[Spring Framework]AOP经典案例、AOP总结
案例①:业务层接口执行效率
需求分析
这个需求也比较简单,前面我们在介绍AOP的时候已经演示过:
- 需求:任意业务层接口执行均可显示其执行效率(执行时长)
这个案例的目的是查看每个业务层执行的时间,这样就可以监控出哪个业务比较耗时,将其查找出来方便优化。
具体实现的思路:
(1) 开始执行方法之前记录一个时间
(2) 执行方法
(3) 执行完方法之后记录一个时间
(4) 用后一个时间减去前一个时间的差值,就是我们需要的结果。
所以要在方法执行的前后添加业务,经过分析我们将采用环绕通知。
说明:原始方法如果只执行一次,时间太快,两个时间差可能为0,所以我们要执行万次来计算时间差。
环境准备
-
创建一个Maven项目
-
pom.xml添加Spring依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.47</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>1.3.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
-
添加AccountService、AccountServiceImpl、AccountDao与Account类
public interface AccountService { void save(Account account); void delete(Integer id); void update(Account account); List<Account> findAll(); Account findById(Integer id); } @Service public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; public void save(Account account) { accountDao.save(account); } public void update(Account account){ accountDao.update(account); } public void delete(Integer id) { accountDao.delete(id); } public Account findById(Integer id) { return accountDao.findById(id); } public List<Account> findAll() { return accountDao.findAll(); } } public interface AccountDao { @Insert("insert into tbl_account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})") void save(Account account); @Delete("delete from tbl_account where id = #{id} ") void delete(Integer id); @Update("update tbl_account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ") void update(Account account); @Select("select * from tbl_account") List<Account> findAll(); @Select("select * from tbl_account where id = #{id} ") Account findById(Integer id); } public class Account implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Double money; //setter..getter..toString方法省略 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
-
resources下提供一个jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db?useSSL=false jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
创建相关配置类
//Spring配置类:SpringConfig @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima") @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") @Import({JdbcConfig.class,MybatisConfig.class}) public class SpringConfig { } //JdbcConfig配置类 public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String userName; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(userName); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; } } //MybatisConfig配置类 public class MybatisConfig { @Bean public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource){ SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.itheima.domain"); ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource); return ssfb; } @Bean public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer(){ MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer(); msc.setBasePackage("com.itheima.dao"); return msc; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
-
编写Spring整合Junit的测试类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class) public class AccountServiceTestCase { @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Test public void testFindById(){ Account ac = accountService.findById(2); } @Test public void testFindAll(){ List<Account> all = accountService.findAll(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
最终创建好的项目结构如下:
实现步骤
步骤1:开启SpringAOP的注解功能
在Spring的主配置文件SpringConfig类中添加注解
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
- 1
步骤2:创建AOP的通知类
-
该类要被Spring管理,需要添加@Component
-
要标识该类是一个AOP的切面类,需要添加@Aspect
-
配置切入点表达式,需要添加一个方法,并添加@Pointcut
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//配置业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt(){}
public void runSpeed(){
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
步骤3:添加环绕通知
在runSpeed()方法上添加@Around
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//配置业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt(){}
//@Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()") 可以简写为下面的方式
@Around("servicePt()")
public Object runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
return ret;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
注意:目前并没有做任何增强
步骤4:完成核心业务,记录万次执行的时间
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//配置业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt(){}
//@Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()") 可以简写为下面的方式
@Around("servicePt()")
public void runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pjp.proceed();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("业务层接口万次执行时间: "+(end-start)+"ms");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
步骤5:运行单元测试类
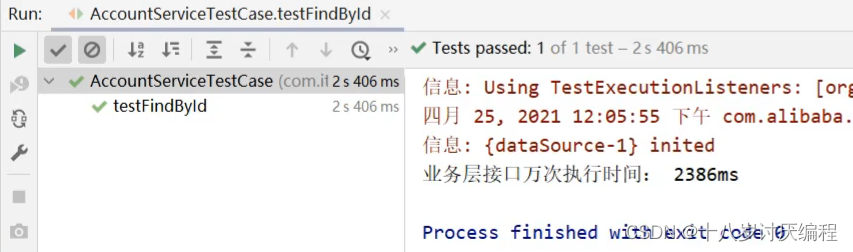
**注意:**因为程序每次执行的时长是不一样的,所以运行多次最终的结果是不一样的。
步骤6:程序优化
目前程序所面临的问题是,多个方法一起执行测试的时候,控制台都打印的是:
业务层接口万次执行时间:xxxms
我们没有办法区分到底是哪个接口的哪个方法执行的具体时间,具体如何优化?
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//配置业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt(){}
//@Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()") 可以简写为下面的方式
@Around("servicePt()")
public void runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
//获取执行签名信息
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
//通过签名获取执行操作名称(接口名)
String className = signature.getDeclaringTypeName();
//通过签名获取执行操作名称(方法名)
String methodName = signature.getName();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pjp.proceed();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("万次执行:"+ className+"."+methodName+"---->" +(end-start) + "ms");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
步骤7:运行单元测试类
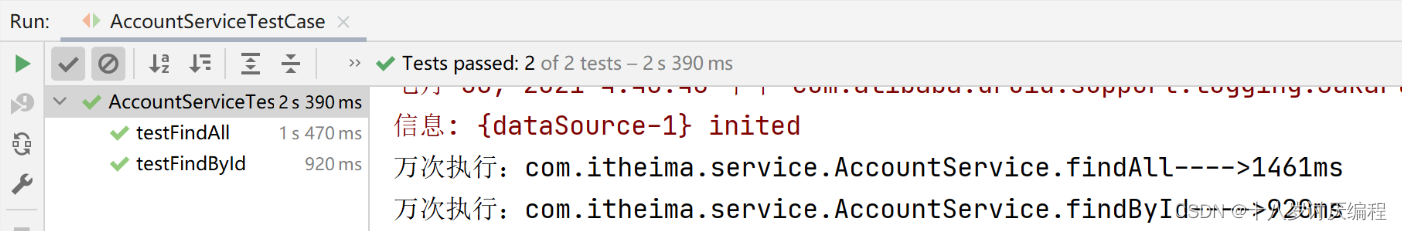
补充说明
当前测试的接口执行效率仅仅是一个理论值,并不是一次完整的执行过程。
这块只是通过该案例把AOP的使用进行了学习,具体的实际值是有很多因素共同决定的。
案例②:百度网盘密码数据兼容处理
需求分析
问题描述:
-
当我们从别人发给我们的内容中复制提取码的时候,有时候会多复制到一些空格,直接粘贴到百度的提取码输入框
-
但是百度那边记录的提取码是没有空格的
-
这个时候如果不做处理,直接对比的话,就会引发提取码不一致,导致无法访问百度盘上的内容
-
所以多输入一个空格可能会导致项目的功能无法正常使用。
-
此时我们就想能不能将输入的参数先帮用户去掉空格再操作呢?
答案是可以的,我们只需要在业务方法执行之前对所有的输入参数进行格式处理——trim()
- 是对所有的参数都需要去除空格么?
也没有必要,一般只需要针对字符串处理即可。
- 以后涉及到需要去除前后空格的业务可能会有很多,这个去空格的代码是每个业务都写么?
可以考虑使用AOP来统一处理。
- AOP有五种通知类型,该使用哪种呢?
我们的需求是将原始方法的参数处理后在参与原始方法的调用,能做这件事的就只有环绕通知。
综上所述,我们需要考虑两件事:
①:在业务方法执行之前对所有的输入参数进行格式处理——trim()
②:使用处理后的参数调用原始方法——环绕通知中存在对原始方法的调用
环境准备
-
创建一个Maven项目
-
pom.xml添加Spring依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.4</version> </dependency> </dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
-
添加ResourcesService,ResourcesServiceImpl,ResourcesDao和ResourcesDaoImpl类
public interface ResourcesDao { boolean readResources(String url, String password); } @Repository public class ResourcesDaoImpl implements ResourcesDao { public boolean readResources(String url, String password) { //模拟校验 return password.equals("root"); } } public interface ResourcesService { public boolean openURL(String url ,String password); } @Service public class ResourcesServiceImpl implements ResourcesService { @Autowired private ResourcesDao resourcesDao; public boolean openURL(String url, String password) { return resourcesDao.readResources(url,password); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-
创建Spring的配置类
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima") public class SpringConfig { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
编写App运行类
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); ResourcesService resourcesService = ctx.getBean(ResourcesService.class); boolean flag = resourcesService.openURL("http://pan.baidu.com/haha", "root"); System.out.println(flag); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
最终创建好的项目结构如下:
现在项目的效果是,当输入密码为"root"控制台打印为true,如果密码改为"root "控制台打印的是false
需求是使用AOP将参数进行统一处理,不管输入的密码root前后包含多少个空格,最终控制台打印的都是true。
实现步骤
步骤1:开启SpringAOP的注解功能
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
步骤2:编写通知类
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.itheima.service.*Service.*(*,*))")
private void servicePt(){}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
步骤3:添加环绕通知
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.itheima.service.*Service.*(*,*))")
private void servicePt(){}
@Around("DataAdvice.servicePt()")
// @Around("servicePt()")这两种写法都对
public Object trimStr(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
return ret;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
步骤4:完成核心业务,处理参数中的空格
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.itheima.service.*Service.*(*,*))")
private void servicePt(){}
@Around("DataAdvice.servicePt()")
// @Around("servicePt()")这两种写法都对
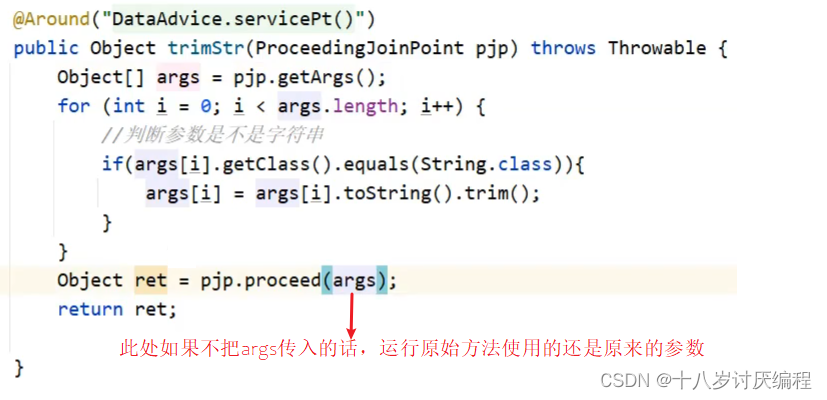
public Object trimStr(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//获取原始方法的参数
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
//判断参数是不是字符串
if(args[i].getClass().equals(String.class)){
args[i] = args[i].toString().trim();
}
}
//将修改后的参数传入到原始方法的执行中
Object ret = pjp.proceed(args);
return ret;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
步骤5:运行程序
不管密码root前后是否加空格,最终控制台打印的都是true
步骤6:优化测试
为了能更好的看出AOP已经生效,我们可以修改ResourcesImpl类,在方法中将密码的长度进行打印
@Repository
public class ResourcesDaoImpl implements ResourcesDao {
public boolean readResources(String url, String password) {
System.out.println(password.length());
//模拟校验
return password.equals("root");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
再次运行成功,就可以根据最终打印的长度来看看,字符串的空格有没有被去除掉。
注意:
AOP总结
AOP的核心概念
- 概念:AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,一种编程范式
- 作用:在不惊动原始设计的基础上为方法进行功能增强
- 核心概念
- 代理(Proxy):SpringAOP的核心本质是采用代理模式实现的
- 连接点(JoinPoint):在SpringAOP中,理解为任意方法的执行
- 切入点(Pointcut):匹配连接点的式子,也是具有共性功能的方法描述
- 通知(Advice):若干个方法的共性功能,在切入点处执行,最终体现为一个方法
- 切面(Aspect):描述通知与切入点的对应关系
- 目标对象(Target):被代理的原始对象成为目标对象
切入点表达式
-
切入点表达式标准格式:动作关键字(访问修饰符 返回值 包名.类/接口名.方法名(参数)异常名)
execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))- 1
-
切入点表达式描述通配符:
- 作用:用于快速描述,范围描述
*:匹配任意符号(常用)..:匹配多个连续的任意符号(常用)+:匹配子类类型
-
切入点表达式书写技巧
1.按标准规范开发
2.查询操作的返回值建议使用*匹配
3.减少使用…的形式描述包
4.对接口进行描述,使用*表示模块名,例如UserService的匹配描述为*Service
5.方法名书写保留动词,例如get,使用*表示名词,例如getById匹配描述为getBy*
6.参数根据实际情况灵活调整
五种通知类型
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知(重点)
- 环绕通知依赖形参ProceedingJoinPoint才能实现对原始方法的调用
- 环绕通知可以隔离原始方法的调用执行
- 环绕通知返回值设置为Object类型
- 环绕通知中可以对原始方法调用过程中出现的异常进行处理
- 返回后通知
- 抛出异常后通知
通知中获取参数
- 获取切入点方法的参数,所有的通知类型都可以获取参数
- JoinPoint:适用于前置、后置、返回后、抛出异常后通知
- ProceedingJoinPoint:适用于环绕通知
- 获取切入点方法返回值,前置和抛出异常后通知是没有返回值,后置通知可有可无,所以不做研究
- 返回后通知
- 环绕通知
- 获取切入点方法运行异常信息,前置和返回后通知是不会有,后置通知可有可无,所以不做研究
- 抛出异常后通知
- 环绕通知
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:十八岁讨厌编程,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/zyb18507175502/article/details/125831057
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)