第10篇:Mybatis的插件设计分析

作者: 西魏陶渊明
博客: https://blog.springlearn.cn/
西魏陶渊明
莫笑少年江湖梦,谁不少年梦江湖
参考文档: 官方文档
一、 插件设计介绍
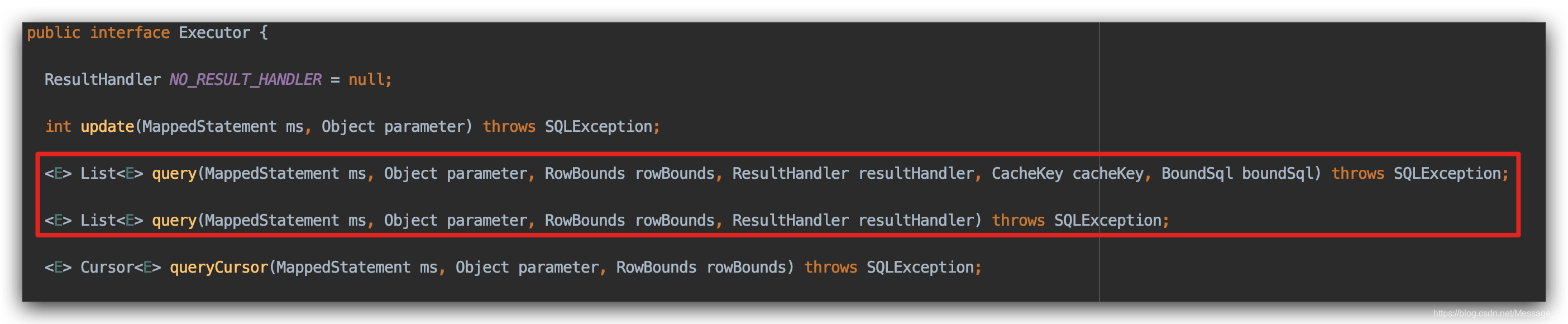
Mybatis 中的插件都是通过代理方式来实现的,通过拦截执行器中指定的方法来达到改变核心执行代码的方式。举一个列子,查询方法核心都是通过 Executor来进行sql执行的。那么我们就可以通过拦截下面的方法来改变核心代码。基本原理就是这样,下面我们在来看 Mybatis 是如何处理插件。
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
...
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
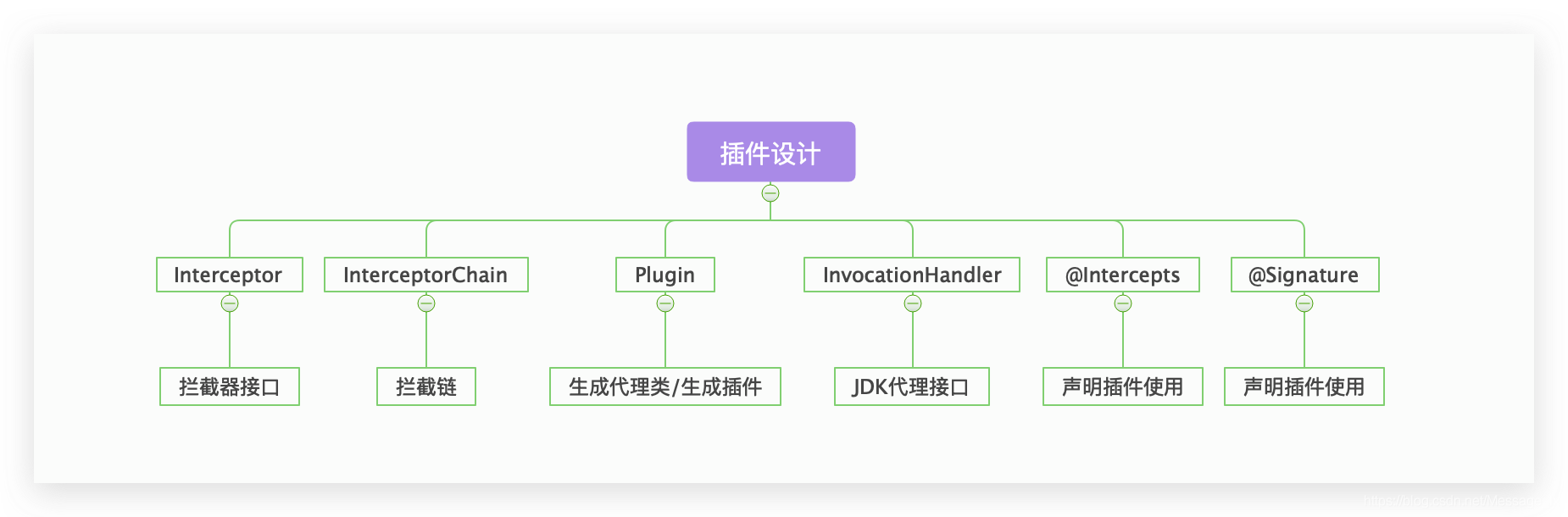
| 名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
Interceptor |
接口 | 插件都需要实现的接口,封装代理执行方法及参数信息 |
InterceptorChain |
类 | 拦截链 |
InvocationHandler |
接口 | JDK代理的接口,凡是JDK中的代理都要实现该接口 |
@Intercepts |
注解 | 用于声明要代理和 @Signature 配合使用 |
@Signature |
注解 | 用于声明要代理拦截的方法 |
Plugin |
类 | 代理的具体生成类 |
1.1 Interceptor
插件都需要实现的接口,封装代理执行方法及参数信息
public interface Interceptor {
// 执行方法体的封装,所有的拦截方法逻辑都在这里面写。
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 如果要代理,就用Plugin.wrap(...),如果不代理就原样返回
Object plugin(Object target);
// 可以添加配置,主要是xml配置时候可以从xml中读取配置信息到拦截器里面自己解析
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
1.2 InterceptorChain
拦截链,为什么需要拦截链,假如我们要对A进行代理, 具体的代理类有B和C。 我们要同时将B和C的逻辑都放到代理类里面,那我们会首先将A和B生成代理类,然后在前面生成代理的基础上将C和前面生成的代理类在生成一个代理对象。这个类就是要做这件事 pluginAll
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
// 这里target就是A,而List中的Interceptor就相当于B和C,通过循环方式生成统一代理类
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
//1. 是否需要代理,需要代理生成代理类放回,不需要原样返回。通过for循环的方式将所有对应的插件整合成一个代理对象
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
...
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
1.3 InvocationHandler
JDK代理的接口,凡是JDK中的代理都要实现该接口。这个比较基础,如果这个不清楚,那么代理就看不懂了。所以就不说了。
public interface InvocationHandler {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.4 @Intercepts 和 @Signature
这两个注解是配合使用的,用于指定要代理的类和方法。前面①说了,插件的核心逻辑是拦截执行器的方法,那么这里我们看下如何声明要拦截的类和方法。我们看一下分页插件如何声明拦截。
| 属性 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| type | 就是要拦截的类(Executor/ParameterHandler/ResultSetHandler/StatementHandler) |
| method | 要拦截的方法 |
| args | 要拦截的方法的参数(因为有相同的方法,所以要指定拦截的方法和方法参数) |
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = { MappedStatement.class, Object.class,
RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class }))
public class MybatisPagerPlugin implements Interceptor {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
args 要拦截的方法的入参(因为有相同的方法,所以要指定拦截的方法和方法参数),比如 Executor 中就有2个 query 方法。所以要通过args来确定要拦截哪一个。
1.5 Plugin
代理的具体生成类,解析 @Intercepts 和 @Signature 注解生成代理。
我们看几个重要的方法。
| 方法名 | 处理逻辑 |
|---|---|
| getSignatureMap | 解析@Intercepts和@Signature,找到要拦截的方法 |
| getAllInterfaces | 找到代理类的接口,jdk代理必须要有接口 |
| invoke | 是否需要拦截判断 |
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
//解析@Intercepts和@Signature找到要拦截的方法
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
//通过方法名和方法参数查找方法
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
//因为是jdk代理所以必须要有接口,如果没有接口,就不会生成代理
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//执行时候看当前执行的方法是否需要被拦截,如果需要就调用拦截器中的方法
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
二、问题总结
2.1 插件能拦截那些类?
前面已经说过了,这里在总结下。这部分的源码在 Configuration。可以看到很简单只有一行。InterceptorChain#pluginAll
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
2.1.1 ParameterHandler
ParameterHandler的核心方法是setParameters()方法,该方法主要负责调用PreparedStatement的set*()方法为SQL语句绑定实参:
这里能做到的扩展不多。
public interface ParameterHandler {
// 对方法的入参进行处理,注意只有在 statementType="CALLABLE" 生效
Object getParameterObject();
// 预处理参数处理
void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
我们来实现一下,我们插入user信息,通过插件的方式修改入参。
/**
* 注意getParameterObject只会在 statementType="CALLABLE"生效
* insert into T_USER (token_id, uid, name)
* values (#{tokenId,jdbcType=CHAR}, #{uid,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{name,jdbcType=CHAR})
*/
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = ParameterHandler.class, method = "setParameters", args = {PreparedStatement.class}))
public static class ParameterInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = (PreparedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
// 插入时候修改第三个参数,也就是name = 孙悟空
int parameterCount = preparedStatement.getParameterMetaData().getParameterCount();
if (parameterCount != 0) {
preparedStatement.setString(3, "孙悟空");
}
return proceed;
}
}
@Test
public void parameterHandler() {
// 读取配置信息(为什么路径前不用加/,因为是相对路径。maven编译后的资源文件和class文件都是在一个包下,所以不用加/就是当前包目录)
InputStream mapperInputStream = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatisConfig.xml");
// 生成SqlSession工厂,SqlSession从名字上看就是,跟数据库交互的会话信息,负责将sql提交到数据库进行执行
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(mapperInputStream, "development");
// 获取Mybatis配置信息
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
configuration.addInterceptor(new ParameterInterceptor());
// 参数: autoCommit,从名字上看就是是否自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(false);
// 获取Mapper
TUserMapper mapper = configuration.getMapperRegistry().getMapper(TUserMapper.class, sqlSession);
TUser tUser = new TUser();
tUser.setName("唐三藏");
tUser.setTokenId("testTokenId1");
mapper.insert(tUser);
// 这里虽然设置的名字是唐三藏,但是插件中修改为了孙悟空
System.out.println(mapper.selectAll());
// 数据插入后,执行查询,然后回滚数据
sqlSession.rollback();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
2.1.2 ResultSetHandler
从名字就可以看出来是对结果集进行处理。这里我们通过插件的方式, 在查询语句中增加一条数据库原本不存在的数据。
/**
* 通过对list集合的数据进行修改,增加一条数据库不存在的数据
*/
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class}))
public static class ResultSetHandlerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
if (proceed instanceof List) {
ArrayList<TUser> newResult = (ArrayList<TUser>) proceed;
TUser tUser = new TUser();
tUser.setName("如来佛祖");
newResult.add(tUser);
proceed = newResult;
}
return proceed;
}
}
@Test
public void resultSetHandlerTest() {
// 读取配置信息(为什么路径前不用加/,因为是相对路径。maven编译后的资源文件和class文件都是在一个包下,所以不用加/就是当前包目录)
InputStream mapperInputStream = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatisConfig.xml");
// 生成SqlSession工厂,SqlSession从名字上看就是,跟数据库交互的会话信息,负责将sql提交到数据库进行执行
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(mapperInputStream, "development");
// 获取Mybatis配置信息
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
configuration.addInterceptor(new ResultSetHandlerInterceptor());
// 参数: autoCommit,从名字上看就是是否自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(false);
// 获取Mapper
TUserMapper mapper = configuration.getMapperRegistry().getMapper(TUserMapper.class, sqlSession);
System.out.println(mapper.selectAll());
// 数据插入后,执行查询,然后回滚数据
sqlSession.rollback();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
2.1.3 StatementHandler
/**
* 我们本来是一条查询语句,我们打印下sql信息
*/
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "query", args = {Statement.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public static class StatementHandlerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
if (args[0] instanceof ClientPreparedStatement) {
ClientPreparedStatement statement = (ClientPreparedStatement) args[0];
if (statement.getQuery() instanceof ClientPreparedQuery) {
System.out.println(((ClientPreparedQuery) statement.getQuery()).getOriginalSql());
}
}
return proceed;
}
}
@Test
public void resultSetHandlerTest() {
// 读取配置信息(为什么路径前不用加/,因为是相对路径。maven编译后的资源文件和class文件都是在一个包下,所以不用加/就是当前包目录)
InputStream mapperInputStream = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatisConfig.xml");
// 生成SqlSession工厂,SqlSession从名字上看就是,跟数据库交互的会话信息,负责将sql提交到数据库进行执行
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(mapperInputStream, "development");
// 获取Mybatis配置信息
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
configuration.addInterceptor(new StatementHandlerInterceptor());
// 参数: autoCommit,从名字上看就是是否自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(false);
// 获取Mapper
TUserMapper mapper = configuration.getMapperRegistry().getMapper(TUserMapper.class, sqlSession);
System.out.println(mapper.selectAll());
// 数据插入后,执行查询,然后回滚数据
sqlSession.rollback();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
2.1.4 Executor
Executor 是个好东西,从他能获取基本你能想到的所有信息。你可以在这里做sql动态变更、也可以做sql语句分析,同时也可以获取某个Mapper的签名信息。总之功能非常强大。一般的插件都是
在这里做文章。如下面例子就是动态的修改了sql。
/**
* 动态修改sql信息。
* 这里因为我们知道要使用查询语句,所以不做sql分析。如果要学习sql分析请看其他文章
*/
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public static class ExecutorInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
if (args[0] instanceof MappedStatement) {
MappedStatement arg = (MappedStatement) args[0];
Configuration configuration = arg.getConfiguration();
StaticSqlSource staticSqlSource = new StaticSqlSource(configuration, "select name from T_USER");
Field sqlSourceField = arg.getClass().getDeclaredField("sqlSource");
sqlSourceField.setAccessible(true);
sqlSourceField.set(arg, staticSqlSource);
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
@Test
public void executor() {
// 读取配置信息(为什么路径前不用加/,因为是相对路径。maven编译后的资源文件和class文件都是在一个包下,所以不用加/就是当前包目录)
InputStream mapperInputStream = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatisConfig.xml");
// 生成SqlSession工厂,SqlSession从名字上看就是,跟数据库交互的会话信息,负责将sql提交到数据库进行执行
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(mapperInputStream, "development");
// 获取Mybatis配置信息
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
configuration.addInterceptor(new ExecutorInterceptor());
// 参数: autoCommit,从名字上看就是是否自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(false);
// 获取Mapper
TUserMapper mapper = configuration.getMapperRegistry().getMapper(TUserMapper.class, sqlSession);
System.out.println(mapper.selectAll());
// 数据插入后,执行查询,然后回滚数据
sqlSession.rollback();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
2.2 如何定义一个拦截器?
| 属性 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| type | 就是要拦截的类(Executor/ParameterHandler/ResultSetHandler/StatementHandler) |
| method | 要拦截的方法 |
| args | 要拦截的方法的参数(因为有相同的方法,所以要指定拦截的方法和方法参数) |
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public static class ExecutorInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
if (args[0] instanceof MappedStatement) {
MappedStatement arg = (MappedStatement) args[0];
Configuration configuration = arg.getConfiguration();
StaticSqlSource staticSqlSource = new StaticSqlSource(configuration, "select name from T_USER");
Field sqlSourceField = arg.getClass().getDeclaredField("sqlSource");
sqlSourceField.setAccessible(true);
sqlSourceField.set(arg, staticSqlSource);
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
2.3 插件的设计缺陷
InterceptorChain 的设计非常简单,里面就是一个list集合。但是在进行代理的时候,并没有顺序。假设我们要对sql进行代理。
- 第一个插件,我们在sql后加上
where id > 1 - 第二个插件,我们在sql后机上
limit 10
按照我们设想的最终sql会变成 select * from users where id > 1 limit 10
但是我们知道mybatis是没有顺序的, 那么很可能会出现最终的sql变成 select * from user limit 10 where id > 1,此时就会报错。
所以我们要注意这里。
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
三、可以借鉴的知识点
3.1 插件的设计模式
拦截链 + 插件设计
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InterceptorChain chain = new InterceptorChain();
PrintInterceptor printInterceptor = new PrintInterceptor();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("name","https://blog.springlearn.cn");
printInterceptor.setProperties(properties);
chain.addInterceptor(printInterceptor);
Animal person = (Animal) chain.pluginAll(new Person());
String nihao = person.say("nihao");
System.out.println(nihao);
}
public interface Animal{
String say(String message);
String say(String name, String message);
}
public static class Person implements Animal {
public String say(String message) {
return message;
}
public String say(String name, String message) {
return name + " say: " + message;
}
}
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Animal.class, method = "say", args = {String.class}))
public static class PrintInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private String name;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(name + ": before print ...");
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println(name + ": after print ...");
return proceed;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
文章来源: springlearn.blog.csdn.net,作者:西魏陶渊明,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:springlearn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125876758
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)