MyBatis基础③
配置文件完成增删改查
条件查询
场景:

分析:
- 当前状态使用精准查询
- 企业名称使用模糊查询
- 品牌名称使用模糊查询
- 且他们同时成立,故使用and连接
sql语句设置多个参数

步骤详解:
①编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义多条件查询的方法。
而该功能有三个参数,我们就需要考虑定义接口时,参数应该如何定义。Mybatis针对多参数有多种实现
-
使用
@Param("参数名称")标记每一个参数,在映射配置文件中就需要使用#{参数名称}进行占位List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status") int status, @Param("companyName") String companyName,@Param("brandName") String brandName);- 1
-
将多个参数封装成一个 实体对象 ,将该实体对象作为接口的方法参数。该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和实体类属性名保持一致。List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);- 1
-
将多个参数封装到map集合中,将map集合作为接口的方法参数。该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和map集合中键的名称一致。List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);- 1
public interface BrandMapper {
List<Brand> selectAll();
Brand selectOne(int id);
List<Brand> multiConditionSelect(@Param("status")int status,@Param("companyName")String companyName,@Param("brandName")String brandName);
List<Brand> multiConditionSelect(Brand brand);
List<Brand> multiConditionSelect(Map map);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
②在sql映射文件中编写SQL语句
<select id="multiConditionSelect" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from
mybatis.tb_brand
where
status = #{status}
and company_name like #{companyName}
and brand_name like #{brandName};
</select>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
③编写测试方法
public class Try3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int status = 1;
String companyName = "%"+"华为"+"%";
String brandName = "%"+"华为"+"%";
//获取SqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; //此处填写相对于resources的路径
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//用SqlSessionFactory对象制造SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// //用SqlSession对象来执行sql语句
// List<User> users = sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll");
BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//使用注解传递多个参数
// List<Brand> brands = mapper.multiConditionSelect(status, companyName, brandName);
//使用对象传递多个参数
// Brand temp = new Brand();
// temp.setStatus(status);
// temp.setCompanyName(companyName);
// temp.setBrandName(brandName);
// List<Brand> brands = mapper.multiConditionSelect(temp);
//使用map传递多个参数
HashMap temp = new HashMap();
temp.put("status",status);
temp.put("companyName",companyName);
temp.put("brandName",brandName);
List<Brand> brands = mapper.multiConditionSelect(temp);
System.out.println(brands);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
注意这里的模糊查询两边加上%,但是这个%不能在映射文件中的#{}中去加,而是只能在传入形参之前对数据进行处理,再进行传入操作。
如上的程序有一个小bug,那就是如果用户没有填写所有的搜索条件,那么结果是查询不到的。
变量名对应关系梳理
当规则变量多起来之后,我们有时候就很容易搞混哪个变量应该叫什么名字,他应该跟什么对应。我们在这里进行一个简单的梳理。
①第一处对应关系:列名和类的属性名应该一样
只有这样我们才能保证MyBatis在封装我们的搜索结果时不会出现null值的情况。
②在接口中的方法引入了参数之后,我们规定了#{}(和${})。这个括号里面原则上可以写任何值,但是我们一般与属性名同名,这方便了我们后续的对应关系。
③后来我们接触到了传入多个参数,要使用上面提到过的三种方法。那么为什么要使用那三种方法呢?我们直接定义多个形参不就行了吗?我们可以思考一下如果这样的话,程序运行,数据传给形参,接口方法运行,进而跳转到sql映射文件中的sql操作,那些形参接收的值最终是要作用到这里来的。那么问题随之而来,程序怎么知道把接收到的值传到哪个#{}(或者${})中去呢?显然此时我们需要一种标记去为他们的值传递引路。而上述的三种方法就启到了引路人的作用。这样的话三种方法中的相关要求也就变得合情合理:
- 方法①:使用
@Param("参数名称")标记每一个参数,在映射配置文件中就需要使用#{参数名称}进行占位 - 方法②:该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和实体类属性名保持一致。 - 方法③:该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和map集合中键的名称一致。
多条件 - 动态条件查询
上述功能实现存在很大的问题。用户在输入条件时,肯定不会所有的条件都填写,这个时候我们的SQL语句就不能那样写的
例如用户只输入 当前状态 时,SQL语句就是
select * from tb_brand where status = #{status}
- 1
而用户如果只输入企业名称时,SQL语句就是
select * from tb_brand where company_name like #{companName}
- 1
而用户如果输入了 当前状态 和 企业名称 时,SQL语句又不一样
select * from tb_brand where status = #{status} and company_name like #{companName}
- 1
针对上述的需要,Mybatis对动态SQL有很强大的支撑:
if
choose (when, otherwise)
trim (where, set)
foreach
我们先学习 if 标签和 where 标签:
-
if 标签:条件判断
- test 属性:逻辑表达式
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap"> select * from tb_brand where <if test="status != null"> and status = #{status} </if> <if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "> and company_name like #{companyName} </if> <if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' "> and brand_name like #{brandName} </if> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
如上的这种SQL语句就会根据传递的参数值进行动态的拼接。如果此时status和companyName有值那么就会值拼接这两个条件。
注意if中的左值要跟#{}保持一致
执行结果如下:
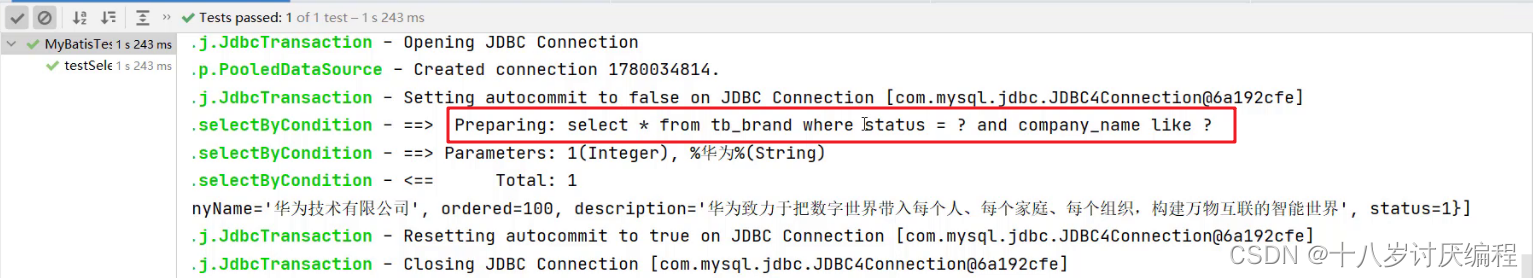
但是它也存在问题,如果此时给的参数值是
Map map = new HashMap();
// map.put("status" , status);
map.put("companyName", companyName);
map.put("brandName" , brandName);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
拼接的SQL语句就变成了
select * from tb_brand where and company_name like ? and brand_name like ?
- 1
而上面的语句中 where 关键后直接跟 and 关键字,这就是一条错误的SQL语句。这个就可以使用 where 标签解决
-
where 标签
- 作用:
- 替换where关键字
- 会动态的去掉第一个条件前的 and
- 如果所有的参数没有值则不加where关键字
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap"> select * from tb_brand <where> <if test="status != null"> and status = #{status} </if> <if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "> and company_name like #{companyName} </if> <if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' "> and brand_name like #{brandName} </if> </where> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
注意:需要给每个条件前都加上 and 关键字。
- 作用:
另外一种解决办法:在where后面加上一个恒等式
使用这个方法同样也要给每个条件前面加上and关键字
单条件 - 动态条件查询

如上图所示,在查询时只能选择 品牌名称、当前状态、企业名称 这三个条件中的一个,但是用户到底选择哪儿一个,我们并不能确定。这种就属于单个条件的动态SQL语句。
这种需求需要使用到 choose(when,otherwise)标签 实现, 而 choose 标签类似于Java 中的switch语句。
步骤:
①编写接口方法
List<Brand> selectByConditionSingle(Brand brand);
- 1
这个地方一般使用对象的方法来传递参数,因为你不知道用户会选择哪个参数。
② 编写SQL语句
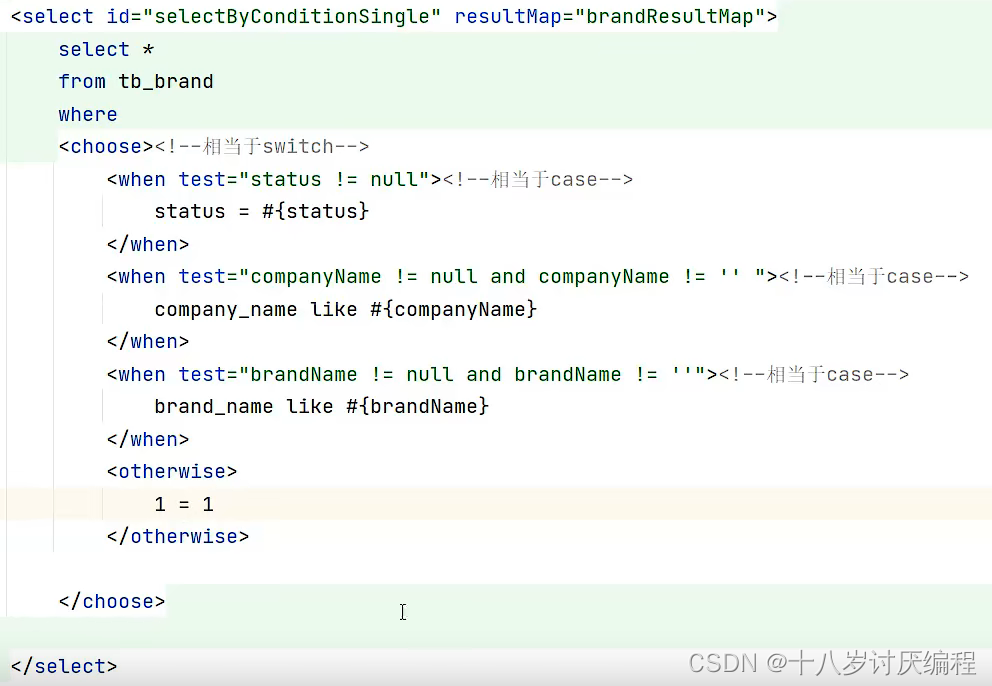
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<choose><!--相当于switch-->
<when test="status != null"><!--相当于case-->
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "><!--相当于case-->
company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''"><!--相当于case-->
brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
注意这个地方使用where是为了处理用户不进行选择就进行查询的情况。这种情况同样有第二种解决办法:恒等式
③测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectByConditionSingle() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "华为";
String brandName = "华为";
// 处理参数
companyName = "%" + companyName + "%";
brandName = "%" + brandName + "%";
//封装对象
Brand brand = new Brand();
//brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
//brand.setBrandName(brandName);
//1. 获取SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4. 执行方法
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByConditionSingle(brand);
System.out.println(brands);
//5. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:十八岁讨厌编程,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/zyb18507175502/article/details/124475415
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者





评论(0)