二值图像处理连通区域分析
OpenCV提供了专门的函数标记连通区域connectedComponents,它有四种形式:
1. int connectedComponents(InputArray image, OutputArray labels, int connectivity, int ltype, int ccltype);
参数说明:
image : 输入原始图像,8bit单通道,二值图像
labels : 输出标记图像
connectivity : 邻域类型,4连通或8连通,所以这个值通常为两个值(4或8)
ltype : 输出标记的类型,只支持 CV_32S和CV_16U
ccltype : 连通标记的算法,这个值有三个选择CCL_WU(8连通和4连通均用SAUF算法),CCL_DEFAULT(8连通用BBDT算法,4连通用SAUF算法)和CCL_GRANA(8连通用BBDT算法,4连通用SAUF算法)。(后两种方法是一样的,这里有疑问)
2. int connectedComponents(InputArray image, OutputArray labels, int connectivity = 8, int ltype = CV_32S);
这个函数实际上就是第一个的简化版
这两个函数的返回值是标记的个数[0,N-1],0表示背景区域
3. int connectedComponentsWithStats(InputArray image, OutputArray labels, OutputArray stats, OutputArray centroids, int connectivity, int ltype, int ccltype);
参数说明:
image : 输入原始图像,8bit单通道,二值图像
labels : 输出标记图像
stats : 每个标记的统计输出,类型为CV_32S,使用格式为stats(label, COLUMN),其中COLUMN为连通类型,包括CC_STAT_LEFT、CC_STAT_TOP、CC_STAT_WIDTH、CC_STAT_HEIGHT、CC_STAT_AREA
centroids : 每个标记区域的质心,类型为CV_64F,使用方法为x = centroids(label,0), y = centroids(label, 1)
connectivity : 邻域类型,4连通或8连通,所以这个值通常为两个值(4或8)
ltype : 输出标记的类型,只支持 CV_32S和CV_16U
4. int connectedComponentsWithStats(InputArray image, OutputArray labels, OutputArray stats, OutputArray centroids, int connectivity = 8, int ltype = CV_32S);
第三个函数的简化版
----------------------华丽的分界线------------------------
以下转自:https://blog.csdn.net/icvpr/article/details/10259577
OpenCV_连通区域分析(Connected Component Analysis/Labeling)
【摘要】
本文主要介绍在CVPR和图像处理领域中较为常用的一种图像区域(Blob)提取的方法——连通性分析法(连通区域标记法)。文中介绍了两种常见的连通性分析的算法:1)Two-pass;2)Seed-Filling种子填充,并给出了两个算法的基于OpenCV的C++实现代码。
一、连通区域分析
连通区域(Connected Component)一般是指图像中具有相同像素值且位置相邻的前景像素点组成的图像区域(Region,Blob)。连通区域分析(Connected Component Analysis,Connected Component Labeling)是指将图像中的各个连通区域找出并标记。
连通区域分析是一种在CVPR和图像分析处理的众多应用领域中较为常用和基本的方法。例如:OCR识别中字符分割提取(车牌识别、文本识别、字幕识别等)、视觉跟踪中的运动前景目标分割与提取(行人入侵检测、遗留物体检测、基于视觉的车辆检测与跟踪等)、医学图像处理(感兴趣目标区域提取)、等等。也就是说,在需要将前景目标提取出来以便后续进行处理的应用场景中都能够用到连通区域分析方法,通常连通区域分析处理的对象是一张二值化后的图像。
二、连通区域分析的算法
从连通区域的定义可以知道,一个连通区域是由具有相同像素值的相邻像素组成像素集合,因此,我们就可以通过这两个条件在图像中寻找连通区域,对于找到的每个连通区域,我们赋予其一个唯一的标识(Label),以区别其他连通区域。
连通区域分析有基本的算法,也有其改进算法,本文介绍其中的两种常见算法:
1)Two-Pass法;2)Seed-Filling种子填充法;
Note:
a、这里的扫描指的是按行或按列访问以便图像的所有像素,本文算法采用的是按行扫描方式;
b、图像记为B,为二值图像:前景像素(pixel value = 1),背景像素(pixel value = 0)
c、label从2开始计数;
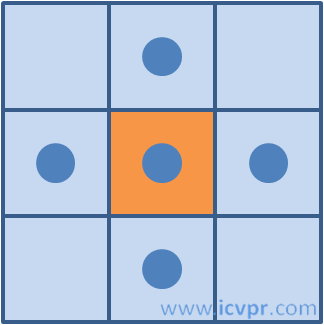
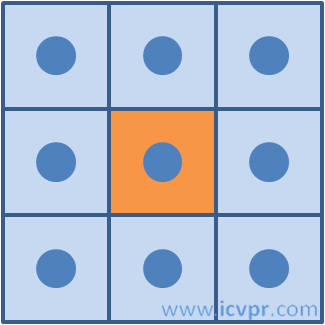
d、像素相邻关系:4-领域、8-领域,本文算法采用4-邻域;


4—领域图例 8—领域图例
1)Two-Pass(两遍扫描法)
两遍扫描法,正如其名,指的就是通过扫描两遍图像,就可以将图像中存在的所有连通区域找出并标记。思路:第一遍扫描时赋予每个像素位置一个label,扫描过程中同一个连通区域内的像素集合中可能会被赋予一个或多个不同label,因此需要将这些属于同一个连通区域但具有不同值的label合并,也就是记录它们之间的相等关系;第二遍扫描就是将具有相等关系的equal_labels所标记的像素归为一个连通区域并赋予一个相同的label(通常这个label是equal_labels中的最小值)。
下面给出Two-Pass算法的简单步骤:
(1)第一次扫描:
访问当前像素B(x,y),如果B(x,y) == 1:
a、如果B(x,y)的领域中像素值都为0,则赋予B(x,y)一个新的label:
label += 1, B(x,y) = label;
b、如果B(x,y)的领域中有像素值 > 1的像素Neighbors:
1)将Neighbors中的最小值赋予给B(x,y):
B(x,y) = min{Neighbors}
2)记录Neighbors中各个值(label)之间的相等关系,即这些值(label)同属同一个连通区域;
labelSet[i] = { label_m, .., label_n },labelSet[i]中的所有label都属于同一个连通区域(注:这里可以有多种实现方式,只要能够记录这些具有相等关系的label之间的关系即可)
(2)第二次扫描:
访问当前像素B(x,y),如果B(x,y) > 1:
a、找到与label = B(x,y)同属相等关系的一个最小label值,赋予给B(x,y);
完成扫描后,图像中具有相同label值的像素就组成了同一个连通区域。
下面这张图动态地演示了Two-pass算法:
2)Seed Filling(种子填充法)
种子填充方法来源于计算机图形学,常用于对某个图形进行填充。思路:选取一个前景像素点作为种子,然后根据连通区域的两个基本条件(像素值相同、位置相邻)将与种子相邻的前景像素合并到同一个像素集合中,最后得到的该像素集合则为一个连通区域。
下面给出基于种子填充法的连通区域分析方法:
(1)扫描图像,直到当前像素点B(x,y) == 1:
a、将B(x,y)作为种子(像素位置),并赋予其一个label,然后将该种子相邻的所有前景像素都压入栈中;
b、弹出栈顶像素,赋予其相同的label,然后再将与该栈顶像素相邻的所有前景像素都压入栈中;
c、重复b步骤,直到栈为空;
此时,便找到了图像B中的一个连通区域,该区域内的像素值被标记为label;
(2)重复第(1)步,直到扫描结束;
扫描结束后,就可以得到图像B中所有的连通区域;
下面这张图动态地演示了Seed-Filling算法:
三、实验演示
1)前景二值图像
2)连通区域分析方法标记后得到的label图像
Two-pass算法:
Seed-filling算法:
注:为了显示方便,将像素值乘以了一个整数进行放大。
3)color后的label图像
Two-pass算法:
Seed-filling算法:

注:颜色是随机生成的。
四、代码
1)Two-pass算法的一种实现
说明:
基于OpenCV和C++实现,领域:4-领域。实现与算法描述稍有差别(具体为记录具有相等关系的label方法实现上)。
- // Connected Component Analysis/Labeling By Two-Pass Algorithm
- // Author: www.icvpr.com
- // Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/icvpr
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <list>
- #include <vector>
- #include <map>
- #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- void icvprCcaByTwoPass(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg)
- {
- // connected component analysis (4-component)
- // use two-pass algorithm
- // 1. first pass: label each foreground pixel with a label
- // 2. second pass: visit each labeled pixel and merge neighbor labels
- //
- // foreground pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 1
- // background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
- if (_binImg.empty() ||
- _binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
- {
- return ;
- }
- // 1. first pass
- _lableImg.release() ;
- _binImg.convertTo(_lableImg, CV_32SC1) ;
- int label = 1 ; // start by 2
- std::vector<int> labelSet ;
- labelSet.push_back(0) ; // background: 0
- labelSet.push_back(1) ; // foreground: 1
- int rows = _binImg.rows - 1 ;
- int cols = _binImg.cols - 1 ;
- for (int i = 1; i < rows; i++)
- {
- int* data_preRow = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i-1) ;
- int* data_curRow = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i) ;
- for (int j = 1; j < cols; j++)
- {
- if (data_curRow[j] == 1)
- {
- std::vector<int> neighborLabels ;
- neighborLabels.reserve(2) ;
- int leftPixel = data_curRow[j-1] ;
- int upPixel = data_preRow[j] ;
- if ( leftPixel > 1)
- {
- neighborLabels.push_back(leftPixel) ;
- }
- if (upPixel > 1)
- {
- neighborLabels.push_back(upPixel) ;
- }
- if (neighborLabels.empty())
- {
- labelSet.push_back(++label) ; // assign to a new label
- data_curRow[j] = label ;
- labelSet[label] = label ;
- }
- else
- {
- std::sort(neighborLabels.begin(), neighborLabels.end()) ;
- int smallestLabel = neighborLabels[0] ;
- data_curRow[j] = smallestLabel ;
- // save equivalence
- for (size_t k = 1; k < neighborLabels.size(); k++)
- {
- int tempLabel = neighborLabels[k] ;
- int& oldSmallestLabel = labelSet[tempLabel] ;
- if (oldSmallestLabel > smallestLabel)
- {
- labelSet[oldSmallestLabel] = smallestLabel ;
- oldSmallestLabel = smallestLabel ;
- }
- else if (oldSmallestLabel < smallestLabel)
- {
- labelSet[smallestLabel] = oldSmallestLabel ;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- // update equivalent labels
- // assigned with the smallest label in each equivalent label set
- for (size_t i = 2; i < labelSet.size(); i++)
- {
- int curLabel = labelSet[i] ;
- int preLabel = labelSet[curLabel] ;
- while (preLabel != curLabel)
- {
- curLabel = preLabel ;
- preLabel = labelSet[preLabel] ;
- }
- labelSet[i] = curLabel ;
- }
- // 2. second pass
- for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
- {
- int* data = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i) ;
- for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
- {
- int& pixelLabel = data[j] ;
- pixelLabel = labelSet[pixelLabel] ;
- }
- }
- }
2)Seed-Filling种子填充方法
说明:
基于OpenCV和C++实现;领域:4-领域。
- // Connected Component Analysis/Labeling By Seed-Filling Algorithm
- // Author: www.icvpr.com
- // Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/icvpr
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <list>
- #include <vector>
- #include <map>
- #include <stack>
- #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- void icvprCcaBySeedFill(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg)
- {
- // connected component analysis (4-component)
- // use seed filling algorithm
- // 1. begin with a foreground pixel and push its foreground neighbors into a stack;
- // 2. pop the top pixel on the stack and label it with the same label until the stack is empty
- //
- // foreground pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 1
- // background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
- if (_binImg.empty() ||
- _binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
- {
- return ;
- }
- _lableImg.release() ;
- _binImg.convertTo(_lableImg, CV_32SC1) ;
- int label = 1 ; // start by 2
- int rows = _binImg.rows - 1 ;
- int cols = _binImg.cols - 1 ;
- for (int i = 1; i < rows-1; i++)
- {
- int* data= _lableImg.ptr<int>(i) ;
- for (int j = 1; j < cols-1; j++)
- {
- if (data[j] == 1)
- {
- std::stack<std::pair<int,int>> neighborPixels ;
- neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(i,j)) ; // pixel position: <i,j>
- ++label ; // begin with a new label
- while (!neighborPixels.empty())
- {
- // get the top pixel on the stack and label it with the same label
- std::pair<int,int> curPixel = neighborPixels.top() ;
- int curX = curPixel.first ;
- int curY = curPixel.second ;
- _lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY) = label ;
- // pop the top pixel
- neighborPixels.pop() ;
- // push the 4-neighbors (foreground pixels)
- if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY-1) == 1)
- {// left pixel
- neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX, curY-1)) ;
- }
- if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY+1) == 1)
- {// right pixel
- neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX, curY+1)) ;
- }
- if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX-1, curY) == 1)
- {// up pixel
- neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX-1, curY)) ;
- }
- if (_lableImg.at<int>(curX+1, curY) == 1)
- {// down pixel
- neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX+1, curY)) ;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
3)颜色标记(用于显示)
- // Connected Component Analysis/Labeling -- Color Labeling
- // Author: www.icvpr.com
- // Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/icvpr
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <list>
- #include <vector>
- #include <map>
- #include <stack>
- #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- cv::Scalar icvprGetRandomColor()
- {
- uchar r = 255 * (rand()/(1.0 + RAND_MAX));
- uchar g = 255 * (rand()/(1.0 + RAND_MAX));
- uchar b = 255 * (rand()/(1.0 + RAND_MAX));
- return cv::Scalar(b,g,r) ;
- }
- void icvprLabelColor(const cv::Mat& _labelImg, cv::Mat& _colorLabelImg)
- {
- if (_labelImg.empty() ||
- _labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1)
- {
- return ;
- }
- std::map<int, cv::Scalar> colors ;
- int rows = _labelImg.rows ;
- int cols = _labelImg.cols ;
- _colorLabelImg.release() ;
- _colorLabelImg.create(rows, cols, CV_8UC3) ;
- _colorLabelImg = cv::Scalar::all(0) ;
- for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
- {
- const int* data_src = (int*)_labelImg.ptr<int>(i) ;
- uchar* data_dst = _colorLabelImg.ptr<uchar>(i) ;
- for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
- {
- int pixelValue = data_src[j] ;
- if (pixelValue > 1)
- {
- if (colors.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
- {
- colors[pixelValue] = icvprGetRandomColor() ;
- }
- cv::Scalar color = colors[pixelValue] ;
- *data_dst++ = color[0] ;
- *data_dst++ = color[1] ;
- *data_dst++ = color[2] ;
- }
- else
- {
- data_dst++ ;
- data_dst++ ;
- data_dst++ ;
- }
- }
- }
- }
4)测试程序
- // Connected Component Analysis/Labeling -- Test code
- // Author: www.icvpr.com
- // Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/icvpr
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <list>
- #include <vector>
- #include <map>
- #include <stack>
- #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- int main(int argc, char** argv)
- {
- cv::Mat binImage = cv::imread("../icvpr.com.jpg", 0) ;
- cv::threshold(binImage, binImage, 50, 1, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV) ;
- // connected component labeling
- cv::Mat labelImg ;
- icvprCcaByTwoPass(binImage, labelImg) ;
- //icvprCcaBySeedFill(binImage, labelImg) ;
- // show result
- cv::Mat grayImg ;
- labelImg *= 10 ;
- labelImg.convertTo(grayImg, CV_8UC1) ;
- cv::imshow("labelImg", grayImg) ;
- cv::Mat colorLabelImg ;
- icvprLabelColor(labelImg, colorLabelImg) ;
- cv::imshow("colorImg", colorLabelImg) ;
- cv::waitKey(0) ;
- return 0 ;
- }
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者









评论(0)