猿创征文 | Spring框架【管理对象(IOC详解)】
目录
1,管理对象(IOC详解)
-
Spring框架是企业使用最多的框架,没有之一。
-
Spring是一站式框架,也就是Spring可以整合其他框架。
-
Spring IoC:对象工厂及依赖注入。
-
Spring AOP:面向切面编程技术,Spring事务管理的基础。
-
Spring Transaction management:Spring事务管理。
-
Spring Web MVC:后面单独学习。
-

1.1 :什么是IOC
-
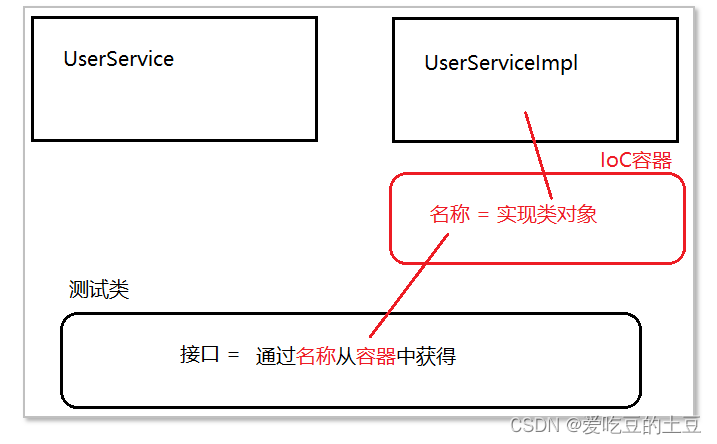
IoC 是 Inversion of Control 的缩写,即“控制反转”。
-
控制反转:将创建对象的权利,由自己(new)反转给spring。
-
图解1:未使用IoC
-

图解2:使用IoC
-

IoC作用:
-
统一管理对象
-
解决对象之间的耦合
-
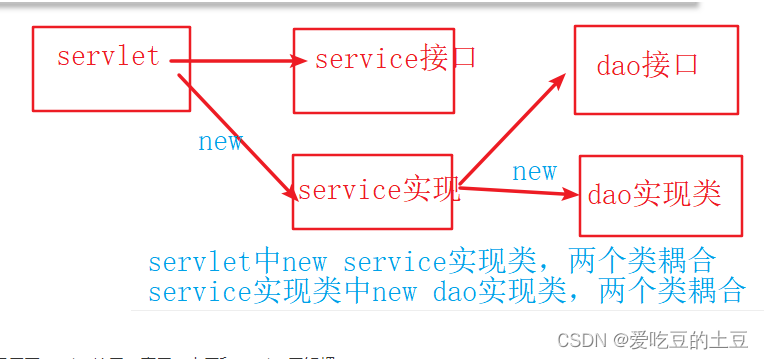
之前使用,类之间存在耦合
-
-

解决程序耦合
-
servlet类中,只用了service接口,表示web层和service层解耦。
-
service实现类中,只用了dao的接口,表示service层和dao层解耦。
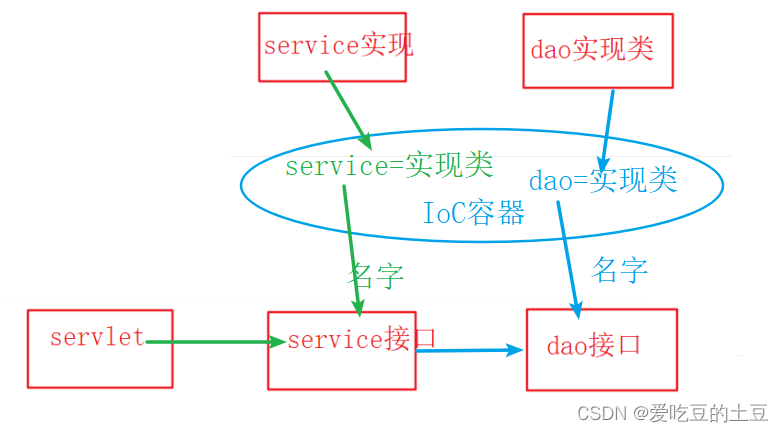
好处: 可以实现解耦, 让类和类之间的耦合度降低, 将对象的创建权交给Spring管理
1.2:Bean创建
-
在spring 容器中管理的对象,统称为
bean。例如:UserDao、UserService 等
1.2.1:Bean相关注解
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Component | 将修饰的资源交予spring管理。 value属性:为资源命名(唯一标识) |
| @Controller | 衍生注解,与@Component作用和属性相同。特用于修饰==表示层==的资源。 |
| @Service | 衍生注解,与@Component作用和属性相同。特用于修饰==业务逻辑层==的资源。 |
| @Repository | 衍生注解,与@Component作用和属性相同。特用于修饰==数据访问层==的资源。 |
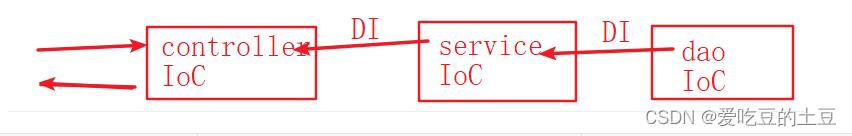
1.3:依赖注入(DI)
1.3.1:什么是DI
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI)Spring 容器在创建被调用者的实例时,会自动将调用者需要的对象实例注入给调用者。
| 注解 | 描述 | 修饰位置 |
|---|---|---|
| @Resource(name=”…”) | 按照指定名称注入对象 | 字段、setter方法 |
| @ Resource | 按照类型注入对象 | 字段、setter方法 |
| @Value | 注入简单值 | 字段、setter方法、参数 |
| @PropertySource | 加载properties配置文件 | 类 |
1.3.2:按照名称注入
-
public class 类名{
-
@Resource(name="名称")
-
private 类型 变量;
-
}
字段注入
-
@Resource(name = "studentService4")
-
private StudentService studentService;
setter方法注入
-
private StudentService studentService;
-
-
@Resource(name = "studentService4")
-
public void setStudentService(StudentService studentService) {
-
this.studentService = studentService;
-
}
1.3.3:按照类型注入
-
public class 类名{
-
@Resource
-
private 类型 变量;
-
}
1.3.4:注入简单数据:@Value
-
简单数据:基本数据类型、字符串等。
-
需要:定义User对象,给User对象注入数据
@Value 可以给成员变量注入、也可以给属性注入(getter/setter)
-
步骤
-
步骤1:目标类,User,进行普通数据注入
-
步骤2:配置类
-
步骤3:测试类
-
步骤1:目标类,User,进行普通数据注入
-
@Component
-
public class User {
-
@Value("jack")
-
private String username;
-
@Value("18")
-
private Integer age;
-
//....
-
}
步骤2:配置类
-
@Configuration
-
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.czxy.demo05_di_value.domain")
-
public class Demo05Configuration {
-
}
步骤3:测试类
-
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
-
@ContextConfiguration(classes = Demo05Configuration.class)
-
public class TestDemo05 {
-
@Resource
-
private User user;
-
-
@Test
-
public void testDemo5() {
-
System.out.println(user);
-
}
-
}
1.3.5:properies数据注入
-
需求:读取数据库配置信息
-
步骤:
-
步骤1:编写demo07.properties文件
-
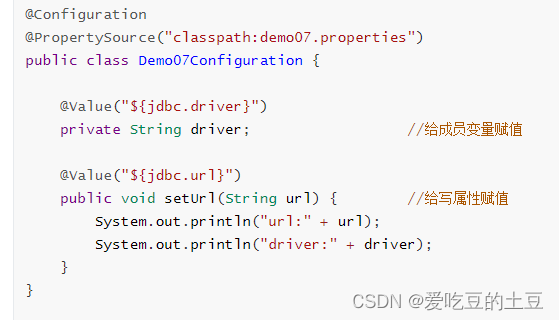
步骤2:编写配置类,读取properties内容。@Value修饰setter
-
步骤3:测试类
-
编写properties文件,key=value
#key=value
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=1234
使用@PropertySource("classpath:properties文件")加载properties文件,使用@Value("${key}")进行注入
测试类
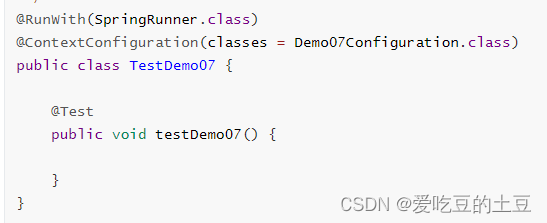
1.4:@Bean注入第三方类
-
在实际开发中,有很多第三方提供类(jar包里),需要在spring中使用。
-
Spring提供@Bean注解,整合第三方类。
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Bean | 将第三方对象,添加到spring容器中,方法名为默认名。 |
| @Bean(name = "") | 按照指定名称,将第三方对象,添加到spring容器中。 |
1.4.1:按照类型
-
需要:假设UserDao是第三方(不能添加注解),需要使用UserDao
-
步骤:
-
步骤1:模拟类
-
步骤2:配置类
-
步骤3:测试类
-
-
模拟类
-

-
配置类

配置类
-
-
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
-
@ContextConfiguration(classes = Demo08Configuration.class)
-
public class TestDemo08 {
-
-
@Resource
-
private UserDao userDao;
-
-
@Test
-
public void testDemo07() {
-
// UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
-
userDao.selectAll();
-
}
-
}
-
1.4.2:按照名称
-
需求:定义一个UserDao接口,编写2个实现类A、B,分别按照名称进行注入
-
步骤:
-
模拟数据类
-
接口
-
实现类A
-
实现类B
-
-
配置类,创建2个实现类,并进行不同的命名
-
测试类,依次注入不同命名的实现类
-
-
实现
-
配置类
-
-
@Configuration
-
public class Demo09Configuration {
-
-
@Bean(name="userDaoA")
-
public UserDao createUserDaoA() {
-
return new UserDaoImplA();
-
}
-
-
@Bean(name="userDaoB")
-
public UserDao createUserDaoB() {
-
return new UserDaoImplB();
-
}
-
}
测试类
-
-
-
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
-
@ContextConfiguration(classes = Demo09Configuration.class)
-
public class TestDemo09 {
-
-
@Resource(name="userDaoA")
-
private UserDao userDaoA;
-
-
@Resource(name="userDaoB")
-
private UserDao userDaoB;
-
-
@Test
-
public void testDemo07() {
-
userDaoA.selectAll();
-
userDaoB.selectAll();
-
}
-
}
-
-
1.4.3:参数类型:引入数据
-
需求:service、dao 都是第三方
-
@Bean 修饰的方法,如果有参数,将自动注入。
-
@Bean
-
public 返回值 方法名(参数类型 参数名) { //主动注入参数对象
-
}
-
步骤:
-
模拟类
-
UserDao
-
UserService
-
-
配置类
-
编写方法,createUserDao
-
编写方法,createUserService( UserDao userDao )
-
-
测试类
-
-
实现
-
模拟类:dao实现类没有注解
-
-
public interface StudentDao {
-
public void selectAll();
-
}
-
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
-
@Override
-
public void selectAll() {
-
System.out.println("demo10 student dao ");
-
}
-
}
模拟类:service,没有注解
-
public interface StudentService {
-
public void selectAll();
-
}
-
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
-
-
private StudentDao studentDao;
-
-
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
-
this.studentDao = studentDao;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public void selectAll() {
-
System.out.println("demo10 student service");
-
studentDao.selectAll();
-
}
-
}
配置类 
-
@Configuration
-
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.czxy.demo10_bean_param"})
-
public class Demo10Configuration {
-
-
@Bean
-
public StudentDao studentDao() {
-
return new StudentDaoImpl();
-
}
-
-
@Bean
-
public StudentService studentService10(StudentDao studentDao) {
-
StudentServiceImpl studentService = new StudentServiceImpl();
-
studentService.setStudentDao(studentDao);
-
return studentService;
-
}
-
}
测试类
-
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
-
@ContextConfiguration(classes = Demo10Configuration.class)
-
public class TestDemo10 {
-
@Resource(name = "studentService10")
-
private StudentService studentService;
-
-
@Test
-
public void testDemo() {
-
studentService.selectAll();
-
}
-
}
1.4.4:参数类型:简单数据
properties配置文件
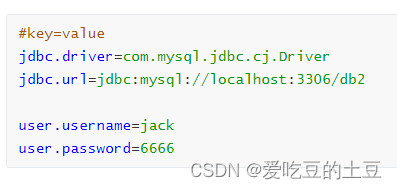
配置类
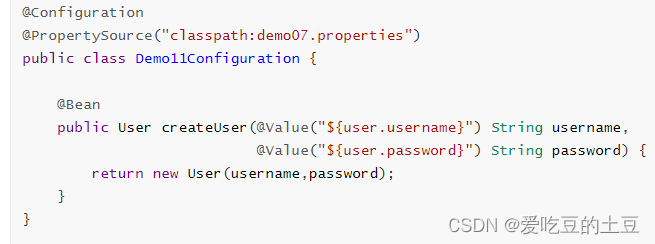
测试类 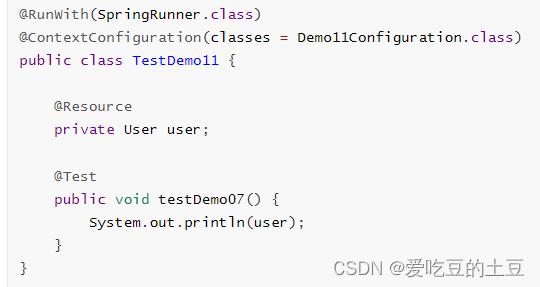
1.5:Bean作用域
1.5.1:概述
-
bean作用域:一个对象的使用范围。
-
通过@Scope可以设置Bean的作用域
| 注解 | 取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| @Scope | singleton | 默认值,单例的。整个spring容器只有一个 |
| prototype | 多例的。每获得一次创建一份 |
-
需求:编写UserDao,获得对象,注入2次。
1.5.2:单例
dao,确定作用域方式
-
@Repository
-
@Scope("singleton")
-
public class UserDao {
-
}
配置类 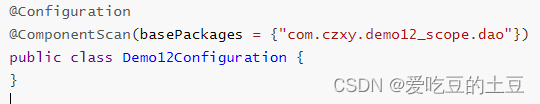
测试类,注入2次,打印结果一样的。 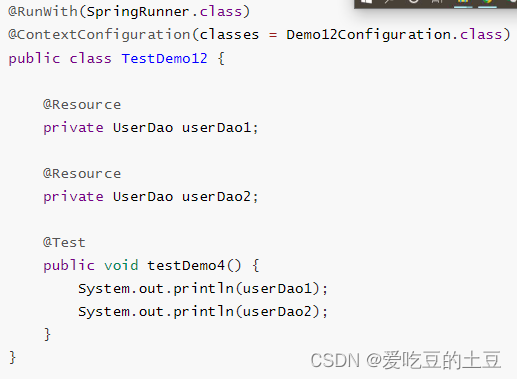
1.5.3:多例
修改单例代码

1.5.4:常量

1.6:生命周期
1.6.1:什么是生命周期
-
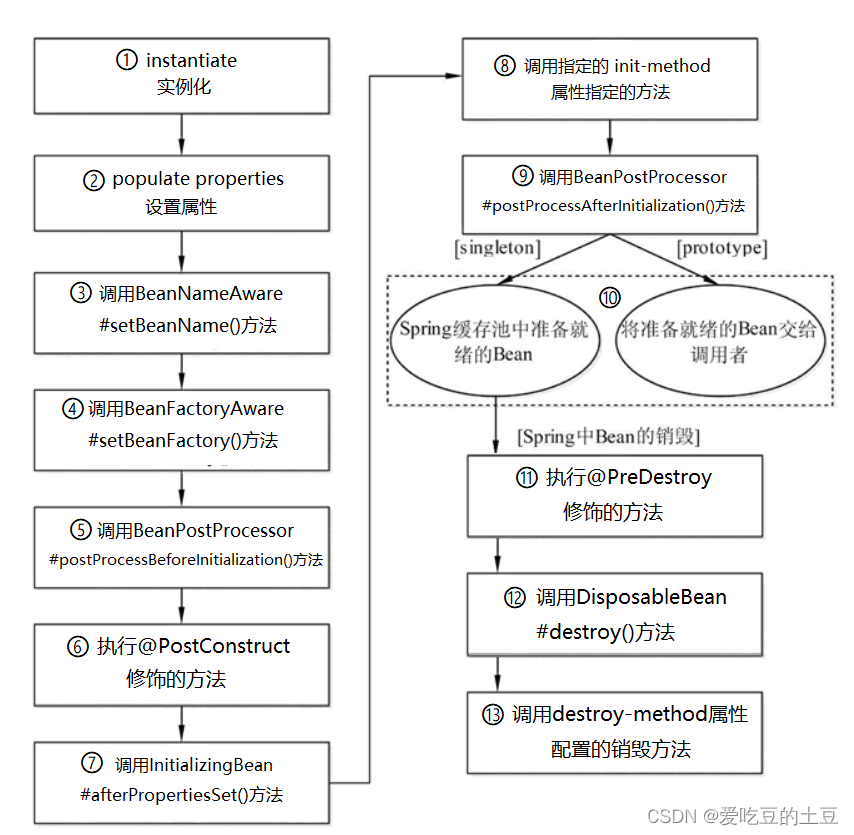
生命周期:指Spring创建Bean到销毁Bean的整个过程。
-
spring bean 完整生命周期参数
-
在实际开发中,最常用的是bean
初始化和销毁。
1.6.2:生命周期详解
-
完整示意图

实例:(⑧、⑬为XML配置内容)
-

步骤1:创建后处理bean
-
-
@Component
-
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
-
@Override
-
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
-
if("dog".equalsIgnoreCase(beanName)) {
-
System.out.println("5. BeanPostProcessor#before --> " + beanName);
-
}
-
return bean;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
-
if("dog".equalsIgnoreCase(beanName)) {
-
System.out.println("9. BeanPostProcessor#after --> " + beanName);
-
}
-
return bean;
-
}
-
}
步骤2:编写目标类Dog
-
-
-
@Component
-
//@Scope("prototype")
-
public class Dog implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
-
-
public Dog() {
-
System.out.println("1. 初始化");
-
}
-
-
@Value("旺财")
-
public void setName(String name) {
-
System.out.println("2. properties --> " + name);
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public void setBeanName(String s) {
-
System.out.println("3. BeanNameAware#setBeanName --> " + s);
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
-
System.out.println("4. BeanFactoryAware#beanFactory ");
-
}
-
-
@PostConstruct //初始化
-
public void init() {
-
System.out.println("6. 小狗 出生了");
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
-
System.out.println("7. InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet");
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
public void eat() {
-
System.out.println("10. 正在吃...");
-
}
-
-
@PreDestroy //销毁
-
public void DogDestroy() {
-
System.out.println("11. 小狗 挂了");
-
}
-
-
-
@Override
-
public void destroy() throws Exception {
-
System.out.println("12. DisposableBean#destroy");
-
}
-
}
步骤3:配置类
-
-
-
@Configuration
-
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.czxy.demo13_lifecycle.domain","com.czxy.demo13_lifecycle.processor"})
-
public class Demo13Configuration {
-
-
}
步骤4:测试类
-
-
-
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
-
@ContextConfiguration(classes = Demo13Configuration.class)
-
public class TestDemo13 {
-
@Resource
-
private Dog dog;
-
-
@Test
-
public void testDemo13() {
-
dog.eat();
-
}
-
}
-
1.6.3:方式一:详解-初始化&销毁
-
需求:
-
编写目标类Dog,并执行eat方法打印
正在吃... -
在eat()前后分别执行初始化
小狗 出生了、销毁小狗 挂了
-
-
目标类:需要完成初始化、销毁功能的类
-
@PostConstruct 用于修饰==初始化==方法。
-
@PreDestroy 用于修饰==销毁==方法。
-

配置类: 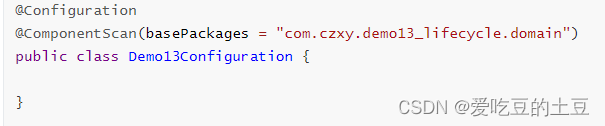
测试类:

1.6.4:方式二:第三方@Bean
-
需求:
-
使用@Bean配置目标类Dog的初始化和销毁
-
-
目录类(假设Dog由第三方jar提供,没有源码,不允许使用注解
@Component)

配置类,使用@Bean注册第三方对象,通过 initMethod 和 destroyMethod 两个属性设置初始化和销毁

测试类

1.6.5:生命周期函数有什么用吗?
释放资源:
-
public class 类名 {
-
@Bean(destroyMethod="close")
-
public DataSource datasource() {
-
return new DruidDataSource();
-
}
-
}
文章来源: qianxu.blog.csdn.net,作者:爱吃豆的土豆,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qianxu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/126726547
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者






评论(0)