Request②
Request请求参数中文乱码问题
POST请求解决办法
- 分析出现中文乱码的原因:
- POST的请求参数是通过request的getReader()来获取流中的数据
- TOMCAT在获取流的时候采用的编码是ISO-8859-1
- ISO-8859-1编码是不支持中文的,所以会出现乱码
乱码问题一般都是编码与解码所使用的字符集不一样造成的
- 解决方案:
- 页面设置的编码格式为UTF-8
- 把TOMCAT在获取流数据之前的编码设置为UTF-8(页面是按照UTF-8的方式编的码,那么我们也应该通过UTF-8的方式去解码)
- 通过request.setCharacterEncoding(“UTF-8”)设置编码,UTF-8也可以写成小写
解决代码:
/**
* 中文乱码问题解决方案
*/
@WebServlet("/req4")
public class RequestDemo4 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. 解决乱码: POST getReader()
//设置字符输入流的编码,设置的字符集要和页面保持一致
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//2. 获取username
String username = request.getParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
GET请求解决办法
首先我们要明确一点POST请求解决乱码的办法与GET请求是不一样的。因为:
- GET请求获取请求参数的方式是
request.getQueryString() - POST请求获取请求参数的方式是
request.getReader() - request.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”)是设置request处理流的编码
- getQueryString方法并没有通过流的方式获取数据
GET请求出现乱码的原因:
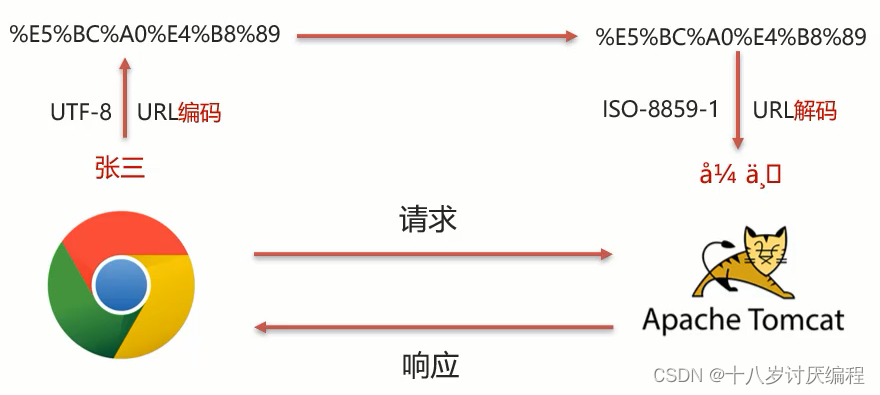
(1)浏览器通过HTTP协议发送请求和数据给后台服务器(Tomcat)
(2)浏览器在发送HTTP的过程中会对中文数据进行URL编码
(3)在进行URL编码的时候会采用页面<meta>标签指定的UTF-8的方式进行编码,张三编码后的结果为%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89
(4)后台服务器(Tomcat)接收到%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89后会默认按照ISO-8859-1进行URL解码
(5)由于前后编码与解码采用的格式不一样,就会导致后台获取到的数据为乱码。
首先我们先来了解一下URL编码:
具体编码过程分两步,分别是:
(1)将字符串按照编码方式转为二进制
(2)每个字节转为2个16进制数并在前边加上%
张三按照UTF-8的方式(也就是说每一个字用三个字节表示,张三有两个字,总共用六个字节来表示,也就是48位。每个字节又占8位,每四位可以用十六进制来表示)转换成二进制的结果为:
1110 0101 1011 1100 1010 0000 1110 0100 1011 1000 1000 1001
- 1
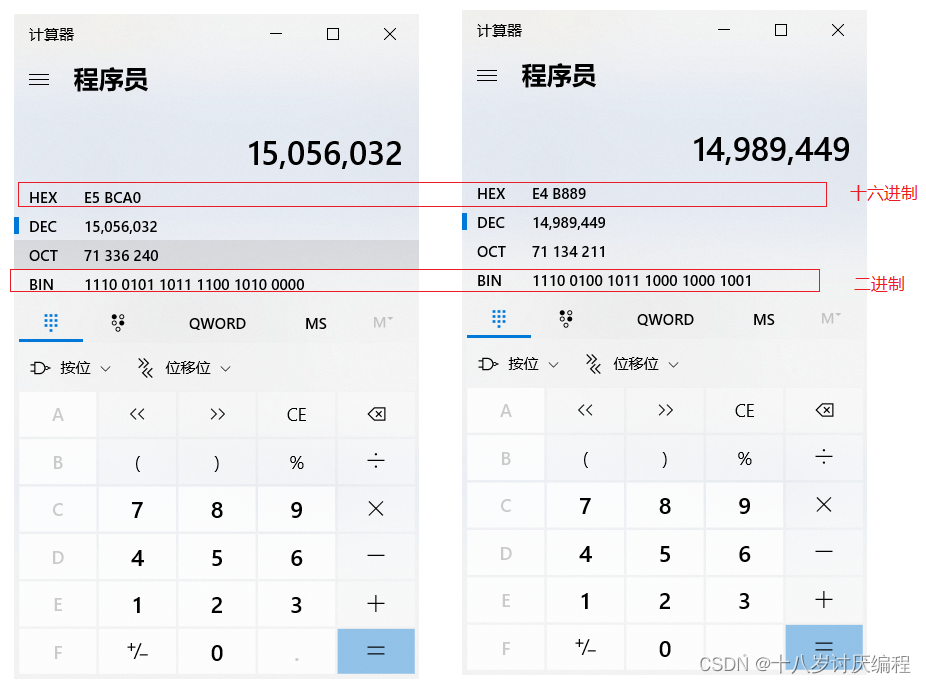
由此可知张三对应的URL编码即为%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89。
我们可以用Java自带的解码编码工具类来进行实验:
编码:
java.net.URLEncoder.encode("需要被编码的内容","字符集(UTF-8)")
- 1
解码:
java.net.URLDecoder.decode("需要被解码的内容","字符集(UTF-8)")
- 1
接下来咱们对张三来进行编码和解码
public class URLDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String username = "张三";
//1. URL编码
String encode = URLEncoder.encode(username, "utf-8");
System.out.println(encode); //打印:%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89
//2. URL解码
//String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode, "utf-8");//打印:张三
String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode, "ISO-8859-1");//打印:`å¼ ä¸ `
System.out.println(decode);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
到这里我们应该就知道乱码产生的原因了。那么我们如何解决呢?核心思想就是:利用乱码字节与我们想要的结果的字节是一样的特点,我们对乱码进行再解码编码的过程。
- 在进行编码和解码的时候,不管使用的是哪个字符集,他们对应的
%E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89是一致的- 那他们对应的二进制值也是一样的,为:
1110 0101 1011 1100 1010 0000 1110 0100 1011 1000 1000 1001
- 1
- 所以我们可以考虑把
å¼ ä¸‰转换成字节,在把字节转换成张三,在转换的过程中是它们的编码一致,就可以解决中文乱码问题。
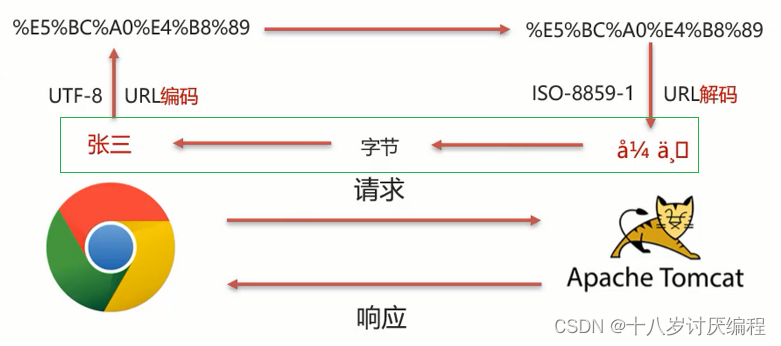
解决办法实现步骤:
-
按照ISO-8859-1编码获取乱码
å¼ ä¸‰对应的字节数组 -
按照UTF-8编码获取字节数组对应的字符串
解决代码:
public class URLDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String username = "张三";
//1. URL编码
String encode = URLEncoder.encode(username, "utf-8");
System.out.println(encode);
//2. URL解码
String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode, "ISO-8859-1");
System.out.println(decode); //此处打印的是对应的乱码数据
//3. 转换为字节数据,编码
byte[] bytes = decode.getBytes("ISO-8859-1");
for (byte b : bytes) {
System.out.print(b + " ");
}
//此处打印的是:-27 -68 -96 -28 -72 -119
//4. 将字节数组转为字符串,解码
String s = new String(bytes, "utf-8");
System.out.println(s); //此处打印的是张三
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
说明:在第18行中打印的数据是
-27 -68 -96 -28 -72 -119和张三转换成的二进制数据1110 0101 1011 1100 1010 0000 1110 0100 1011 1000 1000 1001不一样是因为打印出来的是十进制数据,换算一下其实是一样的。
最终我们简化一下过程:
/**
* 中文乱码问题解决方案
*/
@WebServlet("/req4")
public class RequestDemo4 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. 解决乱码:POST,getReader()
//request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");//设置字符输入流的编码
//2. 获取username
String username = request.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("解决乱码前:"+username);
//3. GET,获取参数的方式:getQueryString
// 乱码原因:tomcat进行URL解码,默认的字符集ISO-8859-1
/* //3.1 先对乱码数据进行编码:转为字节数组
byte[] bytes = username.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
//3.2 字节数组解码
username = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);*/
username = new String(username.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1),StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("解决乱码后:"+username);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
注意:这种办法也可以解决POST请求的情况,只不过对于POST请求参数一般都会比较多,采用这种方式解决乱码起来比较麻烦,所以对于POST请求还是建议使用设置编码的方式进行。
Tomcat8.0之后,已将GET请求乱码问题解决,设置默认的解码方式为UTF-8
Request请求转发
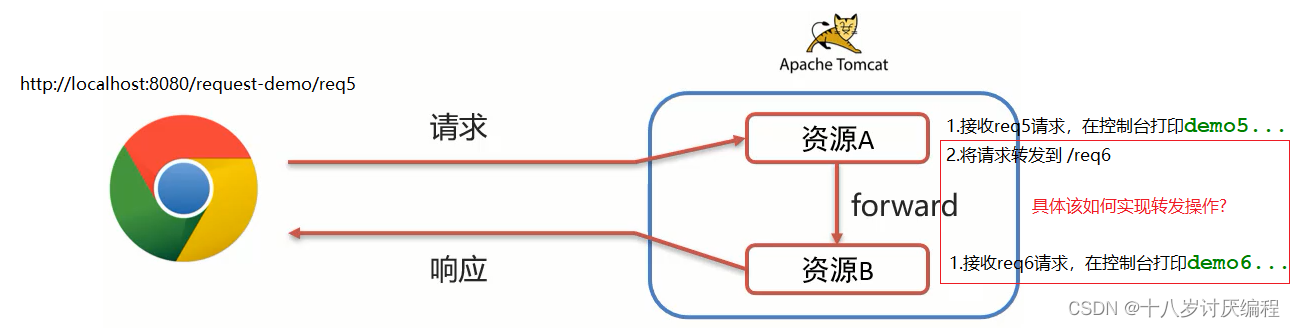
请求转发(forward):一种在服务器内部的资源跳转方式。
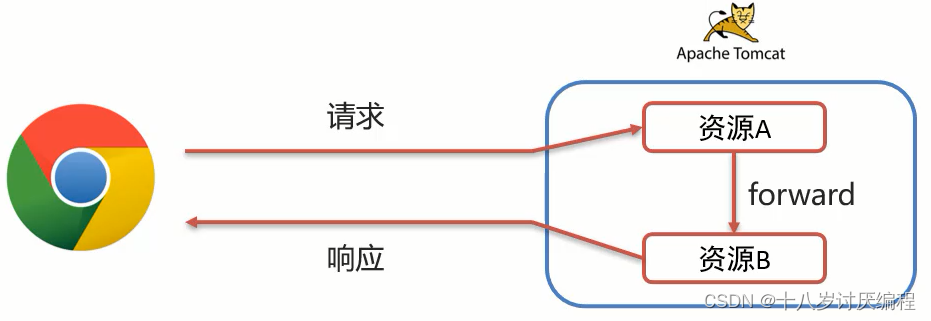
实现过程:
(1)浏览器发送请求给服务器,服务器中对应的资源A接收到请求
(2)资源A处理完请求后将请求发给资源B
(3)资源B处理完后将结果响应给浏览器
(4)请求从资源A到资源B的过程就叫请求转发
请求转发的实现方式:
req.getRequestDispatcher("资源B路径").forward(req,resp);
- 1
我们可以通过一个例子来看看如何使用:
(1)创建RequestDemo5类
/**
* 请求转发
*/
@WebServlet("/req5")
public class RequestDemo5 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("demo5...");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
(2)创建RequestDemo6类
/**
* 请求转发
*/
@WebServlet("/req6")
public class RequestDemo6 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("demo6...");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
(3)在RequestDemo5的doGet方法中进行请求转发
/**
* 请求转发
*/
@WebServlet("/req5")
public class RequestDemo5 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("demo5...");
//请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/req6").forward(request,response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
(4)启动测试
访问http://localhost:8080/request-demo/req5,就可以在控制台看到如下内容:
demo5...
demo6...
- 1
- 2
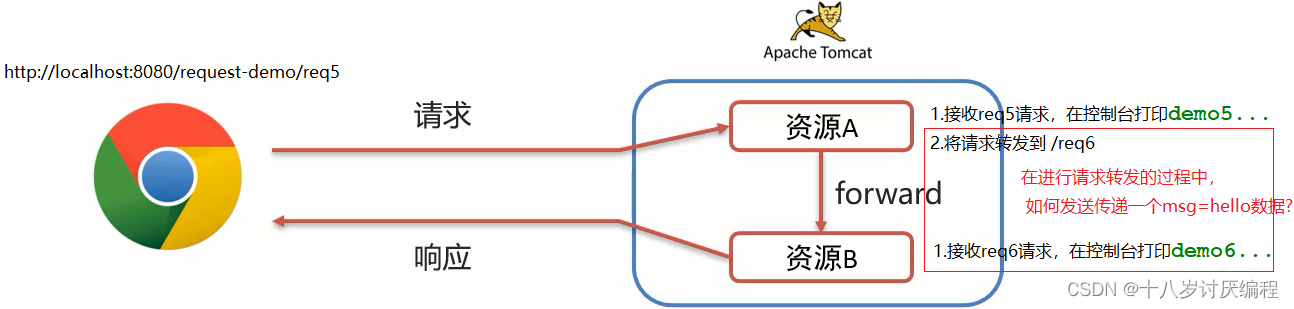
请求转发之间共享数据
方法:借助于Request对象
需要使用request对象提供的三个方法:
- 存储数据到request域[范围,数据是存储在request对象]中
void setAttribute(String name,Object o);
- 1
- 根据key获取值
Object getAttribute(String name);
- 1
- 根据key删除该键值对
void removeAttribute(String name);
- 1
我们可以使用上面的例子进行一次实验:
(1)修改RequestDemo5中的方法
@WebServlet("/req5")
public class RequestDemo5 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("demo5...");
//存储数据
request.setAttribute("msg","hello");
//请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/req6").forward(request,response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
(2)修改RequestDemo6中的方法
/**
* 请求转发
*/
@WebServlet("/req6")
public class RequestDemo6 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("demo6...");
//获取数据
Object msg = request.getAttribute("msg");
System.out.println(msg);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
(3)启动测试
访问http://localhost:8080/request-demo/req5,就可以在控制台看到如下内容:
demo5...
deno6...
hello
- 1
- 2
- 3
此时就可以实现在转发多个资源之间共享数据。
请求转发的特点
-
浏览器地址栏路径不发生变化
虽然后台从
/req5转发到/req6,但是浏览器的地址一直是/req5,未发生变化
-
只能转发到当前服务器的内部资源
不能从一个服务器通过转发访问另一台服务器
-
一次请求,可以在转发资源间使用request共享数据
虽然后台从
/req5转发到/req6,但是这个只有一次请求
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:十八岁讨厌编程,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/zyb18507175502/article/details/124861671
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)