基于 dynamic-datasource 实现 DB 多数据源及事物控制、读写分离、负载均衡解决方案
一、dynamic-datasource
dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter 是一个基于springboot的快速集成多数据源的启动器。
特征
- 支持 数据源分组 ,适用于多种场景 纯粹多库 读写分离 一主多从 混合模式。
- 支持数据库敏感配置信息 加密
ENC()。 - 支持每个数据库独立初始化表结构
schema和数据库database。 - 支持无数据源启动,支持懒加载数据源(需要的时候再创建连接)。
- 支持 自定义注解 ,需继承
DS(3.2.0+)。 - 提供并简化对
Druid,HikariCp,BeeCp,Dbcp2的快速集成。 - 提供对
Mybatis-Plus,Quartz,ShardingJdbc,P6sy,Jndi等组件的集成方案。 - 提供 自定义数据源来源 方案(如全从数据库加载)。
- 提供项目启动后 动态增加移除数据源 方案。
- 提供
Mybatis环境下的 纯读写分离 方案。 - 提供使用
spel动态参数 解析数据源方案。内置spel,session,header,支持自定义。 - 支持 多层数据源嵌套切换 。
(ServiceA >>> ServiceB >>> ServiceC)。 - 提供 基于
seata的分布式事务方案。 - 提供 本地多数据源事务方案。 附:不能和原生
spring事务混用。
约定
- 本框架只做 切换数据源 这件核心的事情,并不限制你的具体操作,切换了数据源可以做任何
CRUD。 - 配置文件所有以下划线 _ 分割的数据源 首部 即为组的名称,相同组名称的数据源会放在一个组下。
- 切换数据源可以是组名,也可以是具体数据源名称。组名则切换时采用负载均衡算法切换。
- 默认的数据源名称为
master,你可以通过spring.datasource.dynamic.primary修改。 - 方法上的注解优先于类上注解。
DS支持继承抽象类上的DS,暂不支持继承接口上的DS。
官方文档地址:https://www.kancloud.cn/tracy5546/dynamic-datasource/2264611
下面分别从 多数据源及事物控制、读写分离实现、负载均衡实现三个方面进行实践。
二、环境准备
在实验开始前,先准备两个数据库,来进行实验测试:
create database db1;
create database db2;
- 1
- 2
然后在两个库中分别创建测试表:
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
接着分别在db1 和 db2 中写入一条数据,数据id一致,但内容不一致,主要用于下面实验的区分:
db1:
INSERT INTO `user`(`id`, `name`, `age`) VALUES (1, '张三', 18);
- 1
db2:
INSERT INTO `user`(`id`, `name`, `age`) VALUES (1, '李四', 20);
- 1
下面首先创建一个 SpringBoot 项目,在 pom 中引入 dynamic-datasource 的依赖,以及 mysql 和 mybatisplus :
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
下面创建上面测试表的实体 entity:
@Data
@TableName("user")
public class UserEntity {
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
三、多数据源及事物控制
dynamic-datasource 针对于多数据源的切换推出了 @DS 注解,@DS 可以注解在方法上或类上,同时存在就近原则 方法上注解 优先于 类上注解。
下面开始实施:
修改配置文件增加数据库连接:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: dynamic-datasource-demo
autoconfigure:
exclude: com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure
datasource:
dynamic:
primary: db1 #设置默认的数据源或者数据源组,默认值即为master
strict: true #设置严格模式,默认false不启动. 启动后在未匹配到指定数据源时候回抛出异常,不启动会使用默认数据源.
datasource:
db1:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://10.32.33.148:3307/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root123
db2:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://10.32.33.148:3307/db2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root123
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: false
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.bxc.dynamicdatasourcedemo.entity
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
然后分别创建两个 DAO,并通过 @DS 切换数据源:
@Repository
@Mapper
@DS("db1")
public interface DB1UserDao extends BaseMapper<UserEntity>{
@Insert("insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
int addUser(UserEntity entity);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
@Repository
@Mapper
@DS("db2")
public interface DB2UserDao extends BaseMapper<UserEntity> {
@Insert("insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
int addUser(UserEntity entity);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
下面创建一个测试类测试一下是否正常:
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class DynamicDatasourceDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DB1UserDao db1UserDao;
@Autowired
DB2UserDao db2UserDao;
@Test
void test1() {
UserEntity db1UserEntity = db1UserDao.selectById(1);
log.info("db1 查询结果:{} ",db1UserEntity.toString());
UserEntity db2UserEntity = db2UserDao.selectById(1);
log.info("db2 查询结果:{} ",db2UserEntity.toString());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
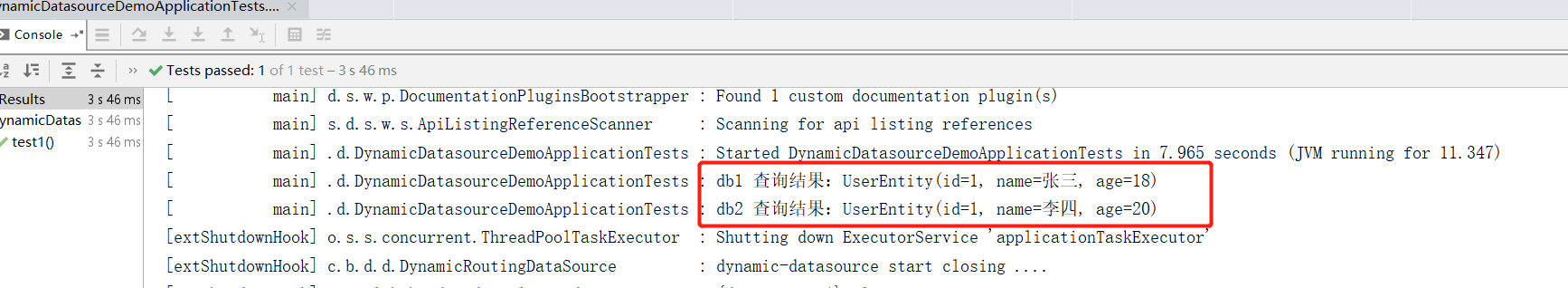
已经实现多数据源查询效果,下面继续事物的控制,应该都了解在 Spring 中事物使用 @Transactional 注解即可,但是仅针对于单个数据源的情况,多数据源下我们可以使用 jta 来控制,不过在 dynamic-datasource 中又推出了 @DSTransactional 注解来代替 Spring 的 @Transactional 注解,下面我们实验一下:
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class DynamicDatasourceDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DB1UserDao db1UserDao;
@Autowired
DB2UserDao db2UserDao;
@Test
@DSTransactional
void test1() {
UserEntity entity = new UserEntity();
entity.setName("王五");
entity.setAge(16);
int db1 = db1UserDao.insert(entity);
log.info("db1写入个数:{} ", db1);
int db2 = db2UserDao.insert(entity);
log.info("db2写入个数:{} ", db2);
//模拟异常
int a = 1 / 0;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
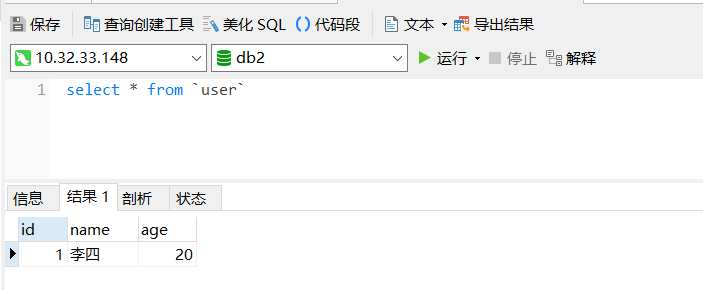
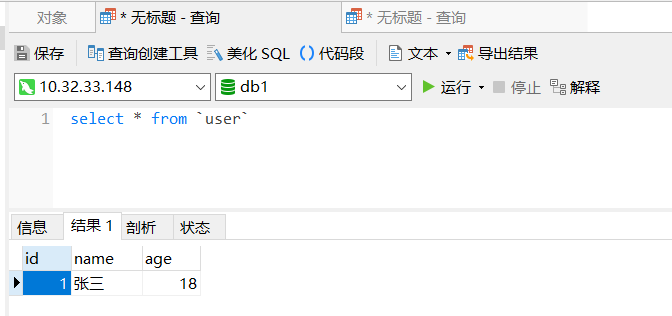
数据已经回滚!
四、读写分离
从上面的步骤中,已经了解到了 @DS 这个注解,那么通过这个注解我们可以简单的实现下读写分离结构,比如:
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface DBUserDao {
@DS("db1")
@Insert("insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
int addUser(UserEntity entity);
@DS("db2")
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
UserEntity findUser(@Param("id") Long id);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
不过这种方式有点繁琐,每个 dao 都需要添加注解,那我们是不是可以通过 mybatis 的拦截器来完成呢,下面开始操作下:
创建一个 mybatis 的拦截器:
@Intercepts({@Signature(
type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}
), @Signature(
type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}
), @Signature(
type = Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}
)})
@Slf4j
@Component
@Primary
public class MasterSlaveAutoRoutingPlugin implements Interceptor {
private static final String MASTER = "db1";
private static final String SLAVE = "db2";
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
try {
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.push(SqlCommandType.SELECT == ms.getSqlCommandType() ? SLAVE : MASTER);
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.clear();
}
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return target instanceof Executor ? Plugin.wrap(target, this) : target;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
修改上面的 Dao 去除 @DS 注解:
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface DBUserDao {
@Insert("insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
int addUser(UserEntity entity);
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
UserEntity findUser(@Param("id") Long id);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
测试:
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class DynamicDatasourceDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DBUserDao dbUserDao;
@Test
void test2() {
UserEntity entity = new UserEntity();
entity.setName("王五");
entity.setAge(16);
int update = dbUserDao.addUser(entity);
log.info("写入个数:{} ", update);
UserEntity user = dbUserDao.findUser(1L);
log.info("读取数据:{} ", user.toString());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
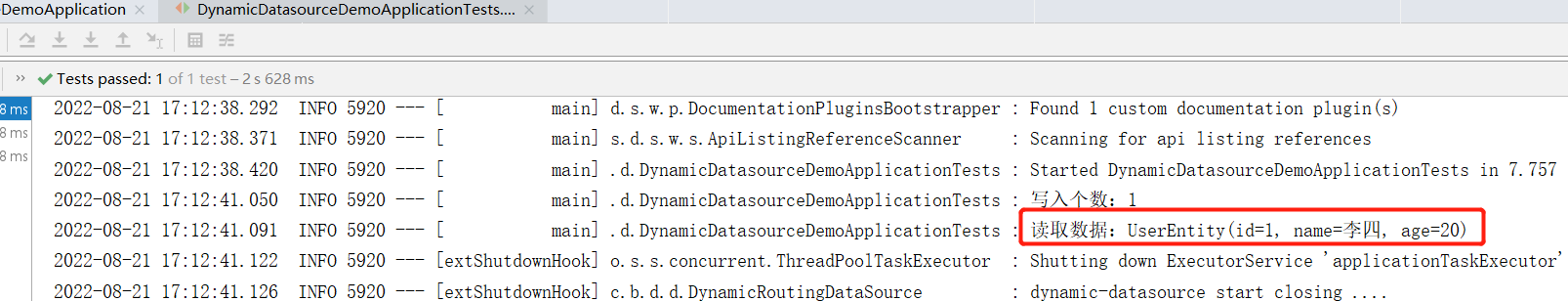
通过日志可以看出,读取的数据库是 db2 ,而写入的数据库呢,来看下db1 中的内容:
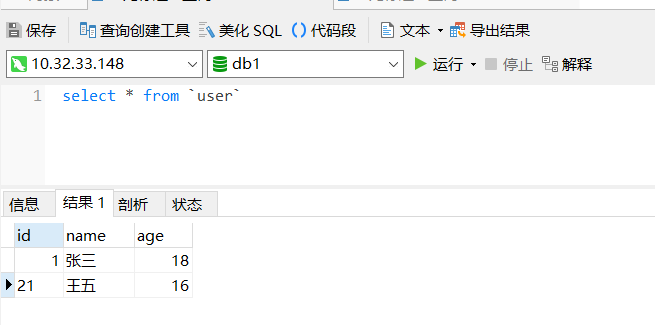
已经实现读写分离的效果。
五、负载均衡
上面通过 mybatis 的拦截器实现了读写分离,同时 dynamic-datasource 还为我们提供了负载的效果,同一个组下的默认就是负载均衡效果,怎么才是同一个组呢,上面有提到只需以下划线 _ 分割即可,下面修改配置文件:
spring:
application:
name: dynamic-datasource-demo
autoconfigure:
exclude: com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure
datasource:
dynamic:
primary: db_1 #设置默认的数据源或者数据源组,默认值即为master
strict: true #设置严格模式,默认false不启动. 启动后在未匹配到指定数据源时候回抛出异常,不启动会使用默认数据源.
datasource:
db_1:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://10.32.33.148:3307/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root123
db_2:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://10.32.33.148:3307/db2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root123
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
声明 Dao ,指定数据源为 db :
@Mapper
@Repository
@DS("db")
public interface FindUserDao extends BaseMapper<UserEntity> {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
测试:
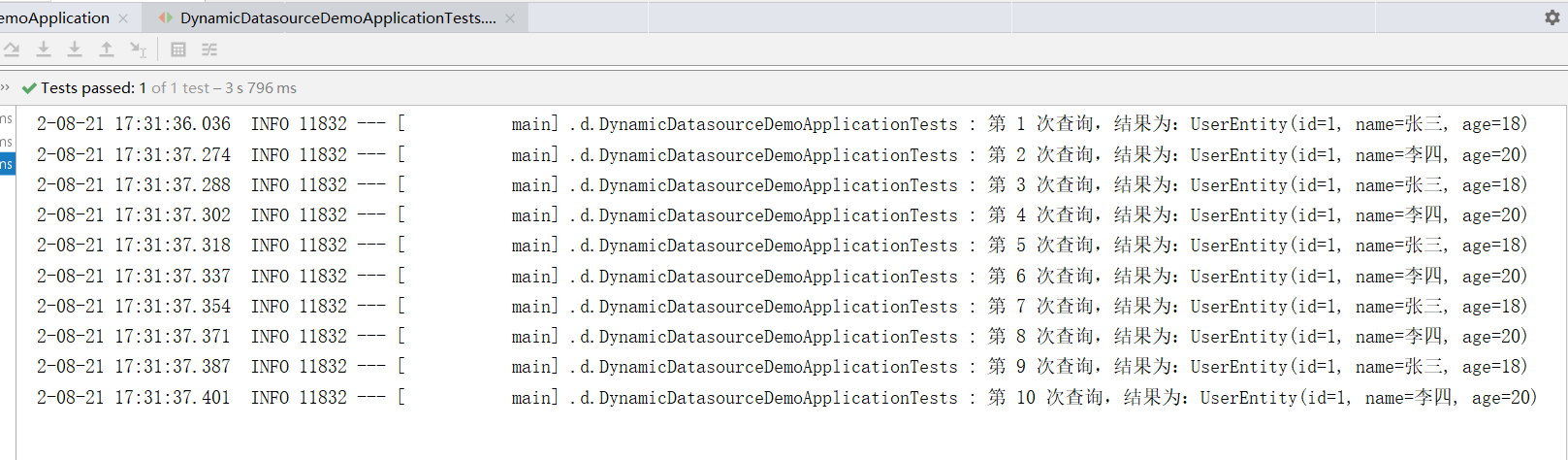
可以看到明显的负载轮训效果了。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:小毕超,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/qq_43692950/article/details/126450821
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)