人脸动漫化——AnimeGAN快速上手
最近看到Github上有个项目很火,于是尝试clone下玩玩。
项目名:animegan2-pytorch
项目地址:https://github.com/bryandlee/animegan2-pytorch
项目简介
AnimeGAN是来自武汉大学和湖北工业大学的一项研究,采用的是神经风格迁移 + 生成对抗网络(GAN)的组合。
AnimeGAN从去年就已经提出,使用的是Tensorflow框架,目前该项目已开发出了第二代版本,支持pytroch框架。
原论文:AnimeGAN: A Novel Lightweight GAN for Photo Animation
https://github.com/TachibanaYoshino/AnimeGAN/blob/master/doc/Chen2020_Chapter_AnimeGAN.pdf
网络结构(图片节选自原论文,原理暂不细究):

该项目可以实现将真人头像动漫化,例如下面的动图所示:

项目上手
文件预览
由于国外服务器下载较慢,本项目所有文件以及所需下载的其它文件我均做了备份。获取方式可以跳转到文末。
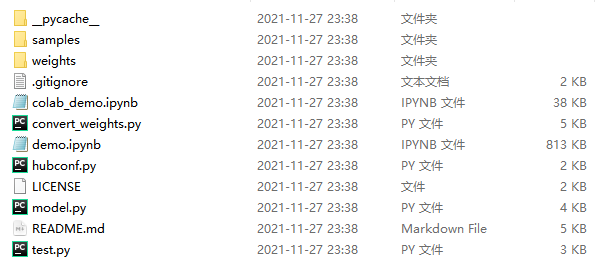
samples:用来放置一些示例图片
weghts:权重文件
colab_demo/demo.ipynb:两个使用案例
convert_weights.py:用来将权重文件夹里的tensorflow模型转换成pytorch模型文件
hubconf.py:在Pytorch.Hub上获取预加载模型
在使用中,只需要用到两个文件:
1、demo.ipynb
2、weights文件夹(内含四个模型,对应不同图片大小、美化程度、鲁棒性等…)
环境安装
首先在jupyter lab中打开demo.ipynb,然后根据import来配置环境。
Pytorch 安装
项目需要使用Pytorch框架,框架的安装可以看我之前的博文:
超简单的pytorch(GPU版)安装教程(亲测有效)
cmake安装
在进行dlib库安装时,直接安装会报错:
CMake must be installed to build the following extensions: dlib
- 1
在此之前,需先进行cmake安装。
安装方式:
pip install cmake
- 1
face_recognition安装
安装完cmake后,先别急着装dlib,先安装face_recognition,这里面包含了一个版本的dlib。
安装方式:
pip install face_recognition
- 1
dlib检查与安装
安装好face_recognition之后,内部自带了一个dlib,此时可尝试运行demo中的第二段程序,如果dlib无报错,可不进行下面的步骤。
若报错,则可能是dlib的版本与python的版本不匹配,需卸载重装。
卸载方式:
pip uninstall dlib
- 1
若使用pip进行dlib的安装,大概率会报错,因此需将dlib的包下载下来本地安装。
下面是dlib不同版本和python版本的对应关系
python3.5版本:19.4.0版本
python3.6版本:19.6.0版本;
python3.7版本:19.14.0版本
python3.8版本:19.19.0版本;
我的安装的python版本为3.8,因此我需要下载dlib的19.19.0版本。
下载链接:https://pypi.org/project/dlib/19.19.0/#files
下载的是.tar.gz格式的文件:
下载好后需进行解压,在命令行切换到解压后的文件夹,运行:
python setup.py
- 1
运行好之后,相应的dlib版本就安装完毕。
scipy安装
scipy是科学工具包,内含很多计算公式,后面有用到,安装比较简单:
pip install scipy
- 1
requests安装(可选)
玩过爬虫的都知道requests可以很方便的向服务器发送请求,后面测试图片如果需要获取网络资源,则需安装此库,本地图片加载可不用安装。
安装方式:
pip install requests
- 1
特征点检测数据库下载
前面安装过的dlib可用来检测人脸特征,但库本身并不带特征点检测库,运行时会报错:
Unable to open shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat
- 1
解决方式:
将shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat该文件放置在项目同文件夹下即可。
该文件在文末我备份的文件中已添加。
权重文件放置
运行代码第一段,它会用torch.hub.load来下载模型文件,如果你的网速不快,很可能会下载中断,产生报错。其实,下载的文件和克隆的项目文件一样,只不过会在C盘的缓冲区进行额外添加。
添加位置如图所示:
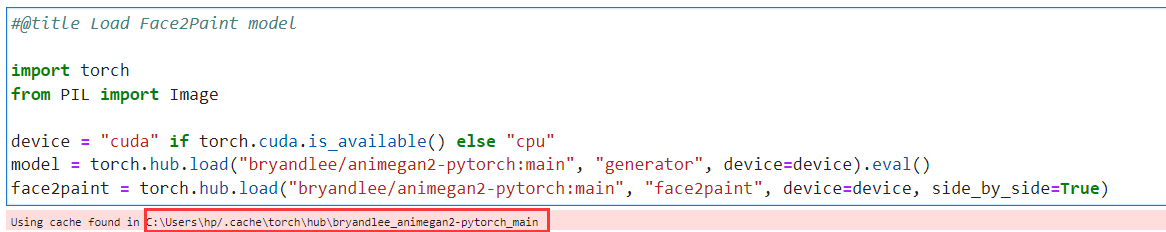
它会在相应文件夹下生成两个文件夹:
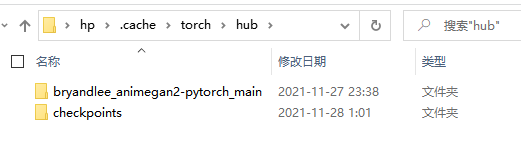
下载失败没关系,只要把项目内的相应文件拷贝进去即可。
第一个文件内容(即项目文件)
第二个文件内容(存放权重文件)
放好之后,在此运行第一段代码,就不会联网去下载,而会提示文件已存在。
代码功能解读
第一段代码,主要用来设置环境。
#@title Load Face2Paint model
import torch
from PIL import Image
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model = torch.hub.load("bryandlee/animegan2-pytorch:main", "generator", device=device).eval()
face2paint = torch.hub.load("bryandlee/animegan2-pytorch:main", "face2paint", device=device, side_by_side=True)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
第二段代码,核心代码,通过dlib将人脸部分进行裁切,并检测出所有人脸特征点,进行标注,产生图片。
#@title Face Detector & FFHQ-style Alignment
# https://github.com/woctezuma/stylegan2-projecting-images
import os
import dlib
import collections
from typing import Union, List
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_dlib_face_detector(predictor_path: str = "shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat"):
if not os.path.isfile(predictor_path):
model_file = "shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2"
os.system(f"wget http://dlib.net/files/{model_file}")
os.system(f"bzip2 -dk {model_file}")
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
shape_predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(predictor_path)
def detect_face_landmarks(img: Union[Image.Image, np.ndarray]):
if isinstance(img, Image.Image):
img = np.array(img)
faces = []
dets = detector(img)
for d in dets:
shape = shape_predictor(img, d)
faces.append(np.array([[v.x, v.y] for v in shape.parts()]))
return faces
return detect_face_landmarks
def display_facial_landmarks(
img: Image,
landmarks: List[np.ndarray],
fig_size=[15, 15]
):
plot_style = dict(
marker='o',
markersize=4,
linestyle='-',
lw=2
)
pred_type = collections.namedtuple('prediction_type', ['slice', 'color'])
pred_types = {
'face': pred_type(slice(0, 17), (0.682, 0.780, 0.909, 0.5)),
'eyebrow1': pred_type(slice(17, 22), (1.0, 0.498, 0.055, 0.4)),
'eyebrow2': pred_type(slice(22, 27), (1.0, 0.498, 0.055, 0.4)),
'nose': pred_type(slice(27, 31), (0.345, 0.239, 0.443, 0.4)),
'nostril': pred_type(slice(31, 36), (0.345, 0.239, 0.443, 0.4)),
'eye1': pred_type(slice(36, 42), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.3)),
'eye2': pred_type(slice(42, 48), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.3)),
'lips': pred_type(slice(48, 60), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.3)),
'teeth': pred_type(slice(60, 68), (0.596, 0.875, 0.541, 0.4))
}
fig = plt.figure(figsize=fig_size)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
for face in landmarks:
for pred_type in pred_types.values():
ax.plot(
face[pred_type.slice, 0],
face[pred_type.slice, 1],
color=pred_type.color, **plot_style
)
plt.show()
# https://github.com/NVlabs/ffhq-dataset/blob/master/download_ffhq.py
import PIL.Image
import PIL.ImageFile
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
def align_and_crop_face(
img: Image.Image,
landmarks: np.ndarray,
expand: float = 1.0,
output_size: int = 1024,
transform_size: int = 4096,
enable_padding: bool = True,
):
# Parse landmarks.
# pylint: disable=unused-variable
lm = landmarks
lm_chin = lm[0 : 17] # left-right
lm_eyebrow_left = lm[17 : 22] # left-right
lm_eyebrow_right = lm[22 : 27] # left-right
lm_nose = lm[27 : 31] # top-down
lm_nostrils = lm[31 : 36] # top-down
lm_eye_left = lm[36 : 42] # left-clockwise
lm_eye_right = lm[42 : 48] # left-clockwise
lm_mouth_outer = lm[48 : 60] # left-clockwise
lm_mouth_inner = lm[60 : 68] # left-clockwise
# Calculate auxiliary vectors.
eye_left = np.mean(lm_eye_left, axis=0)
eye_right = np.mean(lm_eye_right, axis=0)
eye_avg = (eye_left + eye_right) * 0.5
eye_to_eye = eye_right - eye_left
mouth_left = lm_mouth_outer[0]
mouth_right = lm_mouth_outer[6]
mouth_avg = (mouth_left + mouth_right) * 0.5
eye_to_mouth = mouth_avg - eye_avg
# Choose oriented crop rectangle.
x = eye_to_eye - np.flipud(eye_to_mouth) * [-1, 1]
x /= np.hypot(*x)
x *= max(np.hypot(*eye_to_eye) * 2.0, np.hypot(*eye_to_mouth) * 1.8)
x *= expand
y = np.flipud(x) * [-1, 1]
c = eye_avg + eye_to_mouth * 0.1
quad = np.stack([c - x - y, c - x + y, c + x + y, c + x - y])
qsize = np.hypot(*x) * 2
# Shrink.
shrink = int(np.floor(qsize / output_size * 0.5))
if shrink > 1:
rsize = (int(np.rint(float(img.size[0]) / shrink)), int(np.rint(float(img.size[1]) / shrink)))
img = img.resize(rsize, PIL.Image.ANTIALIAS)
quad /= shrink
qsize /= shrink
# Crop.
border = max(int(np.rint(qsize * 0.1)), 3)
crop = (int(np.floor(min(quad[:,0]))), int(np.floor(min(quad[:,1]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,0]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,1]))))
crop = (max(crop[0] - border, 0), max(crop[1] - border, 0), min(crop[2] + border, img.size[0]), min(crop[3] + border, img.size[1]))
if crop[2] - crop[0] < img.size[0] or crop[3] - crop[1] < img.size[1]:
img = img.crop(crop)
quad -= crop[0:2]
# Pad.
pad = (int(np.floor(min(quad[:,0]))), int(np.floor(min(quad[:,1]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,0]))), int(np.ceil(max(quad[:,1]))))
pad = (max(-pad[0] + border, 0), max(-pad[1] + border, 0), max(pad[2] - img.size[0] + border, 0), max(pad[3] - img.size[1] + border, 0))
if enable_padding and max(pad) > border - 4:
pad = np.maximum(pad, int(np.rint(qsize * 0.3)))
img = np.pad(np.float32(img), ((pad[1], pad[3]), (pad[0], pad[2]), (0, 0)), 'reflect')
h, w, _ = img.shape
y, x, _ = np.ogrid[:h, :w, :1]
mask = np.maximum(1.0 - np.minimum(np.float32(x) / pad[0], np.float32(w-1-x) / pad[2]), 1.0 - np.minimum(np.float32(y) / pad[1], np.float32(h-1-y) / pad[3]))
blur = qsize * 0.02
img += (scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter(img, [blur, blur, 0]) - img) * np.clip(mask * 3.0 + 1.0, 0.0, 1.0)
img += (np.median(img, axis=(0,1)) - img) * np.clip(mask, 0.0, 1.0)
img = PIL.Image.fromarray(np.uint8(np.clip(np.rint(img), 0, 255)), 'RGB')
quad += pad[:2]
# Transform.
img = img.transform((transform_size, transform_size), PIL.Image.QUAD, (quad + 0.5).flatten(), PIL.Image.BILINEAR)
if output_size < transform_size:
img = img.resize((output_size, output_size), PIL.Image.ANTIALIAS)
return img
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
第三段代码,设置图片导入方式(第一种网络读取图片,第二种本地加载),之后调用第二段中定义的算法,产生结果输出。
import requests
# img = Image.open(requests.get("https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/85/Elon_Musk_Royal_Society_%28crop1%29.jpg", stream=True).raw).convert("RGB")
img = Image.open(r"C:\Users\hp\Desktop\bidao.png").convert("RGB")
face_detector = get_dlib_face_detector()
landmarks = face_detector(img)
display_facial_landmarks(img, landmarks, fig_size=[5, 5])
for landmark in landmarks:
face = align_and_crop_face(img, landmark, expand=1.3)
display(face2paint(model=model, img=face, size=512))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
查看效果
好了,经历漫长和复杂的环境配置后,导入图片就能看到效果了。
我这里以毕导的图片为例:
原图:

人脸提取标注后:

动漫化对比:
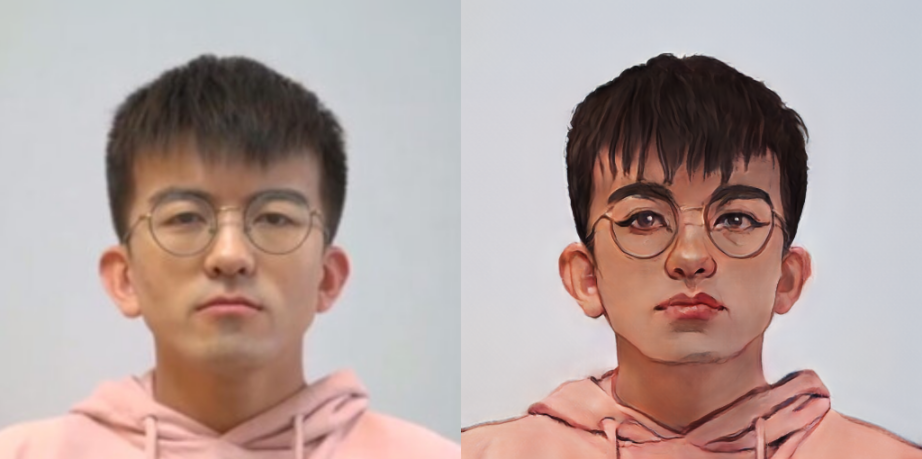

结果非常Amazing啊!
不过,由于原图分辨率不高,动漫化好像并不彻底,比如耳朵部分仍保留着三次元特征,和真正的二次元还有点距离。
资源获取
本项目的文件我已打包放在了我的微信公众号“我有一计”上,回复“动漫”即可获取。
文章来源: zstar.blog.csdn.net,作者:zstar-_,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:zstar.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121584740
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)