != null) {
//两个指针也要移动
slow = slow.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
思路2:重复值变量表示,之后重复比较即可
- 优化思路1,空间复杂度O(n)优化为O(1)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
//保证后面有两个结点存储,满足可能出现重复值情况
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
int temp = cur.next.val;
//遍历判断重复的值
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == temp) {
//删除重复值的结点
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
leetcode
简单
反转链表【简单】
题目描述:给定单链表的头节点 head ,请反转链表,并返回反转后的链表的头节点。
思路:①定义一个前置节点,之后配合前后指针进行移动来进行反转,最终返回前置节点。
方式一:非递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
方式二:递归
// 方式二:采用递归写法
/**
* 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
* 内存消耗:41.2 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了36.33%的用户
*/
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
// 递归来进行反转链表
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur){
if (cur == null) {
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
合并两个排序列表【简单】
题目描述:输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
思路解法:定义一个新节点,并且设置虚拟头结点,接着对两个链表进行依次比较连接。
方式一:非递归反转
/**
* 思路:定义一个新节点,并且设置虚拟头结点,接着对两个链表进行依次比较连接。
* 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
* 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
* 内存消耗:41.2 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了63.20%的用户
*/
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
cur.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}else {
cur.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//处理链表剩余节点
while (l1 != null) {
cur.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
cur.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
方式二:递归处理,不断比较两个值并且返回对应的链表
//方式二:递归解法
/**
* 思路:每个子问题都是比较两个值得大小,最终返回一个已经排好序的链表
*
* 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
* 执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
* 内存消耗:40.9 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了37.67%的用户
*/
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
回文链表【简单】
链接地址:234. 回文链表
题目描述:给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
方式一:添加集合比较法
思路:将链表中所有的结点添加到数组中,然后进行比较。
/**
* @ClassName 回文链表【简单】
* @Author ChangLu
* @Date 4/26/2022 6:07 PM
* @Description 回文链表:给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
* 地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
*/
public class 回文链表 {
//方式一:全部添加到集合中,然后依次比较
/**
* 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
* 执行用时:6 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了51.96%的用户
* 内存消耗:53.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了70.35%的用户
*/
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<ListNode> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null) {
nodes.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
//来进行依次比对
int left = 0;
int right = nodes.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (nodes.get(left).val != nodes.get(right).val) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}
方式二:快慢指针+反转链表
思路:使用快慢指针来进行遍历链表,过程中利用慢指针来进行反转一半链表结点,最终来进行比对。
//方式二:快慢指针+链表反转,最终进行回文比对
/**
* 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
* 执行用时:3 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了99.10%的用户
* 内存消耗:57.4 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了49.65%的用户
*/
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode cur = slow;//根据慢指针来进行不断反转
ListNode pre = null;
//在慢指针移动时顺便反转一半链表
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = slow;
}
//奇数情况
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
//最后进行对比比较值:pre与slow
while (pre != null) {
if (pre.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
141. 环形链表【简单】
学习:leetcode题解
题目链接:141. 环形链表
题目内容:
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
速记:
①哈希表:使用set将每个链表节点进行存储,若是遍历过程中添加失败,则说明有环;若是过程中碰到为null的节点,则说明无环。
②快慢指针:快指针走两步,慢指针走一步。以快慢指针指向节点是否相同来作为判断条件,若是相同则说明有环,若是中途指针指向有null,则说明无环。
思路:
1、哈希表
思路:将每一个链表节点都进行临时存储,遍历下一个节点的时候都尝试插入到哈希表中,若是插入成功说明没有碰到相同的节点,若是失败则表明有环。
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
//哈希表
Set<ListNode> sets = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null){
if (!sets.add(head)){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
2、快慢指针
思路:使用两个指针,一个慢一个快,以两个指针指向节点是否相等来作为条件,若是相等则说明有环,若是遍历过程中若是为null,则表示无环已经走到底了,直接结束。
复杂度分析:时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return false;
}
//定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = slow.next;
//设置快慢指针是否相同作为条件
while (slow != fast){
//让快指针来进行探路判断
if (fast == null || fast.next == null){
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)