Java管理扩展

作者: 西魏陶渊明
博客: https://blog.springlearn.cn/
JMX(Java Management Extensions,即Java管理扩展)是一个为应用程序、设备、系统等植入管理功能的框架。JMX可以跨越一系列异构操作系统平台、系统体系结构和网络传输协议,灵活的开发无缝集成的系统、网络和服务管理应用。
前面是对JMX的介绍,那么JMX在我们日常的开发过程中,有什么实际的意义呢? 相信很多做Java开发的同学都使用过JDK自带的 jconsole 或者 jvisualvm 监控过JVM的运行情况,但不知道有没有留意过它们会有一个MBean的功能/标签,通过MBean可以看到在JVM中运行的组件的一些属性和操作。下面小编就通过一个SpringBoot应用来一探究竟。并教会你如何自定义扩展。
一、实际意义
1. 启动一个SpringBoot应用
下面我们以SpringBoot应用为例子,启动一个SpringBoot项目。端口是 8080
2. 命令行打开Jconsole
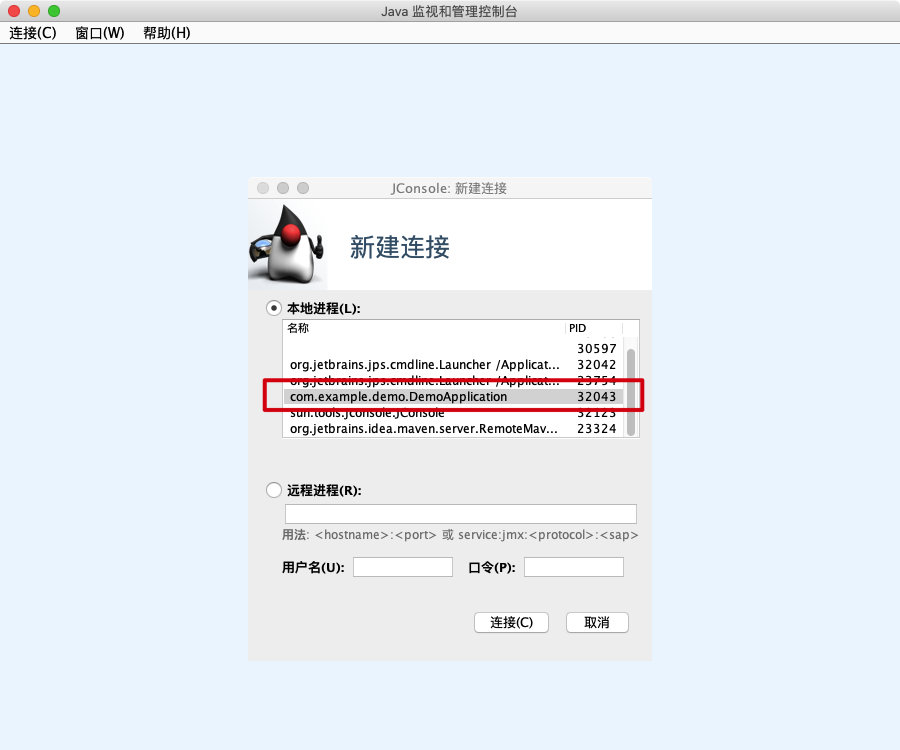
3. 连接前面的应用
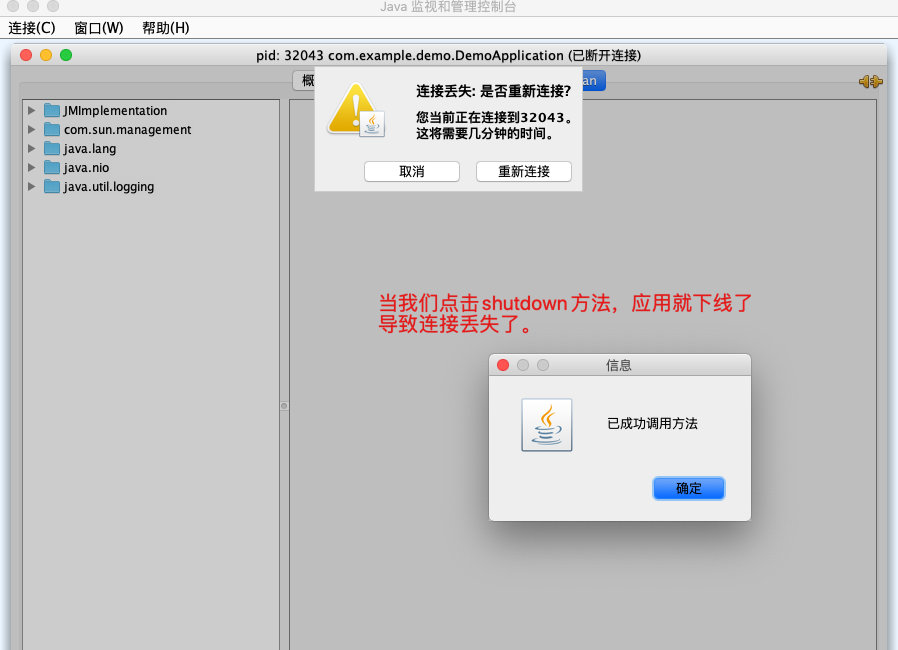
选中MBean标签,然后可以看到一个SpringApplication的类。shutdown是服务下线。
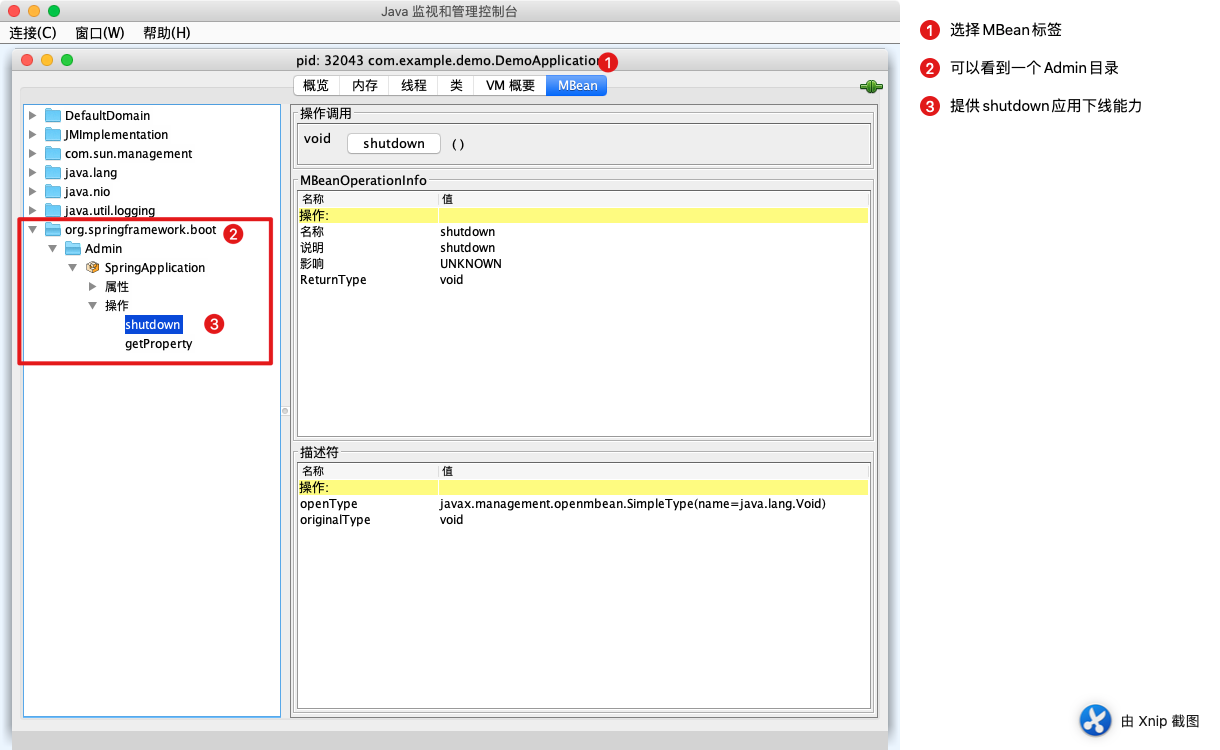
当我们点击了shutdown方法后,应用就会自动的关闭了。导致Jconsole连接丢失
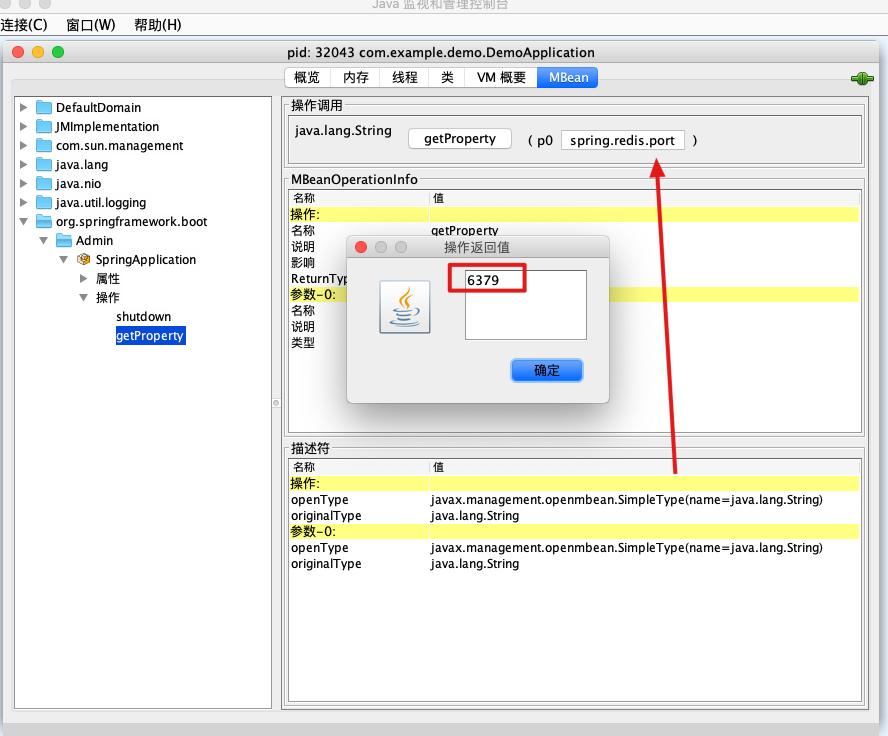
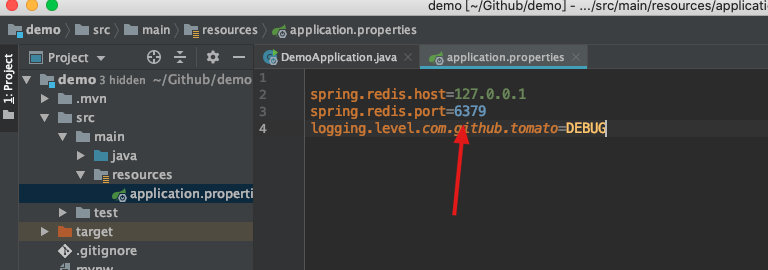
getProperty方法是获取应用中的配置信息。如图我们获取redis的相关信息。可以看到返回值是Spring应用中我们定义的值
6379
那么其实这个能力就是利用JMX提供的接口来实现的。下面我们通过分析SpringBoot中的源码来看他是如何实现的。
二、源码追踪看SpringBoot应用如何实现?
我们通过看Jconsole工具,可以看到工具里面的类名叫SpringApplication,目录是admin,于是我们就根据这个推测SpringBoot中的命名,果然我们找到两个实现类。
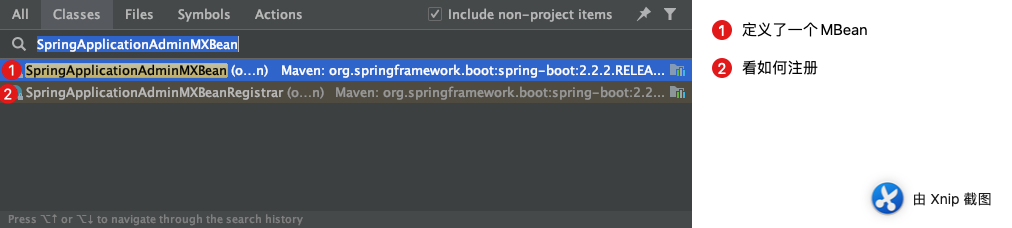
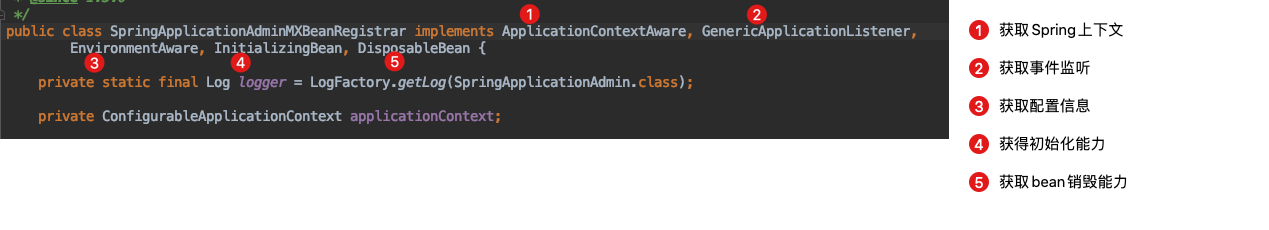
1. SpringApplicationAdminMXBean
这个类就是JMX中的MBean,我们可以简单理解这个里面的方法都是可以通过Jconsole来调用的。
通过将这个类注册给JMX管理器就能实现在Jconsole中的数据展示。
首先看SpringApplicationAdminMXBean
public interface SpringApplicationAdminMXBean {
//是否可读
boolean isReady();
//是否web应用
boolean isEmbeddedWebApplication();
//获取配置信息
String getProperty(String key);
//下线应用
void shutdown();
}
实现类SpringApplicationAdmin,是SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar的内部类
private class SpringApplicationAdmin implements SpringApplicationAdminMXBean {
// 是否可读,当应用还没起来时候这个值是false
@Override
public boolean isReady() {
return SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar.this.ready;
}
// 是否是web应用
@Override
public boolean isEmbeddedWebApplication() {
return SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar.this.embeddedWebApplication;
}
// 从Spring的配置信息中实时读取值
@Override
public String getProperty(String key) {
return SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar.this.environment.getProperty(key);
}
// 关闭Spring应用
@Override
public void shutdown() {
logger.info("Application shutdown requested.");
SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar.this.applicationContext.close();
}
}
2. SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar
提供注册能力。这个类中我们可以知道如何注册JMX以及如何取消注册。下面我看这个类如何利用Spring提供的接口能力,来实现应用下线。及注册到JMX上的吧。
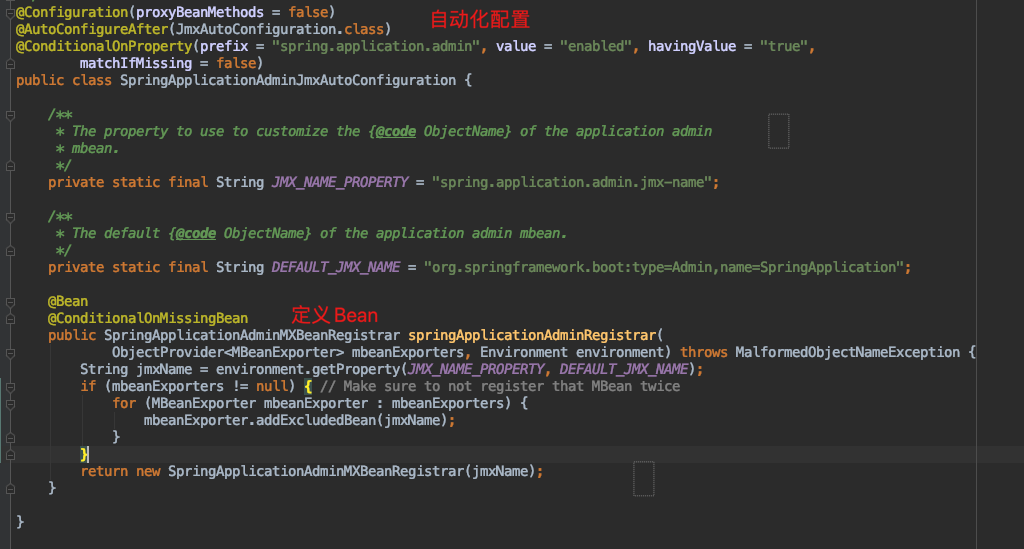
自动化配置将SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar声明成一个Spring中的Bean对象。并配置JMX中的命名及目录。
1. ApplicationContextAware
获得读取上下文能力。在Spring容器中一个bean如何实现了该方法则就可以获取上下文对象。
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
Assert.state(applicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext,
"ApplicationContext does not implement ConfigurableApplicationContext");
this.applicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
}
2. GenericApplicationListener
获取处理事件的能力,同样在Spring中只要实现该接口,就获取了事件监听的能力,不过具体监听什么事件要自己去判断。大家可以根据例子
来理解。
// 根据事件泛型判断是否需要处理,这里判断如果是ApplicationReadyEvent和WebServerInitializedEvent
// 事件就处理
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {
Class<?> type = eventType.getRawClass();
if (type == null) {
return false;
}
return ApplicationReadyEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(type)
|| WebServerInitializedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(type);
}
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(Class<?> sourceType) {
return true;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 如果Spring已经准备好了,就将this.ready = true;
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent) {
onApplicationReadyEvent((ApplicationReadyEvent) event);
}
// 如果是Web应用,this.embeddedWebApplication = true
if (event instanceof WebServerInitializedEvent) {
onWebServerInitializedEvent((WebServerInitializedEvent) event);
}
}
//优先级
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
void onApplicationReadyEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
if (this.applicationContext.equals(event.getApplicationContext())) {
this.ready = true;
}
}
void onWebServerInitializedEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
if (this.applicationContext.equals(event.getApplicationContext())) {
this.embeddedWebApplication = true;
}
}
3. EnvironmentAware
获取应用配置信息, 和上面一样实现了Aware结尾的接口,都能获取对象的Spring内容的对象实例,然后我们就可以根据该实例,来进行功能扩展。
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
4. InitializingBean
这里就要着重看了,在初始化时候将MBean注册到JMX上。当然我们可以通过 @PostConstruct注解来声明初始化方法。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
server.registerMBean(new SpringApplicationAdmin(), this.objectName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Application Admin MBean registered with name '" + this.objectName + "'");
}
}
5. DisposableBean
应用销毁时候,取消注册。同样我们也可以用@PreDestroy注解来实现
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer().unregisterMBean(this.objectName);
}
通过对SpringBoot应用源码的追踪,我们大概已经明白JMX的实际意义了,并且能自定义一个能提供类似能力的MBean了吧,但是JMX能做的远远不止如此。
三、自定义MBean
注意接口名必须是MBean结尾,实现类必须去掉MBean
如CustomMBean接口对应的实现类必须是Custom。
1. 代码实现
@Component
public class CustomMbeanRegistrar implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
private ObjectName objectName = new ObjectName("com.example.demo:type=CustomAdmin,name=CustomMXBean");
public CustomMbeanRegistrar() throws MalformedObjectNameException {
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer().unregisterMBean(this.objectName);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
server.registerMBean(new Custom(), this.objectName);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
}
public interface CustomMBean {
int getDatabaseConnectionPoolSize();
void customShutdown();
}
private class Custom implements CustomMBean {
/**
* 获取数据库连接池大小
*
* @return 模拟
*/
@Override
public int getDatabaseConnectionPoolSize() {
return new Random().nextInt(100);
}
/**
* 自定义一个销毁方法
*/
public void customShutdown() {
CustomMbeanRegistrar.this.applicationContext.close();
}
}
}
2. 演示
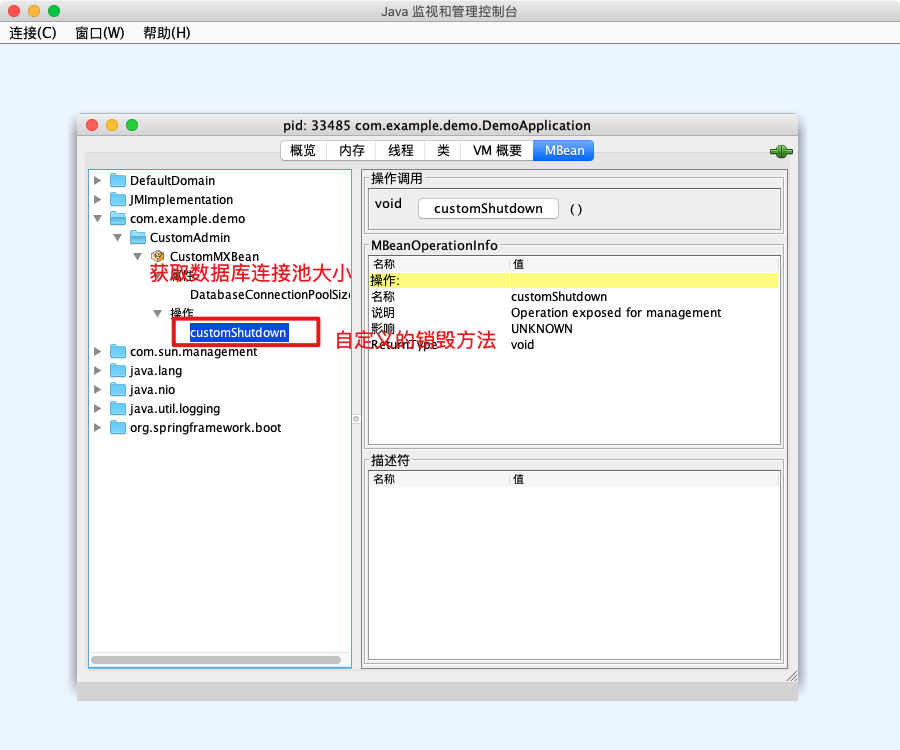
四、总结
通过前面的演示,大概我们对JMX在实际中的用处有一个大概的了解了吧。根据这个特性,我们就可以根据我们的需求来定制属于自己的能力。
最后求关注,求订阅,谢谢你的阅读!

文章来源: springlearn.blog.csdn.net,作者:西魏陶渊明,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:springlearn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125830553
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)