Mysql优化示例

作者: 西魏陶渊明 博客: https://blog.springlearn.cn/ (opens new window)
西魏陶渊明
莫笑少年江湖梦,谁不少年梦江湖
# 创建表
use test;
create table test03
(
a1 int(4) not null,
a2 int(4) not null,
a3 int(4) not null,
a4 int(4) not null
);
alter table test03 add index idx_a1_a2_a3_a4(a1,a2,a3,a4);
# 建议一、按照复合索引顺序查询
需知
- 如果(a,b,c,d)复合索引和查询使用的顺序全部一致,则复合索引全部使用,如果不部分一致或者跨列使用则就是部分使用.
- where和order by拼起来也不要跨列,参考反例2和3
# 1. 建议
- 建议: 按照where后面按照顺序使用复合索引
- 建议: where 和 order by不要跨列
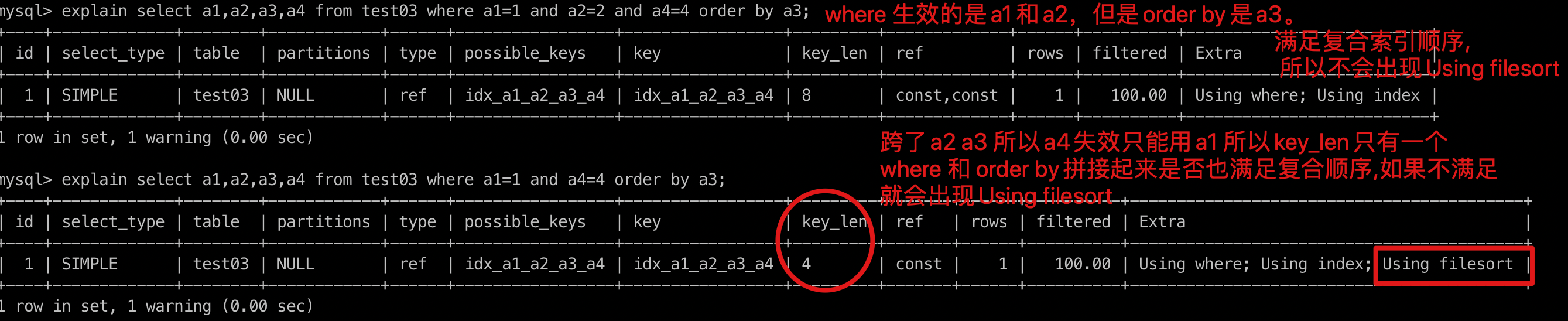
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a2=2 and a3=3 and a4=4;
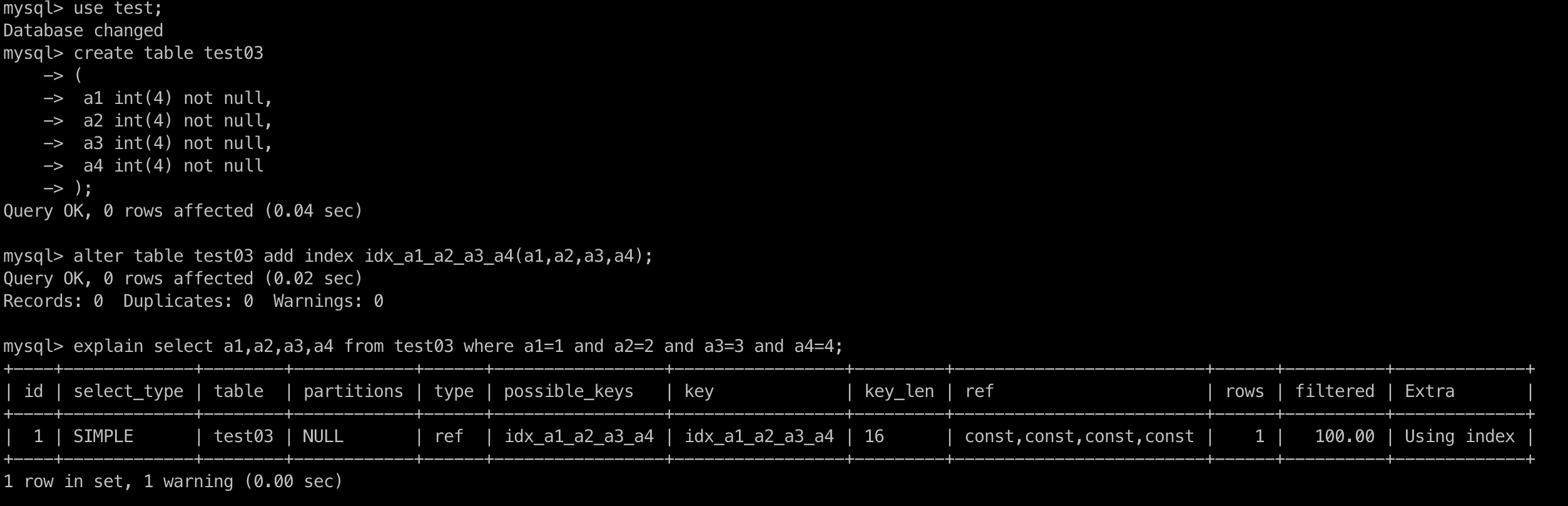
# 2. 反例1
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a4=1 and a3=2 and a2=3 and a1=4;
可以看到还是一样的,索引都用了,原因是sql在执行时候被sql优化器进行了调整,最后被调整成了上面的顺序写法。 这是最理想的情况,但是实际中建议开发按照顺序来进行查询。 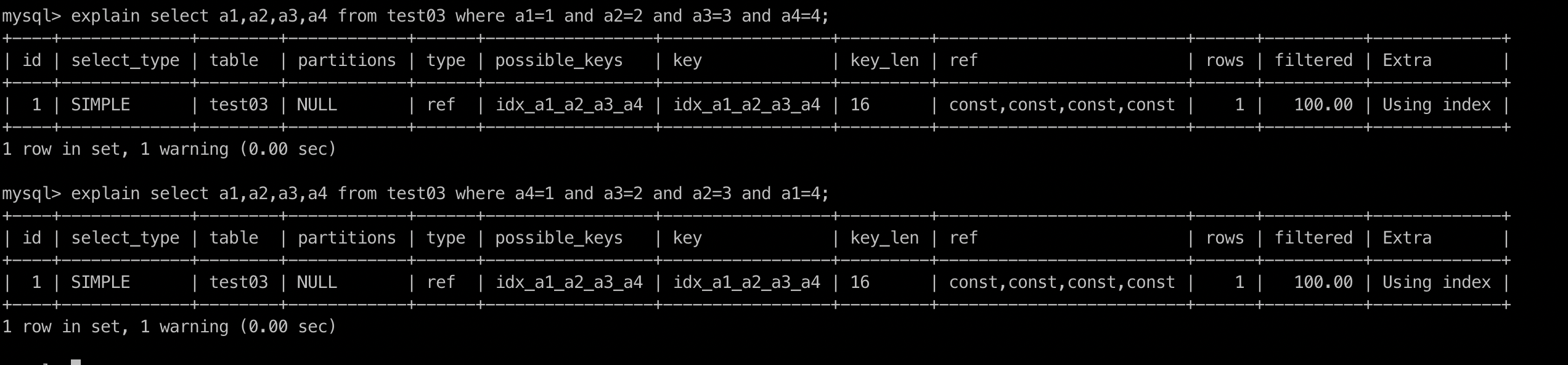
# 3. 反例2
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a2=2 and a4=4 order by a3;
- 因为查询条件中复合索引跨列了(跨了a3),所以导致只能用a1 和a2索引。索引key_len变成8了
- 索引中没有查询a3但是却用a3排序了,导致要回表查询a3

# 4. 反例3
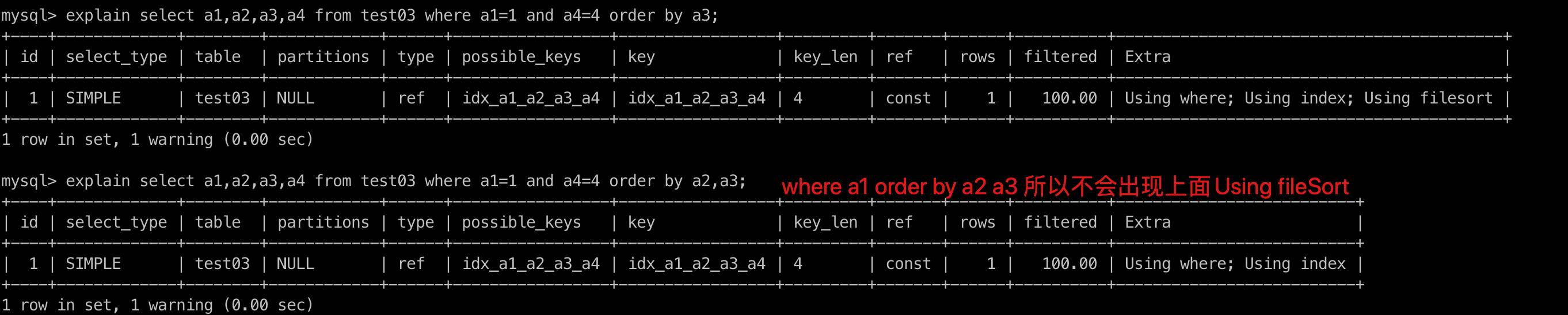
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a4=4 order by a3;
- 跨了a2 a3 所以a4失效只能用a1 所以key_len只有一个 where 和 order by拼接起来是否也满足复合顺序,如果不满足 就会出现Using filesort
- 反例2中where 生效的是a1和a2,但是order by是a3。满足复合索引顺序,所以不会出现Using filesort
explain select a1,a2,a3,a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a4=4 order by a2,a3;
- where a1 order by a2 a3 所以不会出现上面Using fileSort

# 建议二、单表优化
# 建表及需求sql
create table book
(
bid int(4) primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
authorid int(4) not null,
publicid int(4) not null,
typeid int(4) not null
);
insert into book values(1,'tjava',1,1,2);
insert into book values(2,'tjava',2,1,2);
insert into book values(3,'tjava',3,2,1);
insert into book values(4,'tjava',4,2,3);查询authorid = 1 并且 typeid 等于2或者3 然后根据typeid 排序
explain select bid from book where typeid in (2,3) and authorid = 1 order by typeid desc;
mysql> explain select bid from book where typeid in (2,3) and authorid = 1 order by typeid desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 25.00 | Using where; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)可以看出来未用到索引,type是all。就是全表查询了。
# 1. 优化1加索引
alter table book add index idx_bta(bid,typeid,authorid);
mysql> explain select bid from book where typeid in (2,3) and authorid = 1 order by typeid desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | index | NULL | idx_bta | 12 | NULL | 4 | 25.00 | Using where; Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)可以看到通过了加索引type由之前的all变成了index,说明有一点进步。但是我们看到还有一个Using filesort.前面我们说了出现这个 是因为额外多了一次查询。根据sql的解析规则,第一个解析的是typeid,第二个是authorid。那么我们先对索引顺序做一个优化。
# 2. 优化索引顺序
复合索引一旦进行了升级优化,就要删除了,否则会进行干扰。drop index idx_bta on book;
按照sql执行顺序来创建索引。这里我们其实也可以不创建bid,但是如果不创建bid,就要回表去查询bid,所以也建议加上。 alter table book add index idx_tab(typeid,authorid,bid);
mysql> explain select bid,typeid from book where typeid in (2,3) and authorid = 1 order by typeid desc;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | range | idx_tab | idx_tab | 8 | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | Using where; Backward index scan; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)可以看到已经没有了,Using filesort。
# 3. 总结
- 索引优化不会一步到位,要多次优化。
- 索引顺序会影响查询效率,如果不知道怎么优化,建议sql执行顺序,多尝试几次不同顺序。通过看type的级别来调整。
- type如果是range或者ref。其实就可以了。如果是index或者all就要考虑是否要进行优化。
- in会是索引失效
# 建议三、多表优化
# 建表及需求sql
create table teacher2
(
tid int(4) primary key,
cid int(4) not null
);
insert into teacher2 values(1,2);
insert into teacher2 values(2,1);
insert into teacher2 values(3,3);
create table course2
(
cid int(4),
cname varchar(20)
);
insert into course2 values(1,'java');
insert into course2 values(2,'python');
insert into course2 values(3,'kotlin');需求sql
select * from teacher2 t left outer join course2 c on t.cid=c.cid where c.cname = 'java';
mysql> select * from teacher2 t left outer join course2 c on t.cid=c.cid where c.cname = 'java';
+-----+-----+------+-------+
| tid | cid | cid | cname |
+-----+-----+------+-------+
| 2 | 1 | 1 | java |
+-----+-----+------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)执行计划分析
mysql> explain select * from teacher2 t left outer join course2 c on t.cid=c.cid where c.cname = 'java';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)可以看到有一个Using join buffer。 说明Sql写的太差了,mysql给你加了一个缓存。经过下面的索引优化会去掉。
# 优化1小表驱动大表
当编写语句时候,将数据量小的表放左边(假设此时t表小,on t.cid = c.cid);反之如果c表小(on c.cid = t.tic)
# 优化2加索引
索引建立在经常使用的字段上,本例中t.cid使用频繁。
alter table teacher2 add index idx_teacher2_cid(cid);
mysql> explain select * from teacher2 t left outer join course2 c on t.cid=c.cid where c.cname = 'java';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ref | idx_teacher2_cid | idx_teacher2_cid | 4 | test.c.cid | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)给name也加索引
alter table course2 add index idx_course2_name(cname);
mysql> explain select * from teacher2 t left outer join course2 c on t.cid=c.cid where c.cname = 'java';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ref | idx_course2_name | idx_course2_name | 83 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t | NULL | ref | idx_teacher2_cid | idx_teacher2_cid | 4 | test.c.cid | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)这样两个查询就都用到了索引。
# 建议四、sql优化
# 1. exist和in
如果主查询的数据集大用 in ,如果子查询数据量大使用 exist
# 2. order by优化
Using filesort 有两种算法: 双路排序、单路排序(根据IO的次数,即访问磁盘的顺序)
- MySQL4.1前默认使用双路排序,即扫描两次磁盘(1. 从磁盘读取排序字段,2. 扫描其他字段)
- MySQL4.1后默认使用单路排序,即访问一次磁盘(1. 只读取一次字段,然后在buffer中进行排序)
但是单路排序有隐患就是不一定是只访问一次磁盘,因为加入数据量特别大,则无法将所有字段的 数据都放到buffer中,要多次分片读取。此时可以考虑调大buffer容量大小。
set max_length_for_sort_data = 1024 (单位/字节)
如果缓存区大小太小,mysql会自动从单路调整到双路。
建议
- 避免使用
select * - 复合索引不要跨列使用,如果where和order尽量也按照顺序使用
- order by 如果是多个字段,建议都是升序或者都是降序
# 3. 慢查询日志
如何找到垃圾SQL语句,你知道这些方式吗? (opens new window)
慢sql就是mysql提供的一种日志记录,用于记录响应的时间超过阀值得语句;
查询是否开启慢查询
show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
mysql> show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
+---------------------+-----------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------+-----------------------------------------+
| slow_query_log | OFF |
| slow_query_log_file | /usr/local/var/mysql/localhost-slow.log |
+---------------------+-----------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.06 sec)临时开启:
set global slow_query_log = 1;
exit;
services mysql restart查询慢查询日志阀值
show variables like '%long_query_time%';
mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+-----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+-----------+
| long_query_time | 10.000000 |
+-----------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)临时设置阀值
修改完成之后要重新登录生效
set global long_query_time = 5;mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+-----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+-----------+
| long_query_time | 10.000000 |
+-----------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> set global long_query_time = 5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+-----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+-----------+
| long_query_time | 10.000000 |
+-----------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
liuxin@localhost ~ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 9
Server version: 8.0.16 Homebrew
Copyright (c) 2000, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+----------+
| long_query_time | 5.000000 |
+-----------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql># 超过阀值得数量
show global status like '%slow_queries%';
mysql> show global status like '%slow_queries%';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Slow_queries | 0 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)# 总结
- 复合索引,不要跨列或无序使用
- 复合索引,尽量使用全索引匹配
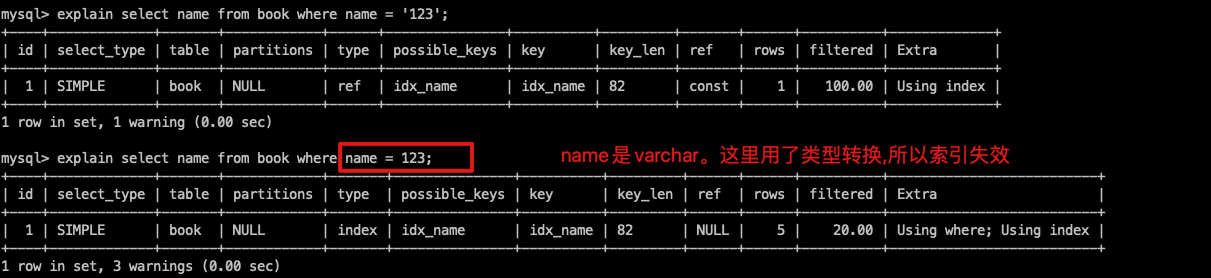
- 不要在索引上进行计算、函数、类型转换
- 复合索引不能使用 != 、 <> 、 is null
- like尽量以"常量"开头,不要以"%"开头,否则索引失效
- 尽量不要使用类型转换(显式、隐式),否则索引失效。where name = 'lx' 可以。where name

- 尽量不要用or,否则左右索引都可能失效

最后求关注,求订阅,谢谢你的阅读!
文章来源: springlearn.blog.csdn.net,作者:西魏陶渊明,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:springlearn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125857979
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)