Java IO流系列⑤ -- 标准输入,输出流
【摘要】
目录
标准输入,输出流的概述输入输出流的练习
标准输入,输出流的概述
System有三个属性,其中有两个属性,一个为in,一个为out System.in和System.out分别代表了...
标准输入,输出流的概述
System有三个属性,其中有两个属性,一个为in,一个为out
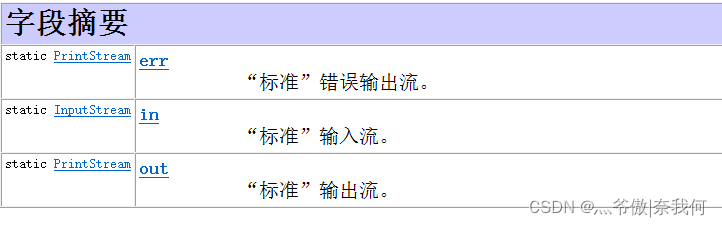
System.in和System.out分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备。默认输入设备是:键盘,输出设备是:显示器。
System.in的类型是InputStream(输入字节流)
System.out的类型是PrintStream(打印流),其是OutputStream的子类FilterOutputStream 的子类(输出字节流)
既然System.in和System.out作为两个属性,那么System类也为他们提供了set()方法,我们一般称为重定向:通过System类的setIn,setOut方法对默认设备进行改变。
- public static void setIn(InputStream in)
- public static void setOut(PrintStream out)
输入输出流的练习
从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。然后继续进行输入操作,
直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序。
方法一:使用Scanner实现,调用next()返回一个字符串
方法二:使用System.in实现。System.in ---> 转换流 ---> BufferedReader的readLine()
- 1
- 2
代码实现:
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
String data = br.readLine();
if ("e".equalsIgnoreCase(data) || "exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
System.out.println("程序结束");
break;
}
String upperCase = data.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(upperCase);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
注: 在单元测试中(@Test)是不能进行键盘的输入的在main方法中是可以的。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:十八岁讨厌编程,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/zyb18507175502/article/details/122491359
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)