【牛客编程题】Python机器学习(入门例题5题)
【摘要】
【牛客编程题】Python机器学习(入门例题5题) 做题链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=Python篇&topicId=329...
【牛客编程题】Python机器学习(入门例题5题)
做题链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page=1&tab=Python篇&topicId=329
AI1 鸢尾花分类_1
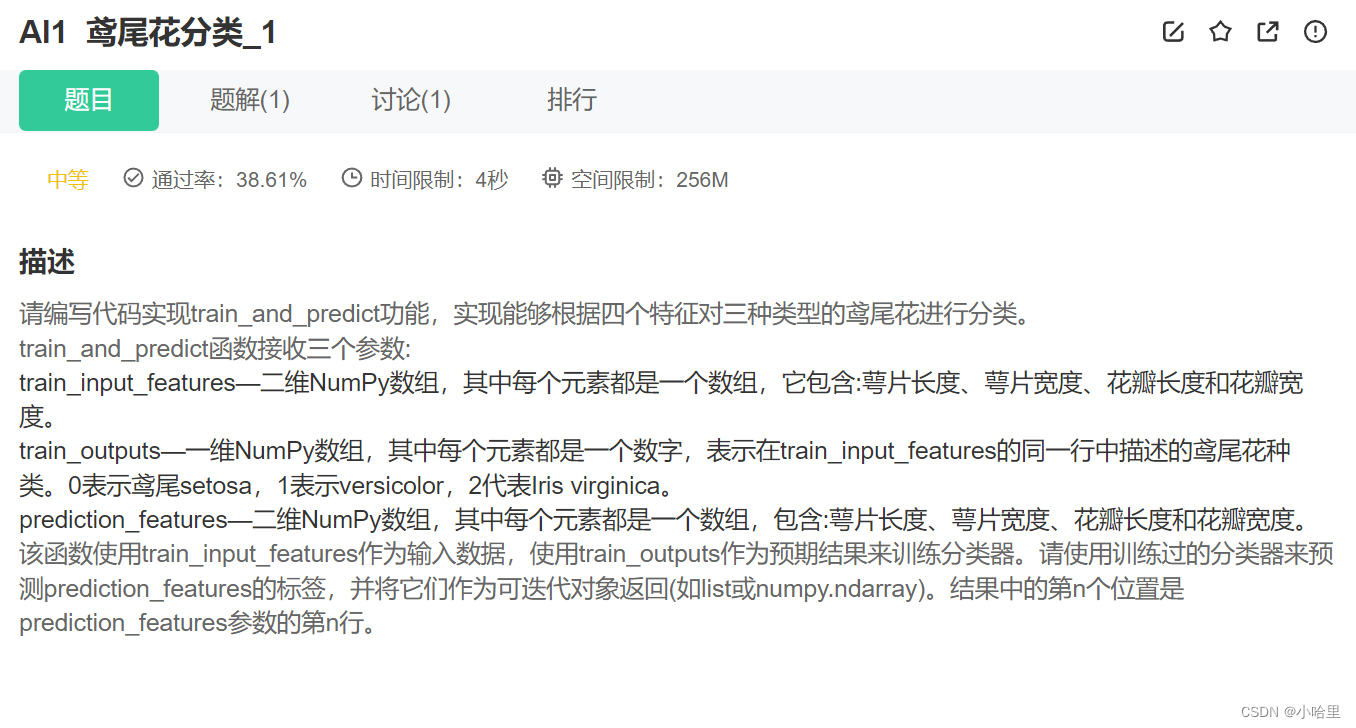
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
def train_and_predict(train_input_features, train_outputs, prediction_features):
#code start here
clf = GaussianNB();
clf.fit(train_input_features, train_outputs);
y_pred = clf.predict(prediction_features);
return y_pred;
#code end here
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target,
test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
y_pred = train_and_predict(X_train, y_train, X_test)
if y_pred is not None:
#code start here
print(metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
#code end here
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
AI2 鸢尾花分类_2

import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, roc_auc_score, accuracy_score
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
def transform_three2two_cate():
data = datasets.load_iris()
# 其中data特征数据的key为data,标签数据的key为target
# 需要取出原来的特征数据和标签数据,移除标签为2的label和特征数据,返回值new_feat为numpy.ndarray格式特征数据,new_label为对应的numpy.ndarray格式label数据
# 需要注意特征和标签的顺序一致性,否则数据集将混乱
# code start here
index2 = np.where(np.array(data.target)==2)
new_feat = np.delete(data.data, index2, axis = 0)
new_label = np.delete(data.target, index2)
# code end here
return new_feat, new_label
def train_and_evaluate():
data_X, data_Y = transform_three2two_cate()
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(data_X, data_Y, test_size=0.2)
# 已经划分好训练集和测试集,接下来请实现对数据的训练
# code start here
dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3) # 建立决策树模型
dtc.fit(train_x, train_y) # 训练模型
y_predict = dtc.predict(test_x) # 预测结果
# code end here
# 注意模型预测的label需要定义为 y_predict,格式为list或numpy.ndarray
print(accuracy_score(y_predict, test_y))
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_and_evaluate()
# 要求执行train_and_evaluate()后输出为:
# 1、{0,1},代表数据label为0和1
# 2、测试集上的准确率分数,要求>0.95
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
AI3 决策树的生成与训练-信息熵的计算

# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from math import log
import pandas as pd
dataSet = pd.read_csv('dataSet.csv', header=None).values.tolist()
def calcInfoEnt(dataSet):
numEntres = len(dataSet) # 数据集样本数量
#code start here
labelCounts = {} # 字典:每一类的样本数量
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel = featVec[-1] # 获取分类标签
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 # 每个类中数据个数统计
infoEnt = 0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntres
infoEnt -= prob*log(prob, 2)
return infoEnt
#code end here
#返回值 infoEnt 为数据集的信息熵,表示为 float 类型
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(calcInfoEnt(dataSet))
#输出为当前数据集的信息熵
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
AI4 决策树的生成与训练-信息增益

# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from math import log
import pandas as pd
dataSet = pd.read_csv('dataSet.csv', header=None).values.tolist()
#给定一个数据集,calcInfoEnt可以用于计算一个数据集的信息熵,可直接调用
#也可不使用,通过自己的方式计算信息增益
def calcInfoEnt(data):
numEntres = len(data)
labelcnt = {} #用于统计正负样本的个数
for item in data:
if item[-1] not in labelcnt:
labelcnt[item[-1]] = 0
labelcnt[item[-1]] += 1
infoEnt = 0.0
for item in labelcnt: #根据信息熵的公式计算信息熵
curr_info_entr = float(labelcnt[item]) / numEntres
infoEnt = infoEnt - curr_info_entr * log(curr_info_entr,2)
return infoEnt
#返回值 infoEnt 为数据集的信息熵
#给定一个数据集,用于切分一个子集,可直接用于计算某一特征的信息增益
#也可不使用,通过自己的方式计算信息增益
#dataSet是要划分的数据集,i 代表第i个特征的索引index
#value对应该特征的某一取值
def create_sub_dataset(dataSet, i, value):
res = []
for item in dataSet:
if item[i] == value:
curr_data = item[:i] + item[i+1:]
res.append(curr_data)
return res
def calc_max_info_gain(dataSet):#计算所有特征的最大信息增益,dataSet为给定的数据集
n = len(dataSet[0])-1 # n 是特征的数量,-1 的原因是最后一列是分类标签
total_entropy = calcInfoEnt(dataSet)#整体数据集的信息熵
max_info_gain = [0,0]#返回值初始化
#code start here
for i in range(n): # 遍历特征, 计算特征i的信息增益
featList = [feat[i] for feat in dataSet]
featValues = set(featList)# 获得所有该特征的数据
newEntropy = 0.0 #计算经验条件熵
for value in featValues:
subDataset = create_sub_dataset(dataSet,i,value)
prob = len(subDataset)/len(dataSet)
newEntropy += prob*calcInfoEnt(subDataset)
infoGain = total_entropy-newEntropy # 信息增益=信息熵-经验条件熵
if(infoGain > max_info_gain[1]): # 信息增益取最大
max_info_gain[1] = infoGain
max_info_gain[0] = i
#code end here
return max_info_gain
if __name__ == '__main__':
info_res = calc_max_info_gain(dataSet)
print("信息增益最大的特征索引为:{0},对应的信息增益为{1}".format(info_res[0],info_res[1]))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
AI5 使用梯度下降对逻辑回归进行训练

import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
def generate_data():
datasets = pd.read_csv('dataSet.csv', header=None).values.tolist()
labels = pd.read_csv('labels.csv', header=None).values.tolist()
return datasets, labels
def sigmoid(X):
#补全 sigmoid 函数功能
#code start here
return 1/(1+np.exp(-X)) # h(x)函数,直接计算并返回即可
#code end here
def gradientDescent(dataMatIn, classLabels): # 输入 datasets,labels
alpha = 0.001 # 学习率,也就是题目描述中的 α
iteration_nums = 100 # 迭代次数,也就是for循环的次数
dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn)
labelMat = np.mat(classLabels).transpose()
m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix) # 返回dataMatrix的大小。m为行数,n为列数。
weight_mat = np.ones((n, 1)) #初始化权重矩阵
#iteration_nums 即为循环的迭代次数
#请在代码完善部分注意矩阵乘法的维度,使用梯度下降矢量化公式
#code start here
for i in range(iteration_nums):
hx = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weight_mat)
weight_mat = weight_mat-alpha*dataMatrix.transpose()*(hx-labelMat)
return weight_mat
#code end here
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataMat, labelMat = generate_data()
print(gradientDescent(dataMat, labelMat))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
文章来源: gwj1314.blog.csdn.net,作者:小哈里,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:gwj1314.blog.csdn.net/article/details/126002570
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)