【目标检测】YOLOv5:添加漏检率和虚检率输出
前言
在目标检测领域,衡量一个模型的优劣的指标往往是mAP,然而实际工程中,有时候更倾向于看漏检率和虚检率。YOLOv5的原始代码并没有这两个指标的输出,因此我想利用原始代码的混淆矩阵,输出这两个指标数值。
指标解释
漏检即原本有目标存在却没有检测出来,换句话说就是原本是目标却检测成了背景。
虚检(虚警)即原本没有目标却误认为有目标,换句话说就是原本是背景却检测成了目标。
首先来看YOLOv5原本输出的混淆矩阵,图中灰色覆盖的地方是原本输出的各类别,也就是输出的正例,最后一行和一列是背景类。
列是模型预测的结果,行是标签的真实结果。可以看到最后一行出现数值,表示出现了漏检;最后一列出现数值,则表示出现了虚检。

代码改进
现在来看YOLOv5输出的混淆矩阵代码部分,代码主要位于metrics.py的ConfusionMatrix类中。
class ConfusionMatrix:
# Updated version of https://github.com/kaanakan/object_detection_confusion_matrix
def __init__(self, nc, conf=0.25, iou_thres=0.45):
"""
params nc: 数据集类别个数
params conf: 预测框置信度阈值
Params iou_thres: iou阈值
"""
self.matrix = np.zeros((nc + 1, nc + 1)) # +1的目的是添加背景类
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.conf = conf
self.iou_thres = iou_thres
self.lou = 0
self.total = 0
self.xu = 0
def process_batch(self, detections, labels):
"""
Return intersection-over-union (Jaccard index) of boxes.
Both sets of boxes are expected to be in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
Arguments:
detections (Array[N, 6]), x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, class
labels (Array[M, 5]), class, x1, y1, x2, y2
Returns:
None, updates confusion matrix accordingly
"""
detections = detections[detections[:, 4] > self.conf] # 筛除置信度过低的预测框(和nms差不多)
gt_classes = labels[:, 0].int()
detection_classes = detections[:, 5].int()
iou = general.box_iou(labels[:, 1:], detections[:, :4])
x = torch.where(iou > self.iou_thres)
if x[0].shape[0]:
matches = torch.cat((torch.stack(x, 1), iou[x[0], x[1]][:, None]), 1).cpu().numpy()
if x[0].shape[0] > 1:
matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 1], return_index=True)[1]]
matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 0], return_index=True)[1]]
else:
matches = np.zeros((0, 3))
n = matches.shape[0] > 0
m0, m1, _ = matches.transpose().astype(np.int16)
for i, gc in enumerate(gt_classes):
j = m0 == i
if n and sum(j) == 1:
# 如果sum(j)=1 说明gt[i]这个真实框被某个预测框检测到了
self.matrix[gc, detection_classes[m1[j]]] += 1 # correct
else:
# 如果sum(j)=0 说明gt[i]这个真实框没用被任何预测框检测到 也就是说这个真实框被检测成了背景框
self.matrix[self.nc, gc] += 1 # background FP
if n:
for i, dc in enumerate(detection_classes):
if not any(m1 == i):
self.matrix[dc, self.nc] += 1 # background FN
self.lou = sum(self.matrix[-1, :])
self.total = sum(sum(self.matrix))
self.xu = sum(self.matrix[:, -1])
def matrix(self):
return self.matrix
def plot(self, save_dir='', names=()):
try:
import seaborn as sn
# 按照每一列进行归一化
array = self.matrix / (self.matrix.sum(0).reshape(1, self.nc + 1) + 1E-6) # normalize
array[array < 0.005] = np.nan # don't annotate (would appear as 0.00)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 9), tight_layout=True)
sn.set(font_scale=1.0 if self.nc < 50 else 0.8) # for label size
labels = (0 < len(names) < 99) and len(names) == self.nc # apply names to ticklabels
sn.heatmap(array, annot=self.nc < 30, annot_kws={"size": 8}, cmap='Blues', fmt='.2f', square=True,
xticklabels=names + ['background FP'] if labels else "auto",
yticklabels=names + ['background FN'] if labels else "auto").set_facecolor((1, 1, 1))
fig.axes[0].set_xlabel('True')
fig.axes[0].set_ylabel('Predicted')
fig.savefig(Path(save_dir) / 'confusion_matrix.png', dpi=250)
except Exception as e:
pass
def print(self):
for i in range(self.nc + 1):
print(' '.join(map(str, self.matrix[i])))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
阅读代码可以发现,混淆矩阵再绘制时对每一列单独进行了归一化,那么再绘制之前,混淆矩阵存储了每一个预测结果和真实结果的数目。
于是我添加了三个属性self.lou、self.total = 0、self.xu = 0,分别统计漏检目标数目,总目标数目和虚检目标数目。
漏检目标数目只需要将混淆矩阵最后一行相加,虚检目标数目只需要将混淆矩阵最后一列相加,总目标数目则将混淆矩阵所有数量相加。
然后在test.py中进行添加:
# Print speeds
t = tuple(x / seen * 1E3 for x in (t0, t1, t0 + t1)) + (imgsz, imgsz, batch_size) # tuple
if not training:
print('Speed: %.1f/%.1f/%.1f ms inference/NMS/total per %gx%g image at batch-size %g' % t)
# 计算漏检率
print("漏检样本数为:")
print(int(confusion_matrix.lou))
print("漏检率为:")
print(confusion_matrix.lou / confusion_matrix.total)
# 计算虚检率
print("虚检样本数为:")
print(int(confusion_matrix.xu))
print("虚检率为:")
print(confusion_matrix.xu / confusion_matrix.total)
# Plots
if plots:
confusion_matrix.plot(save_dir=save_dir, names=list(names.values()))
if wandb_logger and wandb_logger.wandb:
val_batches = [wandb_logger.wandb.Image(str(f), caption=f.name) for f in sorted(save_dir.glob('test*.jpg'))]
wandb_logger.log({"Validation": val_batches})
if wandb_images:
wandb_logger.log({"Bounding Box Debugger/Images": wandb_images})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
输出效果:
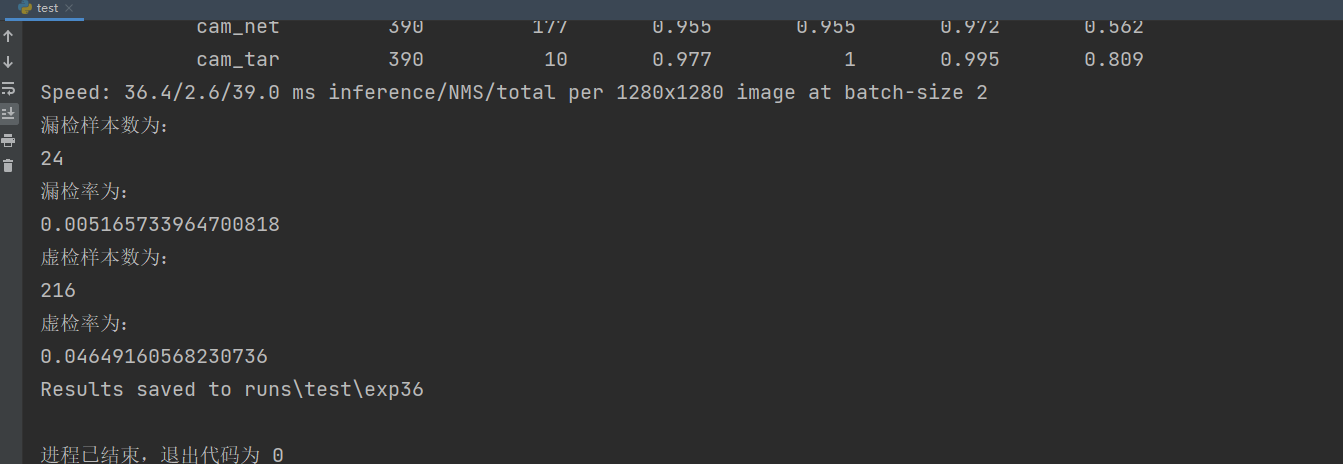
2022.8.8更
Bug修复
突然想到前面的代码有个Bug,计算漏检率不应该采用混淆矩阵的全部内容,而只需采用混淆矩阵中的正例样本数目,否则分母将虚检的目标也混合进去,导致结果偏小。
直观理解,输出混淆矩阵可视化:分母应该是红框内的所有内容

metrics.py修改:
class ConfusionMatrix:
# Updated version of https://github.com/kaanakan/object_detection_confusion_matrix
def __init__(self, nc, conf=0.25, iou_thres=0.45):
"""
params nc: 数据集类别个数
params conf: 预测框置信度阈值
Params iou_thres: iou阈值
"""
self.matrix = np.zeros((nc + 1, nc + 1)) # +1的目的是添加背景类
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.conf = conf
self.iou_thres = iou_thres
self.lou = 0
self.total = 0
self.xu = 0
self.class_total = 0
def process_batch(self, detections, labels):
"""
Return intersection-over-union (Jaccard index) of boxes.
Both sets of boxes are expected to be in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
Arguments:
detections (Array[N, 6]), x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, class
labels (Array[M, 5]), class, x1, y1, x2, y2
Returns:
None, updates confusion matrix accordingly
"""
detections = detections[detections[:, 4] > self.conf] # 筛除置信度过低的预测框(和nms差不多)
gt_classes = labels[:, 0].int()
detection_classes = detections[:, 5].int()
iou = general.box_iou(labels[:, 1:], detections[:, :4])
x = torch.where(iou > self.iou_thres)
if x[0].shape[0]:
matches = torch.cat((torch.stack(x, 1), iou[x[0], x[1]][:, None]), 1).cpu().numpy()
if x[0].shape[0] > 1:
matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 1], return_index=True)[1]]
matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 0], return_index=True)[1]]
else:
matches = np.zeros((0, 3))
n = matches.shape[0] > 0
m0, m1, _ = matches.transpose().astype(np.int16)
for i, gc in enumerate(gt_classes):
j = m0 == i
if n and sum(j) == 1:
# 如果sum(j)=1 说明gt[i]这个真实框被某个预测框检测到了
self.matrix[gc, detection_classes[m1[j]]] += 1 # correct
else:
# 如果sum(j)=0 说明gt[i]这个真实框没用被任何预测框检测到 也就是说这个真实框被检测成了背景框
self.matrix[self.nc, gc] += 1 # background FP
if n:
for i, dc in enumerate(detection_classes):
if not any(m1 == i):
self.matrix[dc, self.nc] += 1 # background FN
self.lou = sum(self.matrix[-1, :])
self.total = sum(sum(self.matrix))
self.xu = sum(self.matrix[:, -1])
self.class_total = sum(sum(self.matrix)[: -1])
def matrix(self):
return self.matrix
def plot(self, save_dir='', names=()):
try:
import seaborn as sn
# 按照每一列进行归一化
array = self.matrix / (self.matrix.sum(0).reshape(1, self.nc + 1) + 1E-6) # normalize
array[array < 0.005] = np.nan # don't annotate (would appear as 0.00)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 9), tight_layout=True)
sn.set(font='SimHei', font_scale=1.0 if self.nc < 50 else 0.8) # for label size
labels = (0 < len(names) < 99) and len(names) == self.nc # apply names to ticklabels
sn.heatmap(array, annot=self.nc < 30, annot_kws={"size": 8}, cmap='Blues', fmt='.2f', square=True,
xticklabels=names + ['background FP'] if labels else "auto",
yticklabels=names + ['background FN'] if labels else "auto").set_facecolor((1, 1, 1))
fig.axes[0].set_xlabel('True')
fig.axes[0].set_ylabel('Predicted')
fig.savefig(Path(save_dir) / 'confusion_matrix.png', dpi=250)
except Exception as e:
pass
def print(self):
for i in range(self.nc + 1):
print(' '.join(map(str, self.matrix[i])))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
test.py修改:
# 计算漏检率
print("漏检样本数为:")
print(int(confusion_matrix.lou))
print("漏检率为:")
print(confusion_matrix.lou / confusion_matrix.class_total)
# 计算虚检率
print("虚检样本数为:")
print(int(confusion_matrix.xu))
print("虚检率为:")
print(confusion_matrix.xu / confusion_matrix.total)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
文章来源: zstar.blog.csdn.net,作者:zstar-_,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:zstar.blog.csdn.net/article/details/126214241
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)