机器学习的练功方式(十)——岭回归
【摘要】
文章目录
十 岭回归10.1 岭回归的接口10.2 岭回归处理房价预测
十 岭回归
岭回归是线性回归的改进,有时候迫不得已我们的参数确实不能少,这时候过拟合的现象就可能发生。为了避免过...
十 岭回归
岭回归是线性回归的改进,有时候迫不得已我们的参数确实不能少,这时候过拟合的现象就可能发生。为了避免过拟合现象的发生,既然不能从减少参数上面下手,那我们转而在线性回归的最后面添加一个罚项,罚项有时也被称为正则化项,其主要用于控制模型的平滑度,当模型参数越多,模型越复杂,那么罚项惩罚值就越大。
罚项可以是L1范数也可以是L2范数,对于使用L1范数的回归我们一般叫做Lasso线性回归。而对于使用L2范数的回归我们一般叫做岭回归。在这一讲中,我们主要讲述岭回归。
10.1 岭回归的接口
Ridge回归通过对系数的大小施加惩罚来解决普通线性模型使用最小二乘法带来的一些问题。
sklearn.linear_model.Ridge(alpha = 1.0,fit_intercept = True,solver = “auto”,normalize = False)
- 具有L2正则化的线性回归
- alpha:正则化力度,也叫 λ λ λ
- λ取值为0~1或 1~10
- solver:会根据数据自动选择优化方法
- SAG:如果数据集、特征都比较大,那么建议选择sag作为优化策略
- normalize:数据是否进行标准化
- normalize = False:可以在fit之前调用preprocessing.StandardScaler标准化数据
- Ridge.coef_:回归权重
- Ridge.intercept_:回归偏置
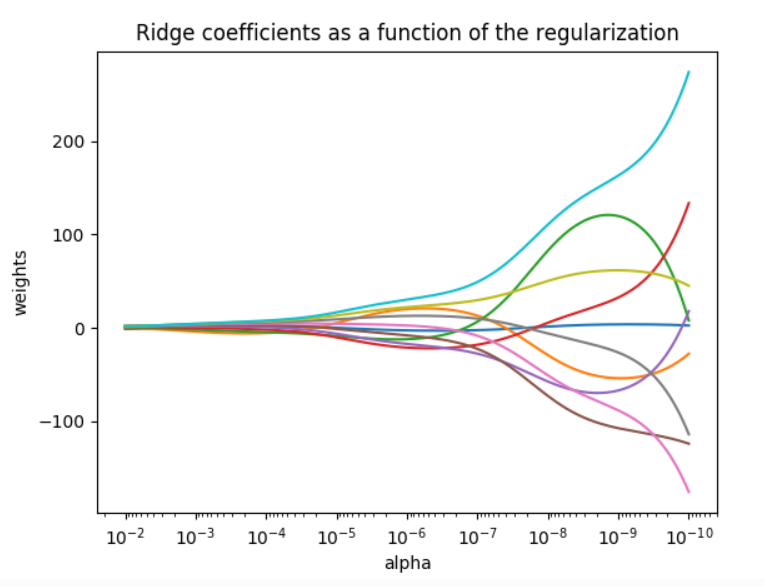
从图上来看,当alpha数值越高,则惩罚力度越大,权重系数越小,曲线越平滑。
10.2 岭回归处理房价预测
让我们用岭回归来预测波士顿房价吧。
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
def load_data():
"""加载数据集"""
boston_data = load_boston()
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston_data.data, boston_data.target, random_state=22)
return x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test
def ridge_linear_model():
"""用岭回归做预测"""
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = load_data()
# 预估器
estimator = Ridge(normalize=True)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 得出模型
print("权重系数为:\n", estimator.coef_)
print("偏置为:\n", estimator.intercept_)
# 模型评估
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("预测房价:\n", y_predict)
error = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
print("岭回归——均方误差为:\n", error)
ridge_linear_model()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:ArimaMisaki,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/chengyuhaomei520/article/details/123499215
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)