[SpringBoot]配置文件①(配置文件格式、yaml配置及读取)
配置文件格式
我们现在启动服务器默认的端口号是 8080,访问路径可以书写为
http://localhost:8080/books/1
- 1
在线上环境我们还是希望将端口号改为 80,这样在访问的时候就可以不写端口号了,如下
http://localhost/books/1
- 1
而 SpringBoot 程序如何修改呢?SpringBoot 提供了多种属性配置方式
-
application.propertiesserver.port=80- 1
-
application.ymlserver: port: 81- 1
- 2
-
application.yamlserver: port: 82- 1
- 2
注意:
SpringBoot程序的配置文件名必须是application,只是后缀名不同而已。
环境准备
创建一个新工程 springboot_02_base_config 用来演示不同的配置文件,工程环境和入门案例一模一样,结构如下:

在该工程中的 com.itheima.controller 包下创建一个名为 BookController 的控制器。内容如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("id ==> "+id);
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
不同配置文件演示
- application.properties配置文件
现在需要进行配置,配合文件必须放在 resources 目录下,而该目录下有一个名为 application.properties 的配置文件,我们就可以在该配置文件中修改端口号,在该配置文件中书写 port ,Idea 就会提示,如下
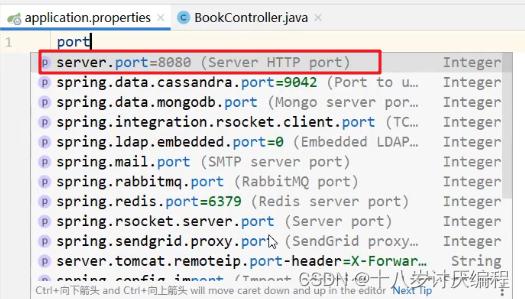
application.properties 配置文件内容如下:
server.port=80
- 1
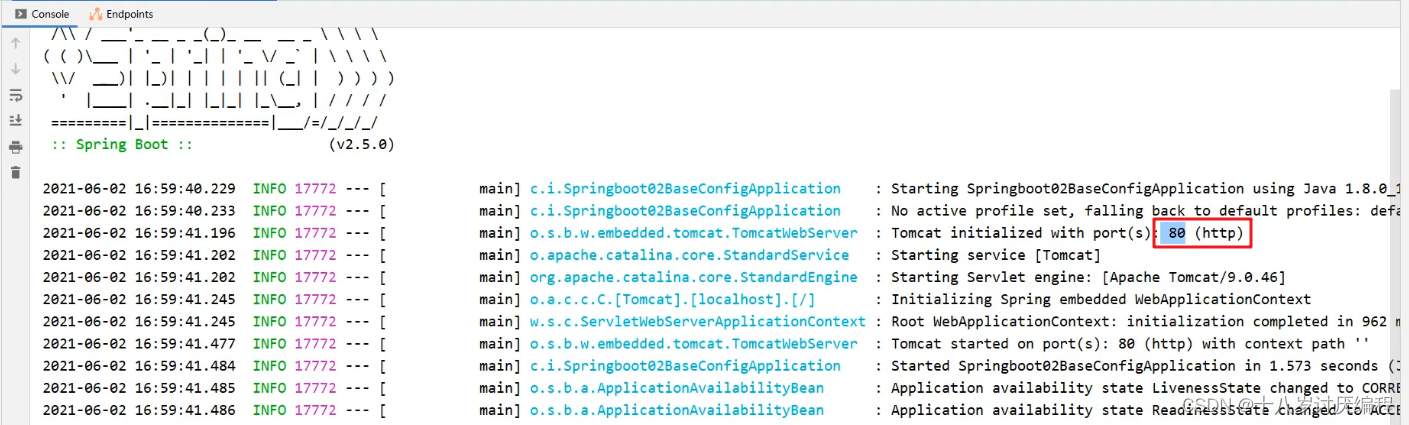
启动服务,会在控制台打印出日志信息,从日志信息中可以看到绑定的端口号已经修改了
- application.yml配置文件
删除 application.properties 配置文件中的内容。在 resources 下创建一个名为 application.yml 的配置文件,在该文件中书写端口号的配置项,格式如下:
server:
port: 81
- 1
- 2
注意: 在
:后,数据前一定要加空格。
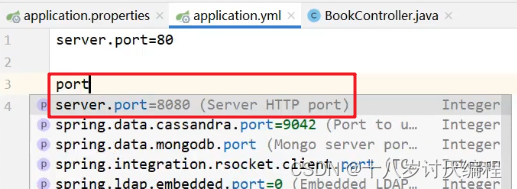
而在 yml 配置文件中也是有提示功能的,我们也可以在该文件中书写 port ,然后 idea 就会提示并书写成上面的格式
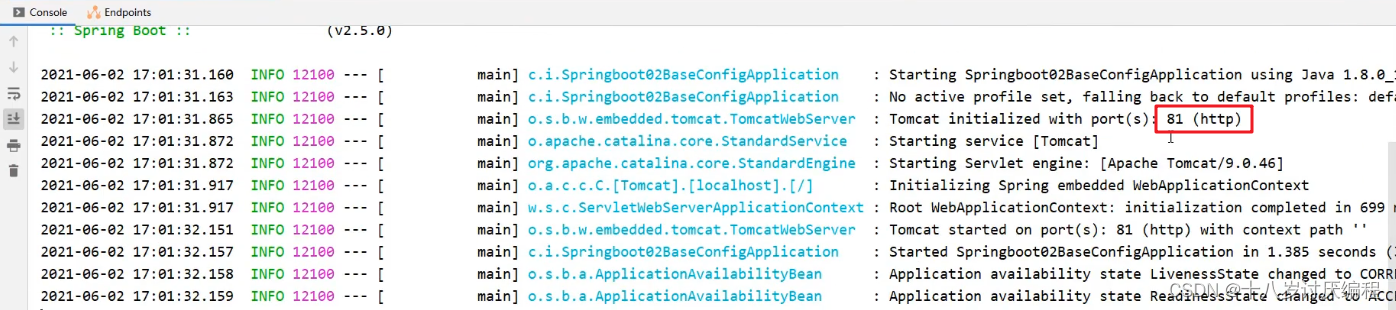
启动服务,可以在控制台看到绑定的端口号是 81
- application.yaml配置文件
删除 application.yml 配置文件和 application.properties 配置文件内容,然后在 resources 下创建名为 application.yaml 的配置文件,配置内容和后缀名为 yml 的配置文件中的内容相同,只是使用了不同的后缀名而已
application.yaml 配置文件内容如下:
server:
port: 83
- 1
- 2
启动服务,在控制台可以看到绑定的端口号
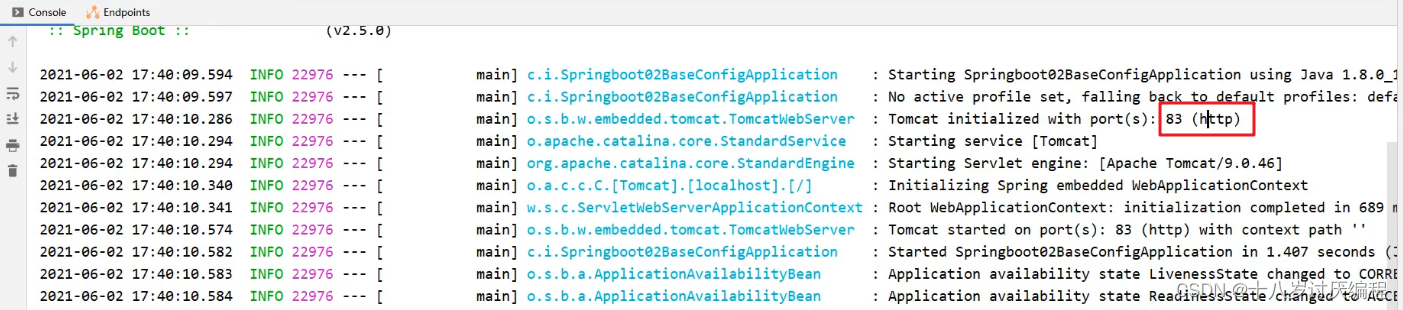
注意:在配合文件中如果没有提示,可以使用一下方式解决
- 点击
File选中Project Structure
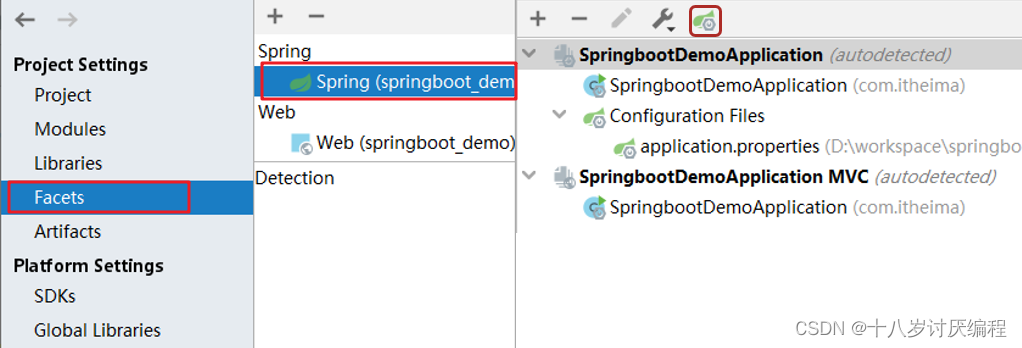
- 弹出如下窗口,按图中标记红框进行选择
- 通过上述操作,会弹出如下窗口
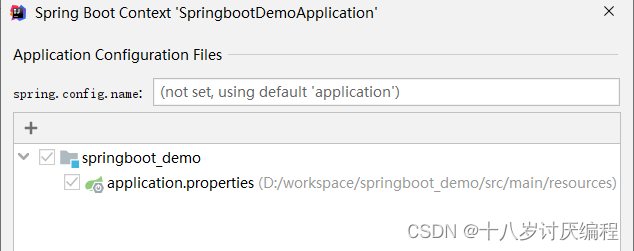
- 点击上图的
+号,弹出选择该模块的配置文件
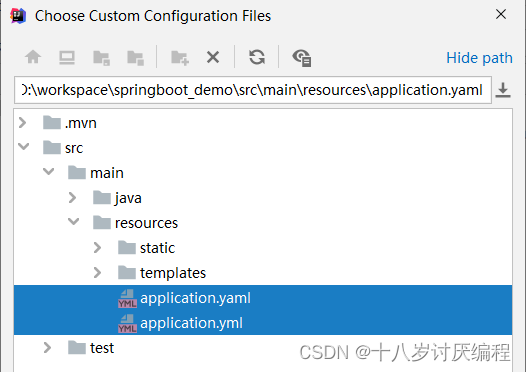
- 通过上述几步后,就可以看到如下界面。
properties类型的配合文件有一个,ymal类型的配置文件有两个
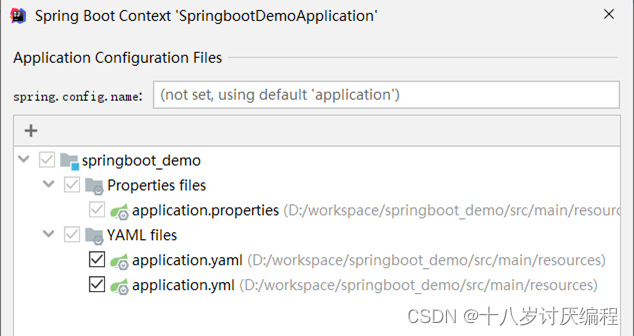
三种配合文件的优先级
在三种配合文件中分别配置不同的端口号,启动服务查看绑定的端口号。用这种方式就可以看到哪个配置文件的优先级更高一些
application.properties 文件内容如下:
server.port=80
- 1
application.yml 文件内容如下:
server:
port: 81
- 1
- 2
application.yaml 文件内容如下:
server:
port: 82
- 1
- 2
启动服务,在控制台可以看到使用的端口号是 80。说明 application.properties 的优先级最高
注释掉 application.properties 配置文件内容。再次启动服务,在控制台可以看到使用的端口号是 81,说明 application.yml 配置文件为第二优先级。
从上述的验证结果可以确定三种配置文件的优先级是:
application.properties > application.yml > application.yaml
注意:
SpringBoot核心配置文件名为application
SpringBoot内置属性过多,且所有属性集中在一起修改,在使用时,通过提示键+关键字修改属性例如要设置日志的级别时,可以在配置文件中书写
logging,就会提示出来。配置内容如下logging: level: root: info
- 1
- 2
- 3
root可以设为warn(比较干净)、debug(很长)
yaml格式
上面讲了三种不同类型的配置文件,而 properties 类型的配合文件之前我们学习过,接下来我们重点学习 yaml 类型的配置文件。
YAML(YAML Ain’t Markup Language),一种数据序列化格式。这种格式的配置文件在近些年已经占有主导地位,那么这种配置文件和前期使用的配置文件是有一些优势的,我们先看之前使用的配置文件。
最开始我们使用的是 xml ,格式如下:
<enterprise>
<name>itcast</name>
<age>16</age>
<tel>4006184000</tel>
</enterprise>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
而 properties 类型的配置文件如下
enterprise.name=itcast
enterprise.age=16
enterprise.tel=4006184000
- 1
- 2
- 3
yaml 类型的配置文件内容如下
enterprise:
name: itcast
age: 16
tel: 4006184000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
优点:
-
容易阅读
yaml类型的配置文件比xml类型的配置文件更容易阅读,结构更加清晰 -
容易与脚本语言交互
-
以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
yaml更注重数据,而xml更注重格式
YAML 文件扩展名:
.yml(主流).yaml
上面两种后缀名都可以,以后使用更多的还是 yml 的。
语法规则
-
大小写敏感
-
属性层级关系使用多行描述,每行结尾使用冒号结束
-
使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用Tab键)
空格的个数并不重要,只要保证同层级的左侧对齐即可。
-
属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
-
# 表示注释
核心规则:数据前面要加空格与冒号隔开
数组数据在数据书写位置的下方使用减号作为数据开始符号,每行书写一个数据,减号与数据间空格分隔,例如
enterprise:
name: itcast
age: 16
tel: 4006184000
subject:
- Java
- 前端
- 大数据
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
yaml配置文件数据读取
我们在 resources 下创建一个名为 application.yml 的配置文件,里面配置了不同的数据,内容如下:
lesson: SpringBoot
server:
port: 80
enterprise:
name: itcast
age: 16
tel: 4006184000
subject:
- Java
- 前端
- 大数据
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
接下来我们尝试去读取他们:
使用 @Value注解
使用 @Value("表达式") 注解可以从配合文件中读取数据,注解中用于读取属性名引用方式是:${一级属性名.二级属性名……}
我们可以在 BookController 中使用 @Value 注解读取配合文件数据,如下
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Value("${lesson}")
private String lesson;
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${enterprise.subject[0]}")
private String subject_00;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(lesson);
System.out.println(port);
System.out.println(subject_00);
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
Environment对象
上面方式读取到的数据特别零散,SpringBoot 还可以使用 @Autowired 注解注入 Environment 对象的方式读取数据。这种方式 SpringBoot 会将配置文件中所有的数据封装到 Environment 对象中,如果需要使用哪个数据只需要通过调用 Environment 对象的 getProperty(String name) 方法获取。具体代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(env.getProperty("lesson"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.name"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.subject[0]"));
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
注意:这种方式,框架内容大量数据,而在开发中我们很少使用。
自定义对象
SpringBoot 还提供了将配置文件中的数据封装到我们自定义的实体类对象中的方式。具体操作如下:
-
将实体类
bean的创建交给Spring管理。在类上添加
@Component注解 -
使用
@ConfigurationProperties注解表示加载配置文件在该注解中也可以使用
prefix属性指定只加载指定前缀的数据 -
在
BookController中进行注入
具体代码如下:
Enterprise 实体类内容如下:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "enterprise")
public class Enterprise {
private String name;
private int age;
private String tel;
private String[] subject;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public String[] getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String[] subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Enterprise{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", tel='" + tel + '\'' +
", subject=" + Arrays.toString(subject) +
'}';
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
BookController 内容如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private Enterprise enterprise;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(enterprise.getName());
System.out.println(enterprise.getAge());
System.out.println(enterprise.getSubject());
System.out.println(enterprise.getTel());
System.out.println(enterprise.getSubject()[0]);
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
注意:
使用第三种方式,在实体类上有如下警告提示
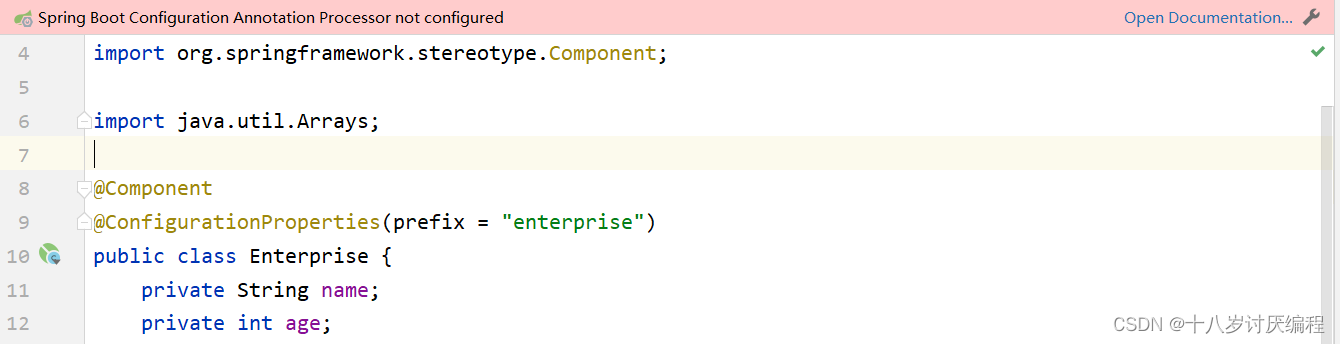
这个警告提示解决是在 pom.xml 中添加如下依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:十八岁讨厌编程,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/zyb18507175502/article/details/125985268
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)