[Spring Framework]AOP配置管理②(AOP通知类型)
通知类型概述
我们前面的案例中,出现过:

@Before,这个就属于通知类型。
它所代表的含义是将通知添加到切入点方法执行的前面。
那么我们很自然地就想到,有没有可以添加到其他位置的?
我们先来回顾下AOP通知:
- AOP通知描述了抽取的共性功能,根据共性功能抽取的位置不同,最终运行代码时要将其加入到合理的位置
通知具体要添加到切入点的哪里?
共提供了5种通知类型:
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知(重点)
- 返回后通知(了解)
- 抛出异常后通知(了解)
为了更好的理解这几种通知类型,我们来看一张图:
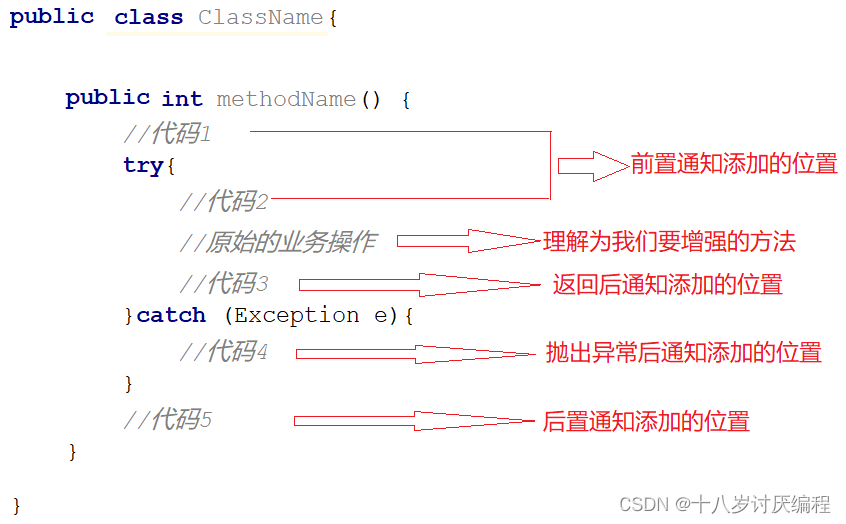
-
前置通知,追加功能到方法执行前,类似于在代码1或者代码2添加内容 -
后置通知,追加功能到方法执行后,不管方法执行的过程中有没有抛出异常都会执行,类似于在代码5添加内容 -
返回后通知,追加功能到方法执行后,只有方法正常执行结束后才进行,类似于在代码3添加内容,如果方法执行抛出异常,返回后通知将不会被添加 -
抛出异常后通知,追加功能到方法抛出异常后,只有方法执行出异常才进行,类似于在代码4添加内容,只有方法抛出异常后才会被添加 -
环绕通知,环绕通知功能比较强大,它可以追加功能到方法执行的前后,这也是比较常用的方式,它可以实现其他四种通知类型的功能
接下来我们一个个地去使用他们
通知类型的使用
项目环境介绍
通知类:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice1 {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
public void pt(){}
public void before() {
System.out.println("before advice ...");
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("after advice ...");
}
public void around(){
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
}
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning advice ...");
}
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
然后我们的测试demo:
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
bookDao.update();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
前置通知
修改MyAdvice,在before方法上添加@Before注解
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
//此处也可以写成 @Before("MyAdvice.pt()"),不建议
public void before() {
System.out.println("before advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
结果:
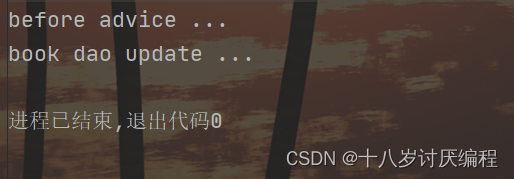
后置通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before advice ...");
}
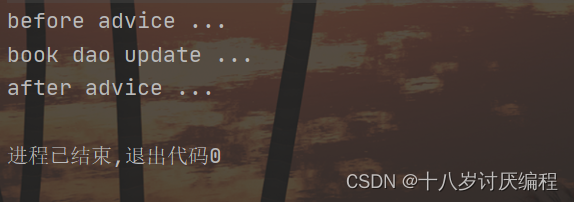
@After("pt()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
环绕通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public void around(){
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
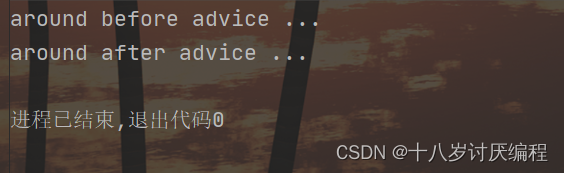
运行结果中,通知的内容打印出来,但是原始方法的内容却没有被执行。
因为环绕通知需要在原始方法的前后进行增强,所以环绕通知就必须要能对原始操作进行调用,具体如何实现?
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Around("pt()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
//表示对原始操作的调用
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
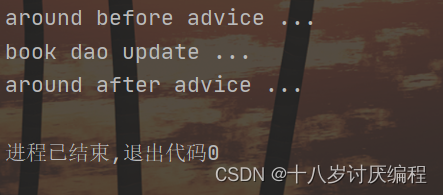
说明:proceed()为什么要抛出异常?
原因很简单,看下源码就知道了:

再次运行,程序可以看到原始方法已经被执行了:
注意事项
(1)原始方法有返回值的处理
- 修改MyAdvice,对BookDao中的select方法添加环绕通知,
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.select())")
private void pt2(){}
@Around("pt2()")
public void aroundSelect(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
//表示对原始操作的调用
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 修改App类,调用select方法
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
int num = bookDao.select();
System.out.println(num);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
运行后会报错,错误内容为:
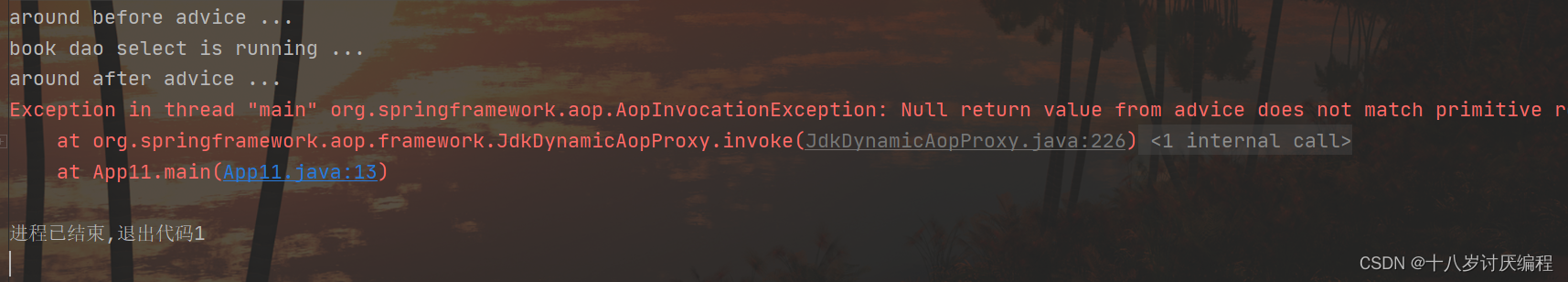
错误大概的意思是:空的返回不匹配原始方法的int返回
- void就是返回Null
- 原始方法就是BookDao下的select方法
所以如果我们使用环绕通知的话,要根据原始方法的返回值来设置环绕通知的返回值,具体解决方案为:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Pointcut("execution(int impl.BookDaoImpl4.select())")
private void pt2(){}
@Around("pt2()")
public Object aroundSelect(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before advice ...");
//表示对原始操作的调用
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("around after advice ...");
return ret;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
说明:
- 为什么返回的是Object而不是int的主要原因是Object类型更通用。
- 在环绕通知中是可以对原始方法返回值就行修改的。
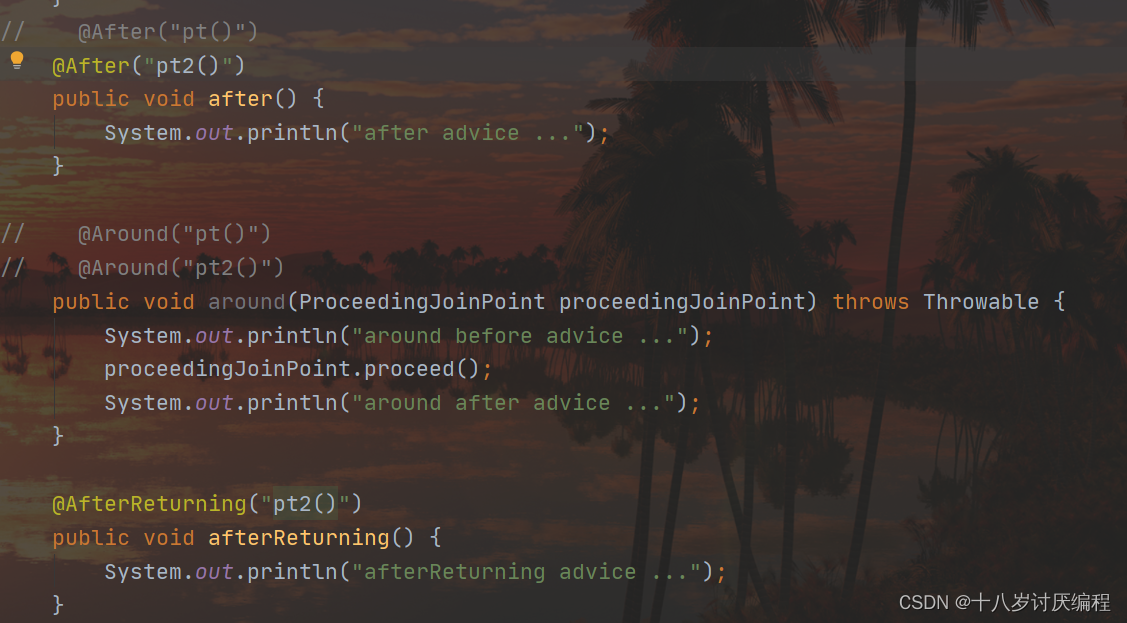
返回后通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Pointcut("execution(int impl.BookDaoImpl4.select())")
private void pt2(){}
@AfterReturning("pt2()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

注意:返回后通知是需要在原始方法
select正常执行后才会被执行,如果select()方法执行的过程中出现了异常,那么返回后通知是不会被执行。后置通知是不管原始方法有没有抛出异常都会被执行
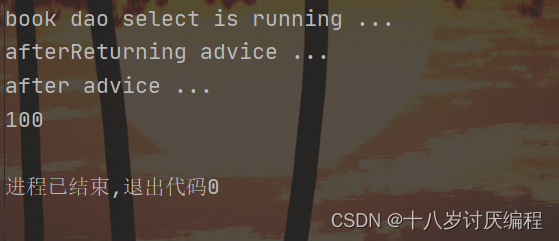
我们可以试验一下:
结果:
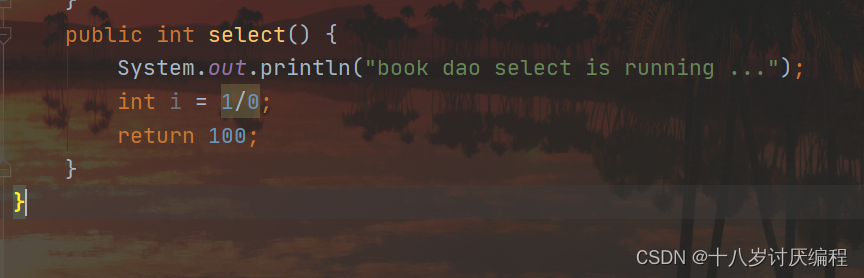
然后我们在select中添加一个错误:
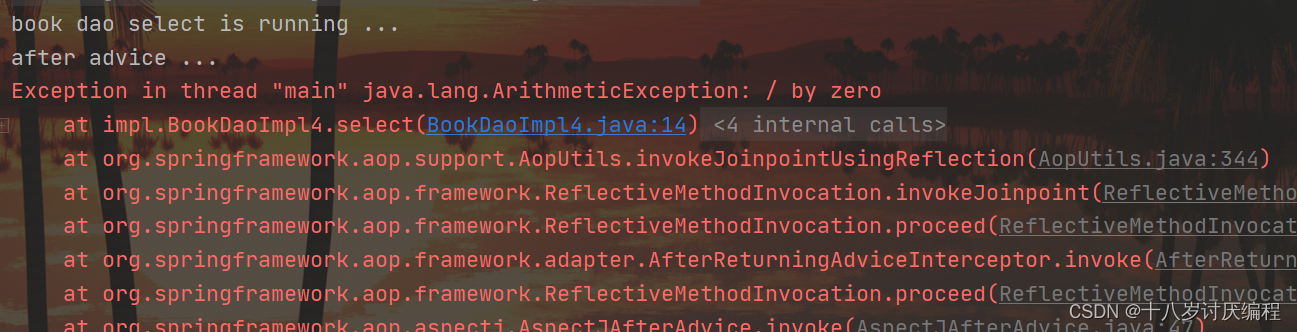
再运行:
异常后通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void impl.BookDaoImpl4.update())")
private void pt(){}
@Pointcut("execution(int impl.BookDaoImpl4.select())")
private void pt2(){}
@AfterReturning("pt2()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing advice ...");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
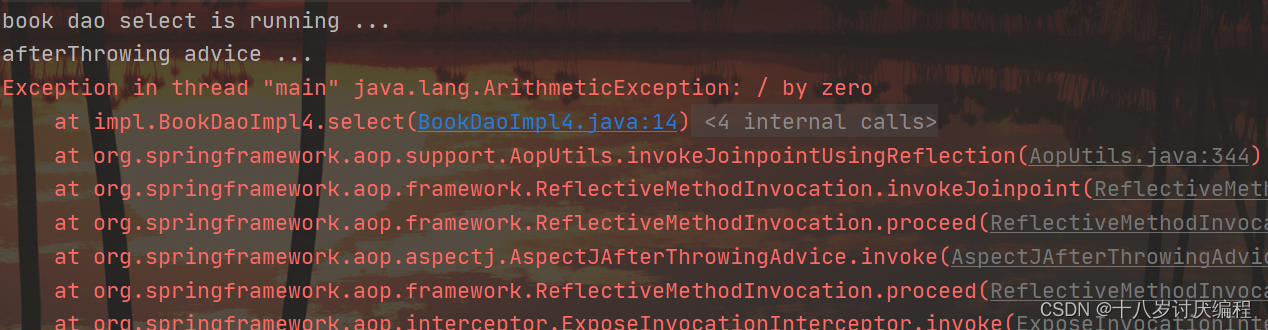
注意:异常后通知是需要原始方法抛出异常,可以在select()方法中添加一行代码int i = 1/0即可。如果没有抛异常,异常后通知将不会被执行。
学习完这5种通知类型,我们来思考下环绕通知是如何实现其他通知类型的功能的?
因为环绕通知是可以控制原始方法执行的,所以我们把增强的代码写在调用原始方法的不同位置就可以实现不同的通知类型的功能,如:

通知类型总结
知识点1:@After
| 名称 | @After |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 通知方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前通知方法与切入点之间的绑定关系,当前通知方法在原始切入点方法后运行 |
知识点2:@AfterReturning
| 名称 | @AfterReturning |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 通知方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前通知方法与切入点之间绑定关系,当前通知方法在原始切入点方法正常执行完毕后执行 |
知识点3:@AfterThrowing
| 名称 | @AfterThrowing |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 通知方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前通知方法与切入点之间绑定关系,当前通知方法在原始切入点方法运行抛出异常后执行 |
知识点4:@Around
| 名称 | @Around |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 通知方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前通知方法与切入点之间的绑定关系,当前通知方法在原始切入点方法前后运行 |
通知类型注意事项
环绕通知注意事项
- 环绕通知必须依赖形参ProceedingJoinPoint才能实现对原始方法的调用,进而实现原始方法调用前后同时添加通知
- 通知中如果未使用ProceedingJoinPoint对原始方法进行调用将跳过原始方法的执行
- 对原始方法的调用可以不接收返回值,通知方法设置成void即可,如果接收返回值,最好设定为Object类型
- 原始方法的返回值如果是void类型,通知方法的返回值类型可以设置成void,也可以设置成Object
- 由于无法预知原始方法运行后是否会抛出异常,因此环绕通知方法必须要处理Throwable异常
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:十八岁讨厌编程,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/zyb18507175502/article/details/125822075
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)