SpringCloud实战---第四篇:传统的分布式方法
前言
说起来容易做起来难,一步一步都干完!!!
学习一定要自己动手搞一搞,不能只眼会。
学习笔记是跟着尚硅谷的视频学的:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18E411x7eT?p=1
本篇使用传统的方式(未使用Cloud框架)RestTemplate来进行各模块间通信。
场景大纲
我们以这样一个场景来学习、构建我们的微服务
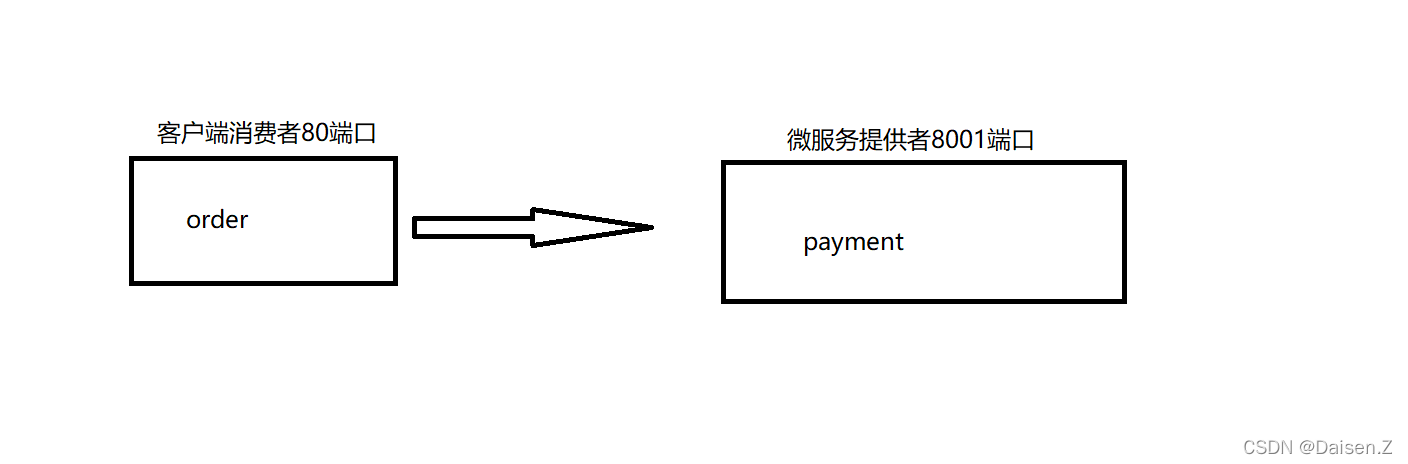
构建服务消费者模块
步骤不会的请参见:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43464964/article/details/121980366
这里不多赘述了,直接上内容,CV大法用起来就可以。
- 模块名:
cloud-customer-order80
- maven依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
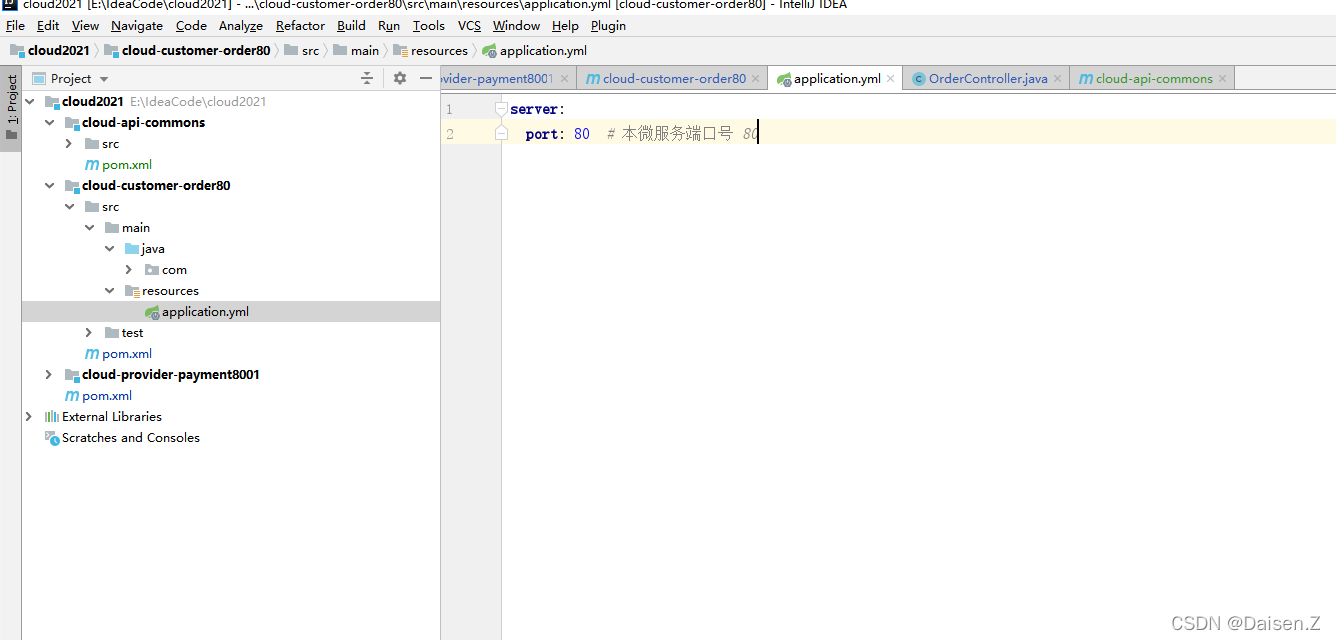
- 配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 80 # 本微服务端口号 80
- 启动类OrderMain80
package com.atguigu.springcloud;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @Author: Daisen.Z
* @Date: 2021/12/17 14:46
* @Version: 1.0
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderMain80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class,args);
}
}
基础框架完成
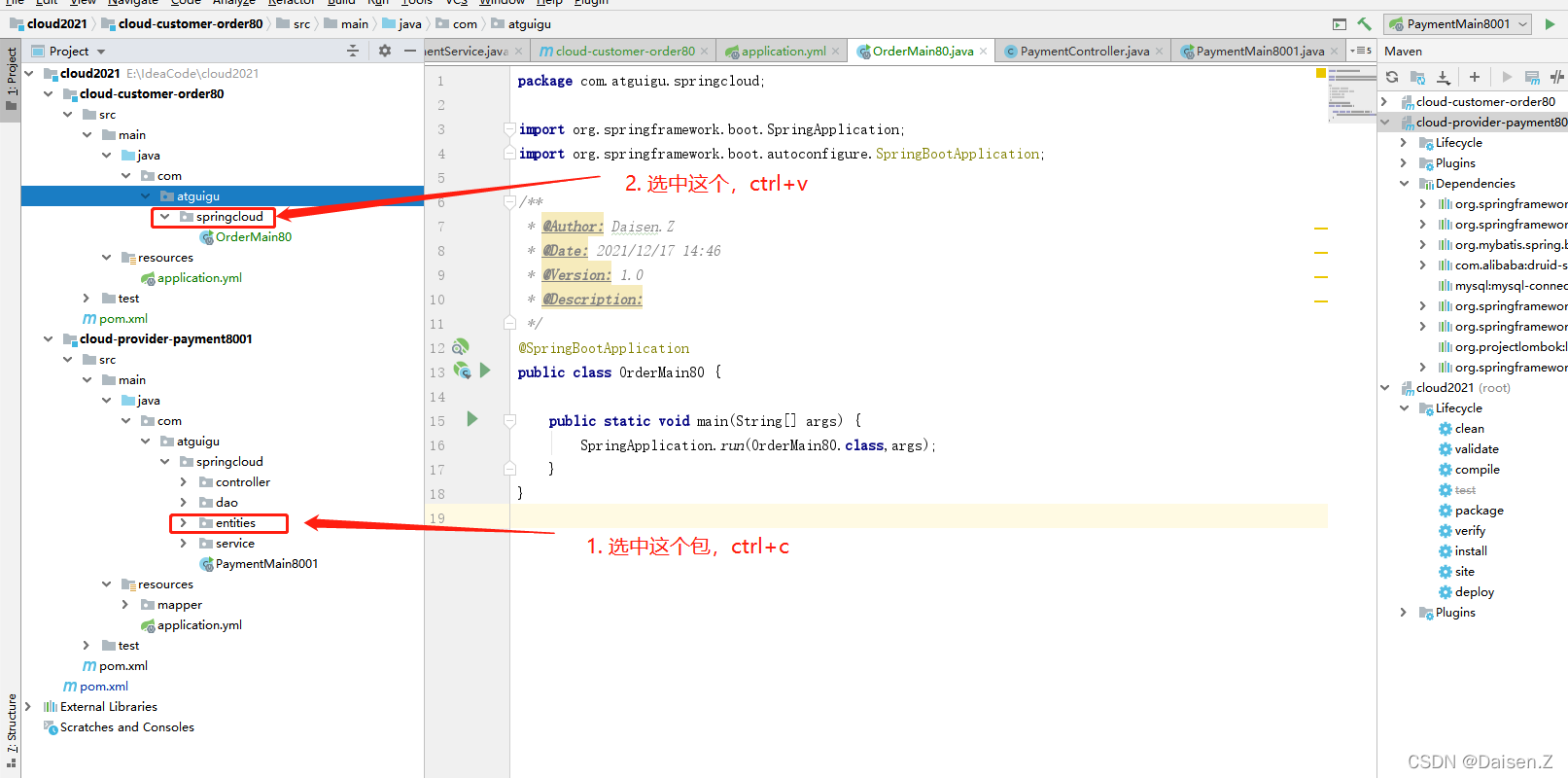
5. 创建entities
先创建com.atguigu.springcloud包
这里我们需要了解下,由于是微服务架构,所以构建的customer模块不需要操作数据库和service层,本篇customer模块只调用上篇的服务就可以。
但是对应的视图JSON类等还是需要用的。
将上篇建立的生产方实体类包copy过来。
编写业务
由于是微服务,我们是分模块调用的,所以只能使用http的方式进行调用。
- 使用SpringBoot自带的RestTemplate,需要增加一个配置类ApplicationContextConfig

package com.atguigu.springcloud.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
/**
* @Author: Daisen.Z
* @Date: 2021/12/17 15:01
* @Version: 1.0
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
- 编写OrderController调用服务提供方

package com.atguigu.springcloud.controller;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entities.CommonResult;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.entities.Payment;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @Author: Daisen.Z
* @Date: 2021/12/17 14:58
* @Version: 1.0
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class OrderController {
// provider服务的地址
private static final String PAYMENT_URL="http://localhost:8001";
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/customer/payment/create")
public CommonResult<Payment> create(Payment payment){
// 调用8001工程的服务
return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/create",payment,CommonResult.class);
}
@GetMapping("/customer/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
// 调用8001工程的服务
return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/get/"+id,CommonResult.class);
}
}
开始测试
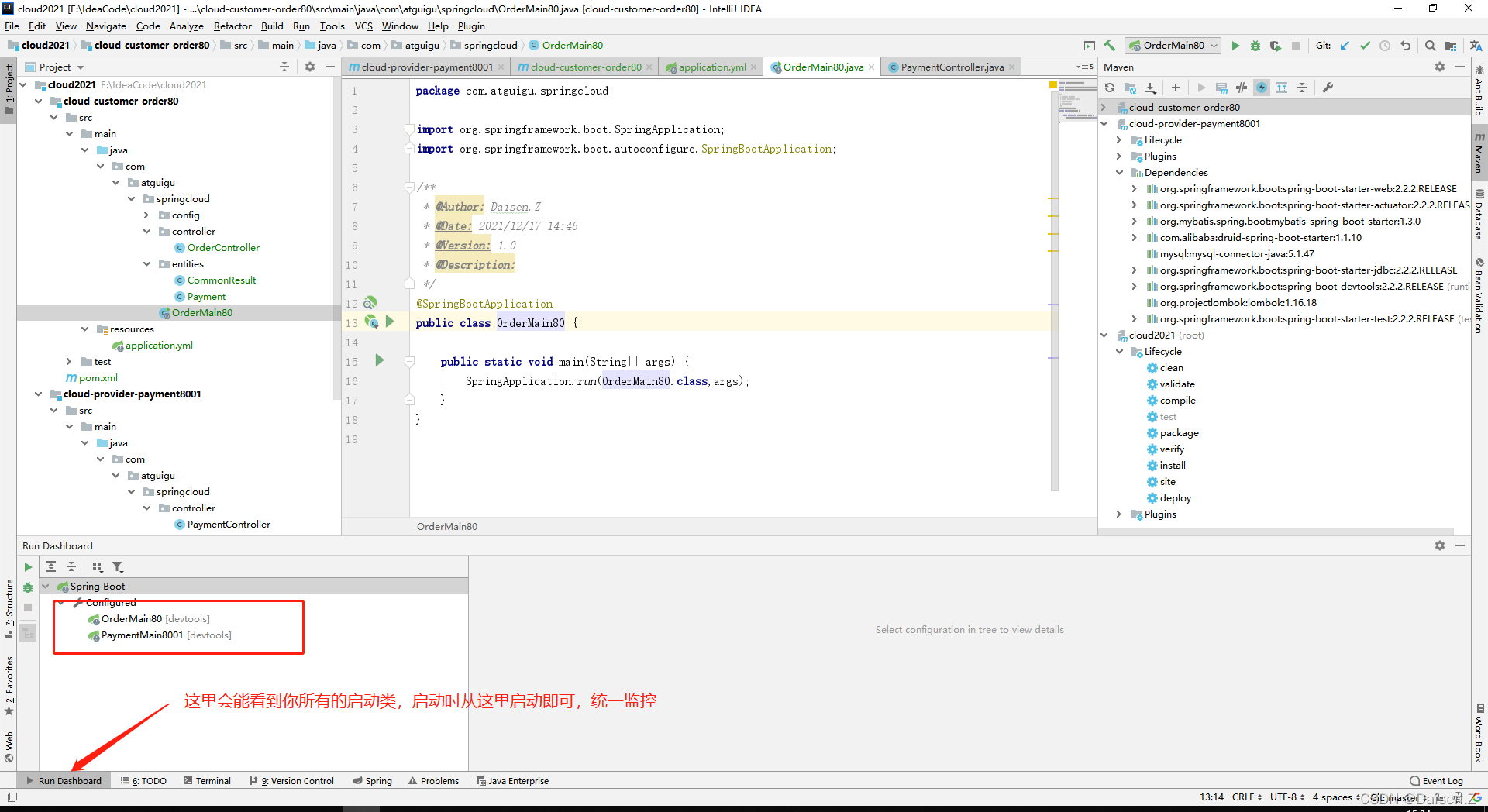
使用Run Dashbord
-
当你工程中有多个启动类时,你启动其中一个右下角会出来一个弹框


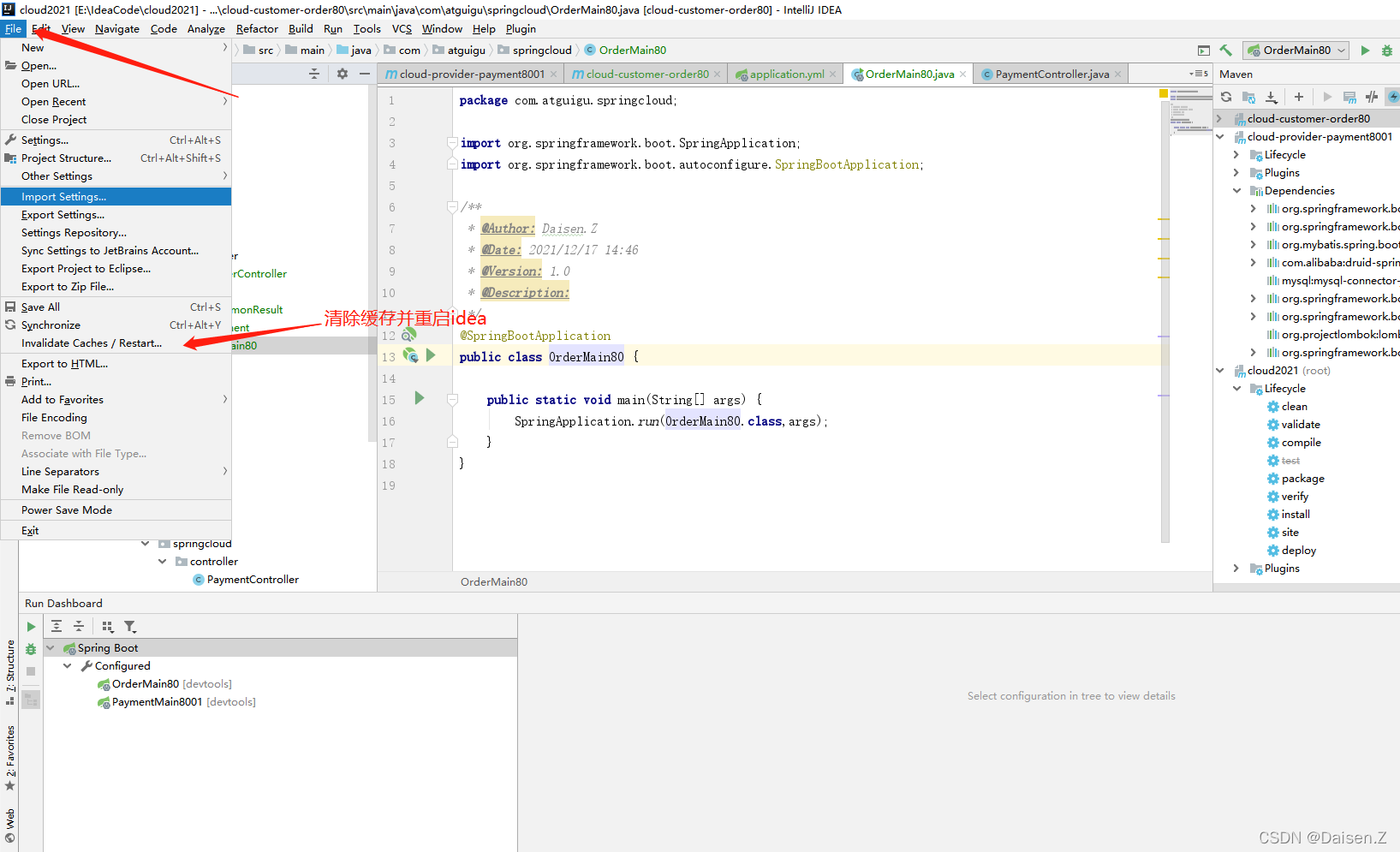
如果不小心关闭该弹框或者没有弹出不用担心,使用如下方式重启下idea即可。

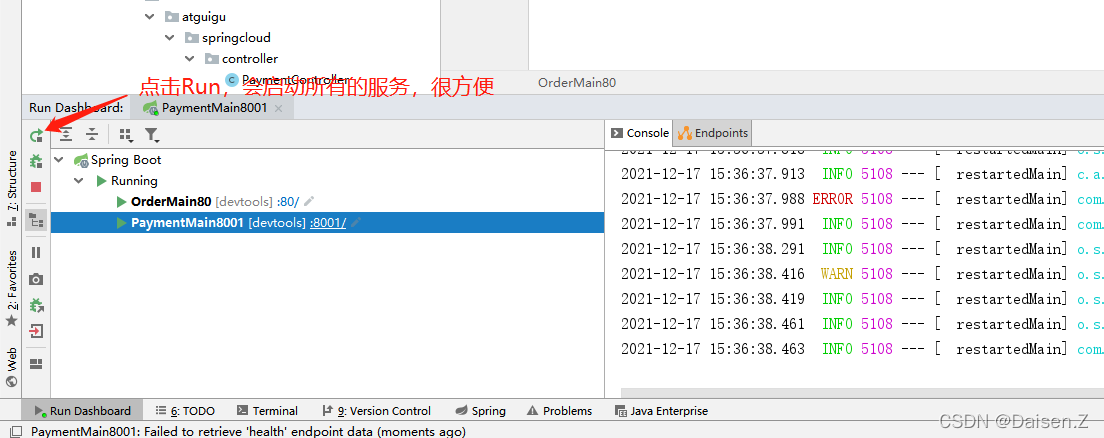
以后就可以在这里统一查看管理启动的服务啦!!!

-
启动两个服务

-
测试查询
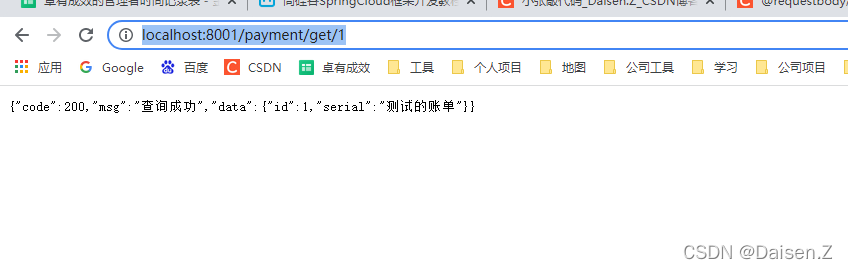
测试服务提供方,访问网址
http://localhost:8001/payment/get/1
测试服务调用方,访问http://localhost/customer/payment/get/1 ,80端口可以省略
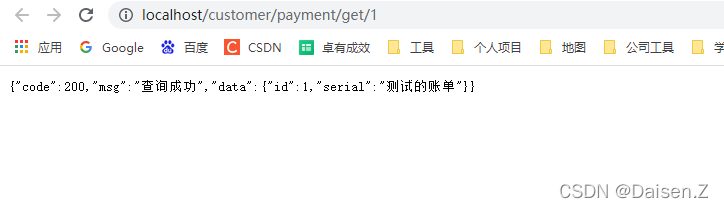
注意:最后一个/跟的是id,需要在上篇创建的表里有该数据,测试完成查询没问题。
- 测试添加
测试服务提供方,访问
http://localhost:8001/payment/create?serial=123
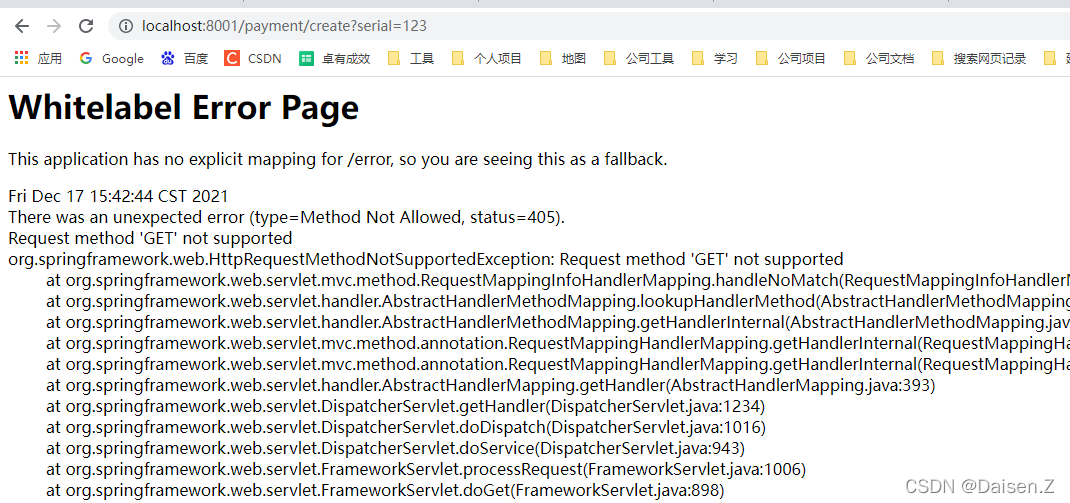
页面上出现了报错,检查一下,原来服务提供方我们限制了只能使用post请求,这里可以使用postman(程序员必备PostMan接口调试工具安装及使用传送门)再进行测试。
我们可以直接使用服务调用方进行测试,不再演示服务的提供方。
提供方可以看到我们限定的是get请求。
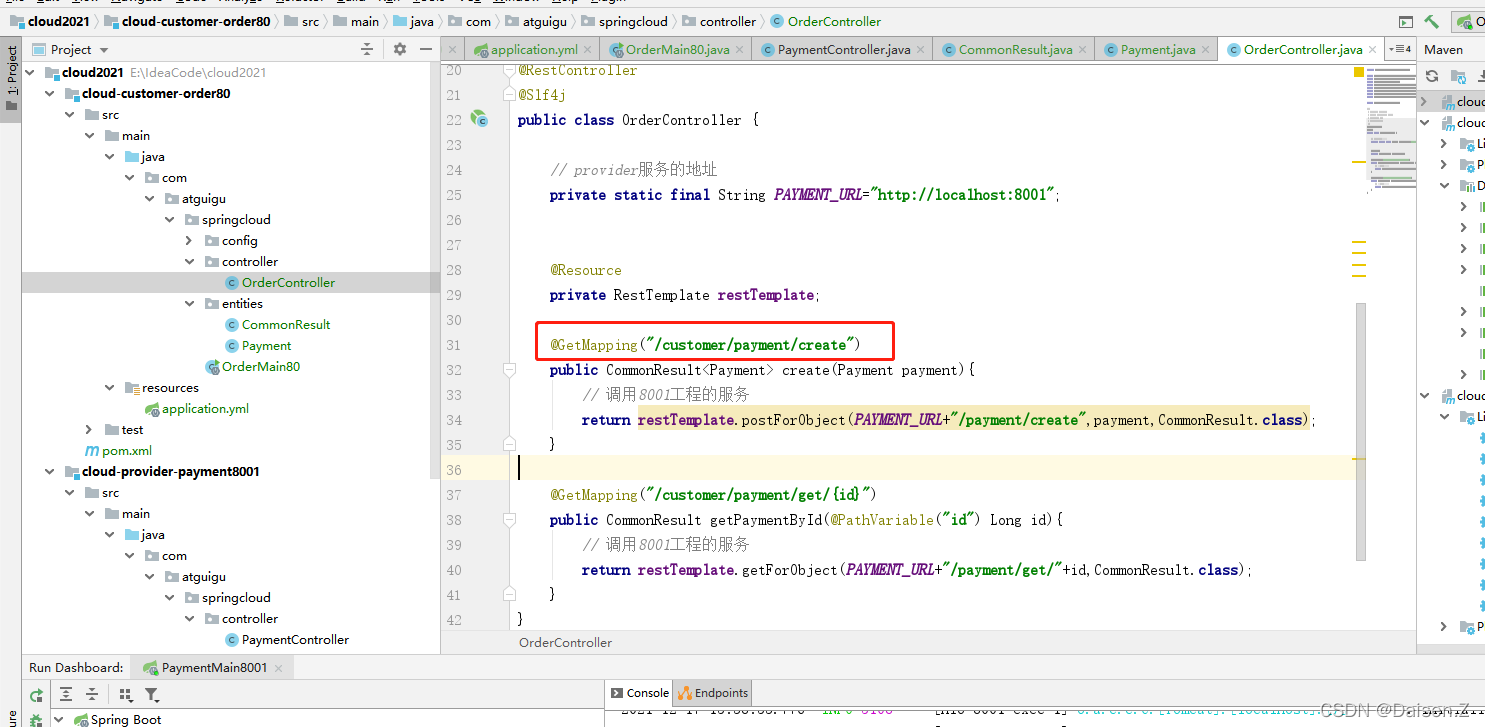
测试服务调用方:
http://localhost/customer/payment/create?serial=123
页面上显示成功
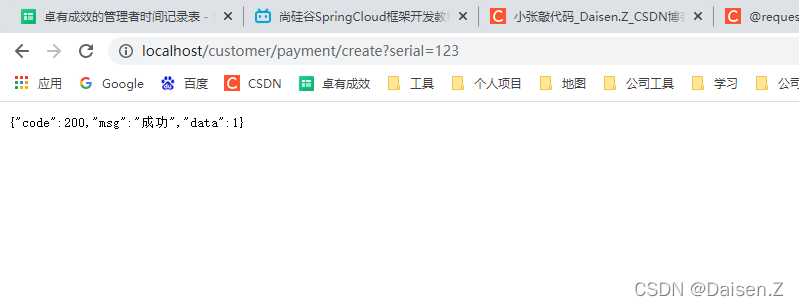
检查下数据库,发现serial没有获取到值
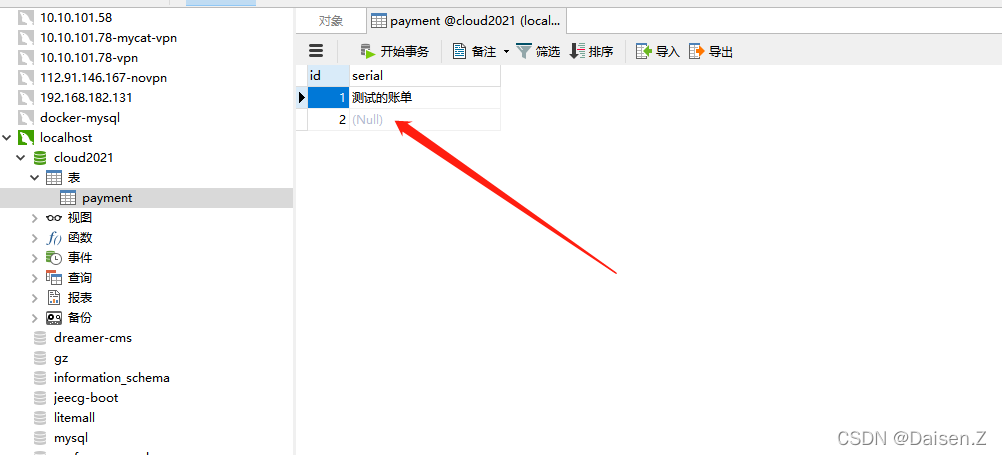
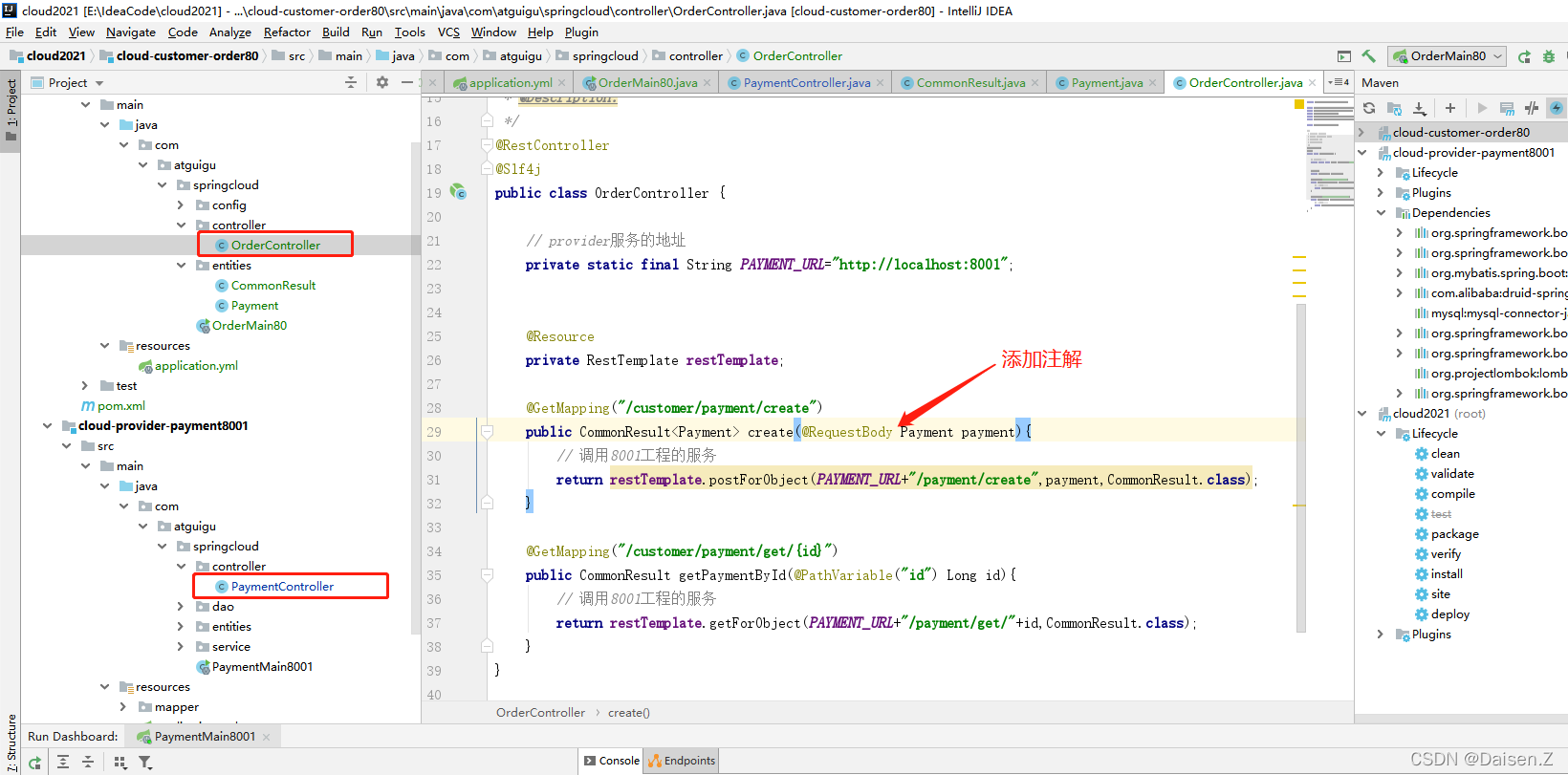
这里说明一下,当接口接收的参数是复杂参数(我们封装的实体类时),需要添加@RequestBody注解,否则参数无法映射到实体类上。
我们给两个模块的controller的create接口参数添加上@RequestBody注解。
这里顺便也可以测试下我们上篇配置的热部署,热部署生效的话不需要手动重启程序,改代码后会自动重启生效。
reload或打印重启信息代表热部署生效。如未生效请查找上篇的热部署配置。上篇传送门
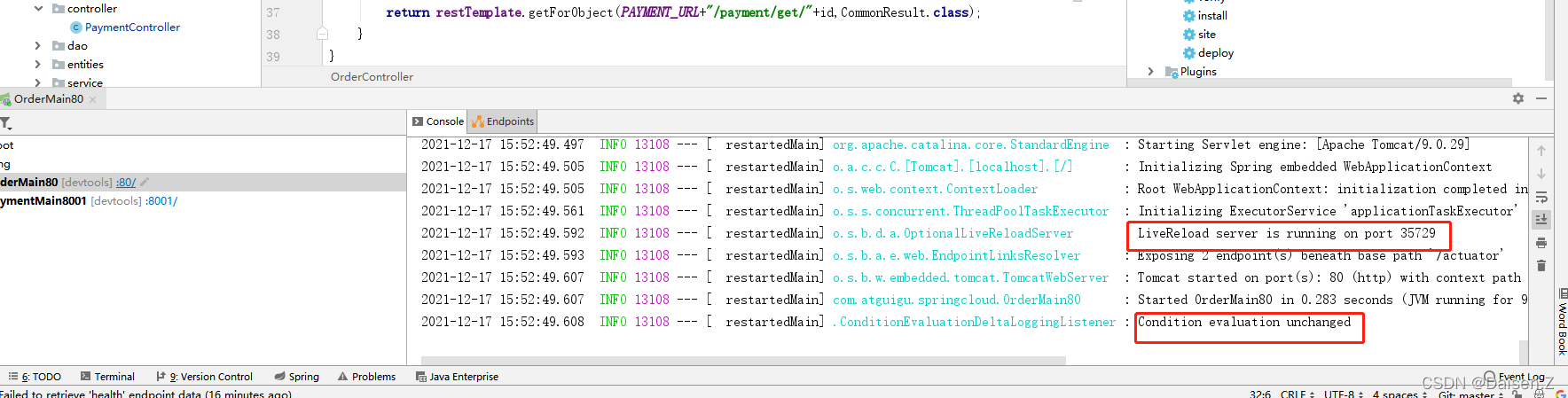
再次测试customer模块添加。
http://localhost/customer/payment/create?serial=123
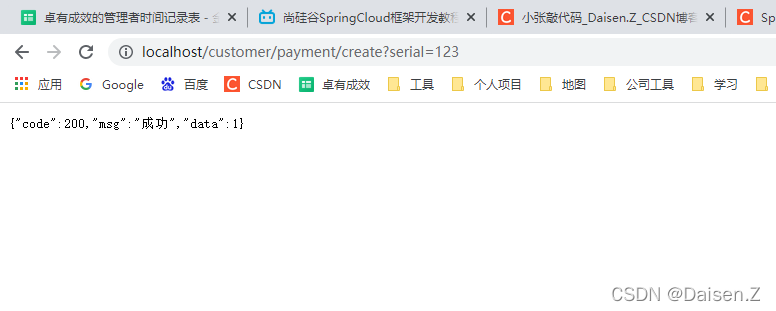
添加成功,检查数据库。
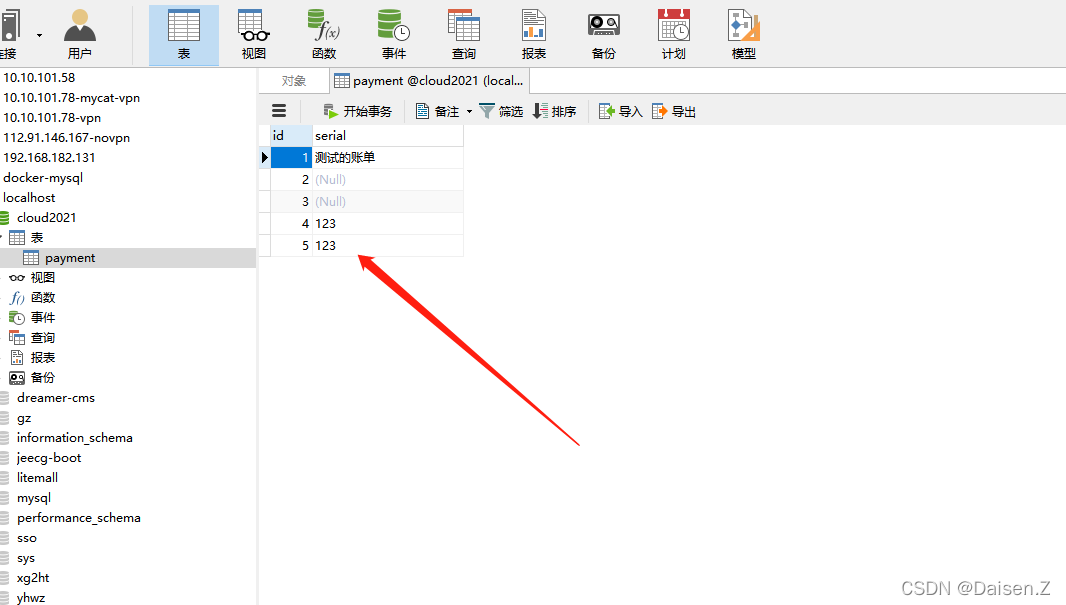
数据库也增加成功,并且无异常,测试完毕。
小结
- 细节决定成败,一个小的疏忽可能需要很长时间来排查解决。
- 简单项目的架构是枯燥的,我们要学习的是设计的思路,知道为什么要这样,这样有什么好处。
- 推荐一个必备的接口测试工具PostManhttps://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=121999824
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)