Map 接口和常用方法
【摘要】 Map 接口和常用方法 1. Map 接口实现类的特点 2. Map 接口源码分析 3. Map 接口常用方法 4. Map 接口遍历方法 5. Map 接口实战 Map 接口和常用方法 1. Map 接口实现类的特点这里讲的是JDK8的Map接口特点Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-ValueMap中的key和value可以是任何引用类型的数据,会...
Map 接口和常用方法

1. Map 接口实现类的特点
这里讲的是JDK8的Map接口特点
- Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:
Key-Value - Map中的key和value可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到
HashMap$Node对象中 - Map中的key不允许重复,原因和HashSet一样
- Map 中的 value 可以重复
- Map的key可以为
null, value也可以为null,注意key为null,只能有一个,value为null,可以多个. - 常用
String类作为Map的key - key和value之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的key总能找到对应的value
- 当 key 相同时,就等价于替换
2. Map 接口源码分析
-
Map 接口的特点
-
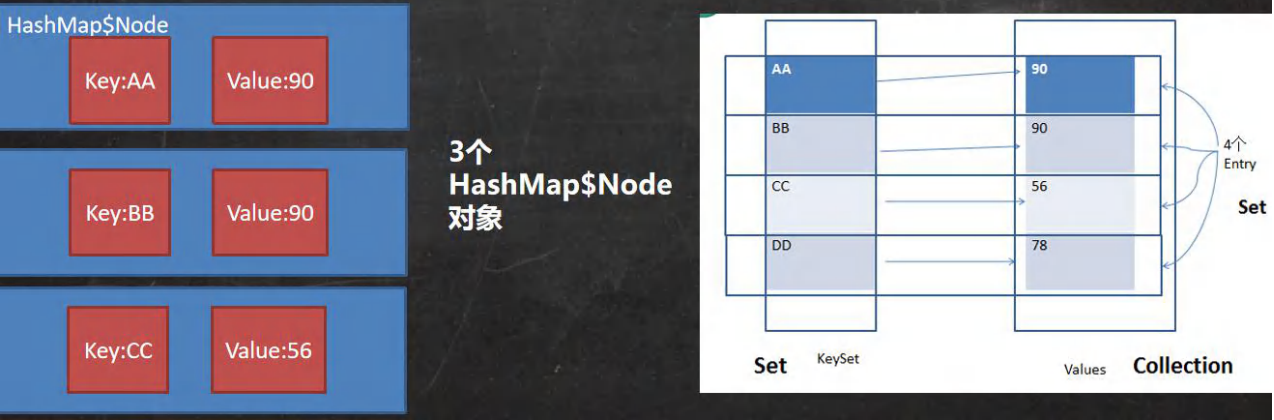
Map存放数据的
key-value示意图,一对k-v是放在一个HashMap$Node中的, 因为Node实现了Entry接口,一对k- v就是一个Entry,Entry 再放到 EntrySet 里面

-
Key:Value 的类型:
Key(Set):Value(Collection) -
真正的Key:Value 是放在
HashMap$Node中,下面的 Set 和 Collection 集合只是指向了HashMap$Node而已(引用),为了遍历方便

-
源码解读:
- k-v 最后是:
HashMap$Node node = newNode(hash, key, value, null); - k-v 为了方便遍历,还会创建
EntrySet(集合),该集合存放的元素的类型:Entry,而一个Entry对象就有k-v,EntrySet<Entry<k,v>>
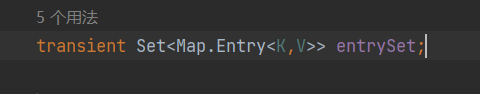
查看 HashMap 源码可以发现,即:transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
证明:entrySet 类型是 HashMap$EntrySet
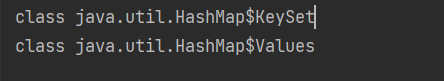
Set set = map.entrySet();
System.out.println(set.getClass()); // HashMap$EntrySet
- 在 entrySet 中,定义的类型是 Map.Entry,但实际上存放的还是 HashMap$Node
- 验证 EntrySet 放的是 Entry
for (Object entry : set) {
System.out.println(entry.getClass()); // HashMap$Node
}
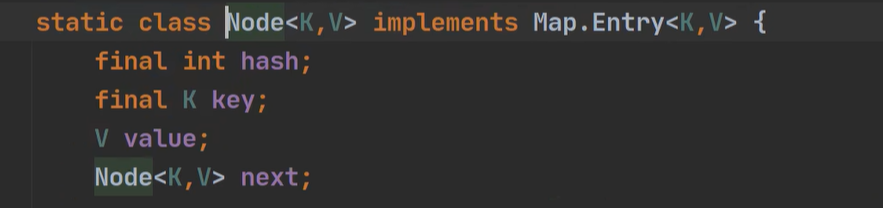
- 因为 HashMap$Node implements Map.Entry,即:static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V>
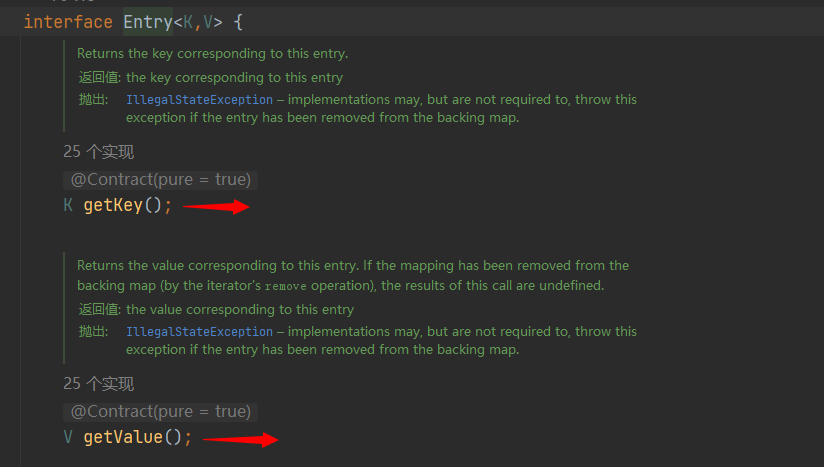
- 当把 HashMap$Node 对象存放到 entrySet 就方便遍历,因为 Map.Entry 提供了两个重要发方法
-
查看Entry源码可以发现,K getKey(); V getValue();

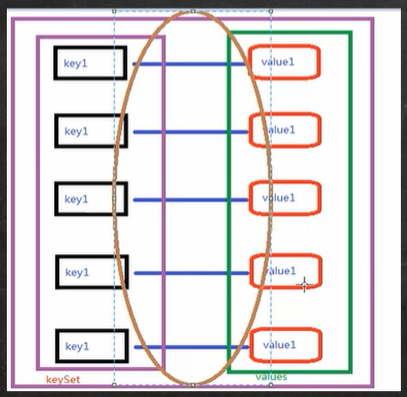
-
直观理解:就是先把 上图 中 HashMap$Node 中的 k-v 转成一个 entry ,再把 entry 放在右边图中 entrySet 中
Set set = map.keySet();
System.out.println(set.getClass());
Collection values = map.values();
System.out.println(values.getClass());
3. Map 接口常用方法
- put:添加
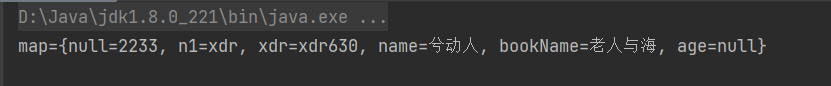
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("bookName", new Book("未来的未来", 100));//OK
map.put("bookName", "老人与海");//替换
map.put("n1", "xdr");//OK
map.put("name", "兮动人");//OK
map.put("age", null);//OK
map.put(null, "2233");//OK
map.put("xdr", "xdr630");//OK
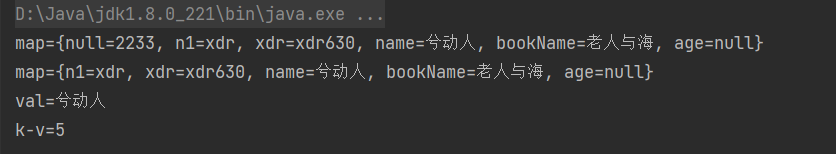
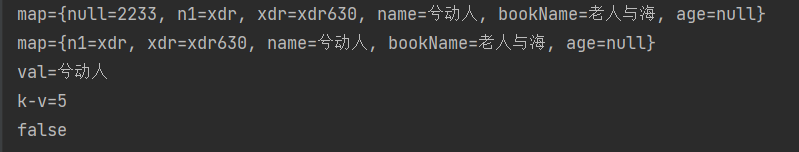
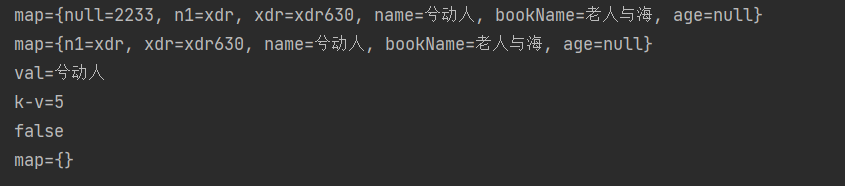
System.out.println("map=" + map);
- remove:根据键删除映射关系
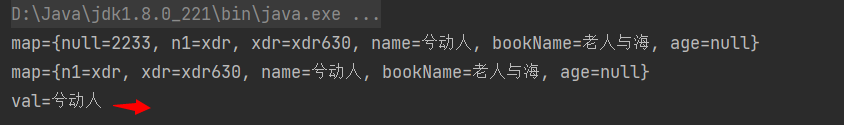
map.remove(null);
System.out.println("map=" + map);

- get:根据键获取值
Object val = map.get("name");
System.out.println("val=" + val);
- size:获取元素个数
System.out.println("k-v=" + map.size());
- isEmpty:判断个数是否为空
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
6.clear:清除k-v
map.clear();
System.out.println("map=" + map);
- containsKey:查找键是否存在
System.out.println(map.containsKey("name"));

4. Map 接口遍历方法
- Map遍历 (比List和Set复杂点,但是基本原理样)

- 第一种方法: 先取出所有的Key , 通过Key 取出对应的Value
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("n1", "xdr");
map.put("n2", "兮动人");
map.put("n3", null);
map.put(null, "2233");
map.put("xdr", "xdr630");
Set keyset = map.keySet();
//(1) 增强for
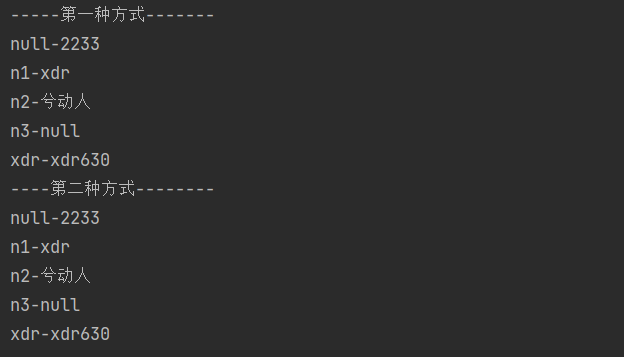
System.out.println("-----第一种方式-------");
for (Object key : keyset) {
System.out.println(key + "-" + map.get(key));
}
//(2) 迭代器
System.out.println("----第二种方式--------");
Iterator iterator = keyset.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + "-" + map.get(key));
}
- 第二种方法: 把所有的
values取出
Collection values = map.values();
//这里可以使用所有的Collections使用的遍历方法
//(1) 增强for
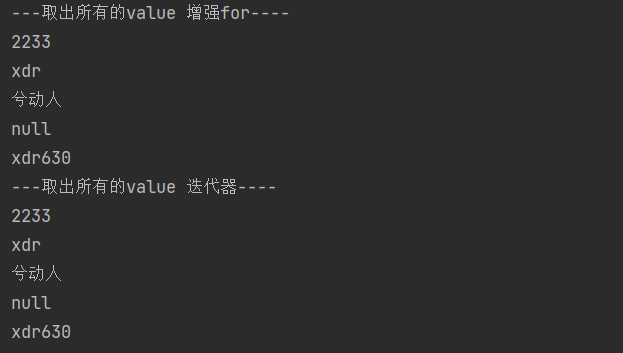
System.out.println("---取出所有的value 增强for----");
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
//(2) 迭代器
System.out.println("---取出所有的value 迭代器----");
Iterator iterator2 = values.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object value = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
- 第三种方法: 通过
EntrySet来获取 k-v
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();// EntrySet<Map.Entry<K,V>>
//(1) 增强for
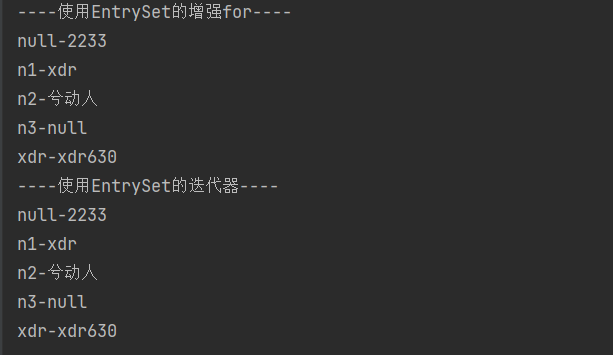
System.out.println("----使用EntrySet的增强for----");
for (Object entry : entrySet) {
//为了方便遍历,将entry 转成 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
//(2) 迭代器
System.out.println("----使用EntrySet的迭代器----");
Iterator iterator3 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator3.hasNext()) {
Object entry = iterator3.next();
//System.out.println(next.getClass());//HashMap$Node -实现-> Map.Entry (getKey,getValue)
//向下转型 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
5. Map 接口实战
- 使用HashMap添加3个员工对象,要求 键:员工id,值:员工对象,并遍历显示 工资> 18000 的员工 (遍历方式最少两种)
- 员工类:姓名、工资、员工id
public class MapExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map hashMap = new HashMap();
//添加对象
hashMap.put(1, new Emp("xdr", 30000, 1));
hashMap.put(2, new Emp("mike", 20000, 2));
hashMap.put(3, new Emp("jack", 10000, 3));
//遍历2种方式
//并遍历显示工资>18000的员工(遍历方式最少两种)
//1. 使用keySet -> 增强for
Set keySet = hashMap.keySet();
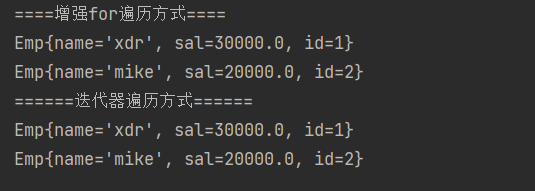
System.out.println("====增强for遍历方式====");
for (Object key : keySet) {
//先获取value
Emp emp = (Emp) hashMap.get(key);
if(emp.getSal() >18000) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
//2. 使用EntrySet -> 迭代器
Set entrySet = hashMap.entrySet();
System.out.println("======迭代器遍历方式======");
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
//通过entry 取得key 和 value
Emp emp = (Emp) entry.getValue();
if(emp.getSal() > 18000) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
}
}
class Emp {
private String name;
private double sal;
private int id;
// 省略 set/get toString 构造方法
}
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)