PostgreSQL在Linux和Windows安装和入门基础教程
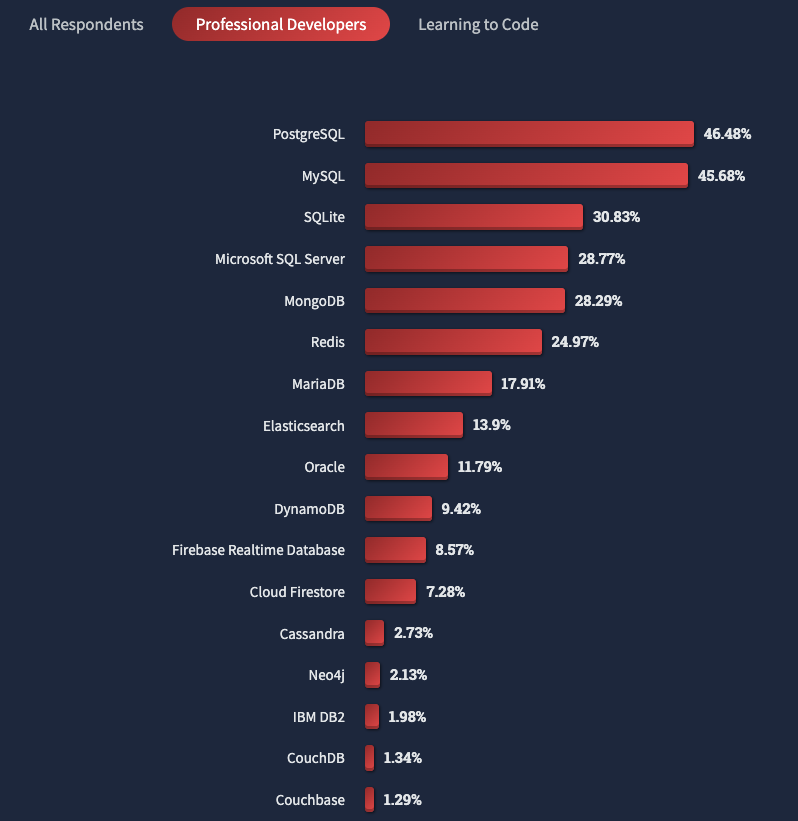
StackOverflow 2022 开发者报告:总体而言,MySQL 依然是最受欢迎的的数据库。但在专业开发者群体中,PostgreSQL(46.48%)已经超越 MySQL(45.68%)夺得了第一名。看来必须得学一波了啊。

PostgreSQL是一种特性非常齐全的自由软件的对象-关系型数据库管理系统(ORDBMS),是以加州大学计算机系开发的POSTGRES,4.2版本为基础的对象关系型数据库管理系统。POSTGRES的许多领先概念只是在比较迟的时候才出现在商业网站数据库中。PostgreSQL支持大部分的SQL标准并且提供了很多其他现代特性,如复杂查询、外键、触发器、视图、事务完整性、多版本并发控制等。同样,PostgreSQL也可以用许多方法扩展,例如通过增加新的数据类型、函数、操作符、聚集函数、索引方法、过程语言等。另外,因为许可证的灵活,任何人都可以以任何目的免费使用、修改和分发PostgreSQL。
今天给大家带来PostgreSQL安装和一些基础教程。
安装和使用
https://www.runoob.com/postgresql/windows-install-postgresql.html
打开PostgreSQL官网地址:https://www.postgresql.org/,点击上方的Download。可以看到很多平台的安装包,有Linux,macOS,Windows,BSD,Solaris。
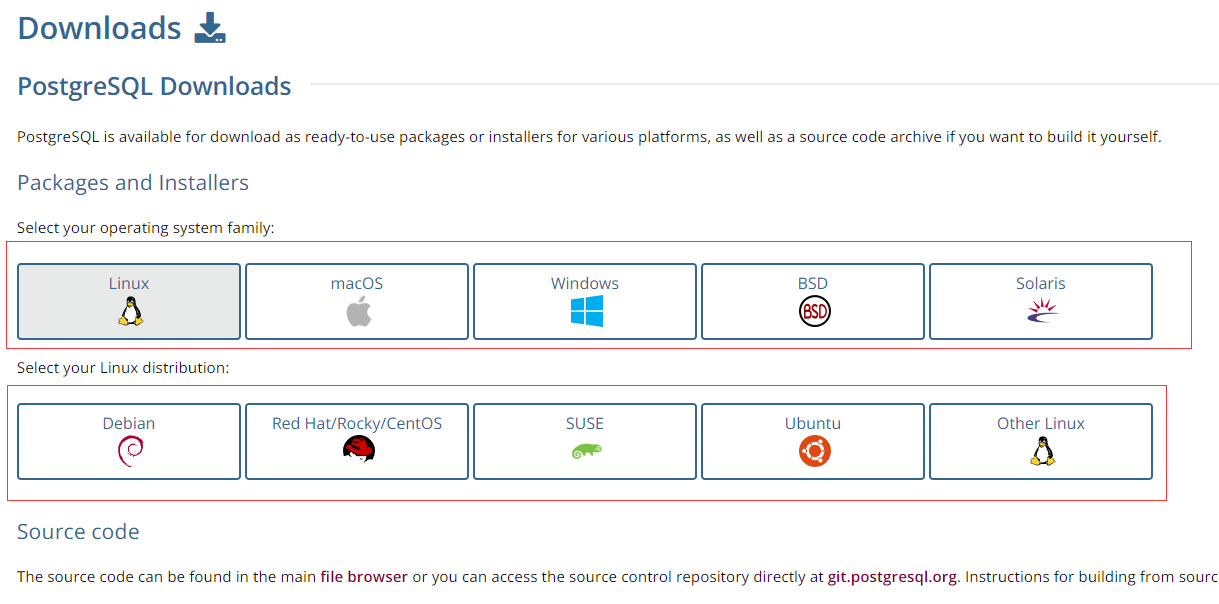
Linux 上安装 PostgreSQL
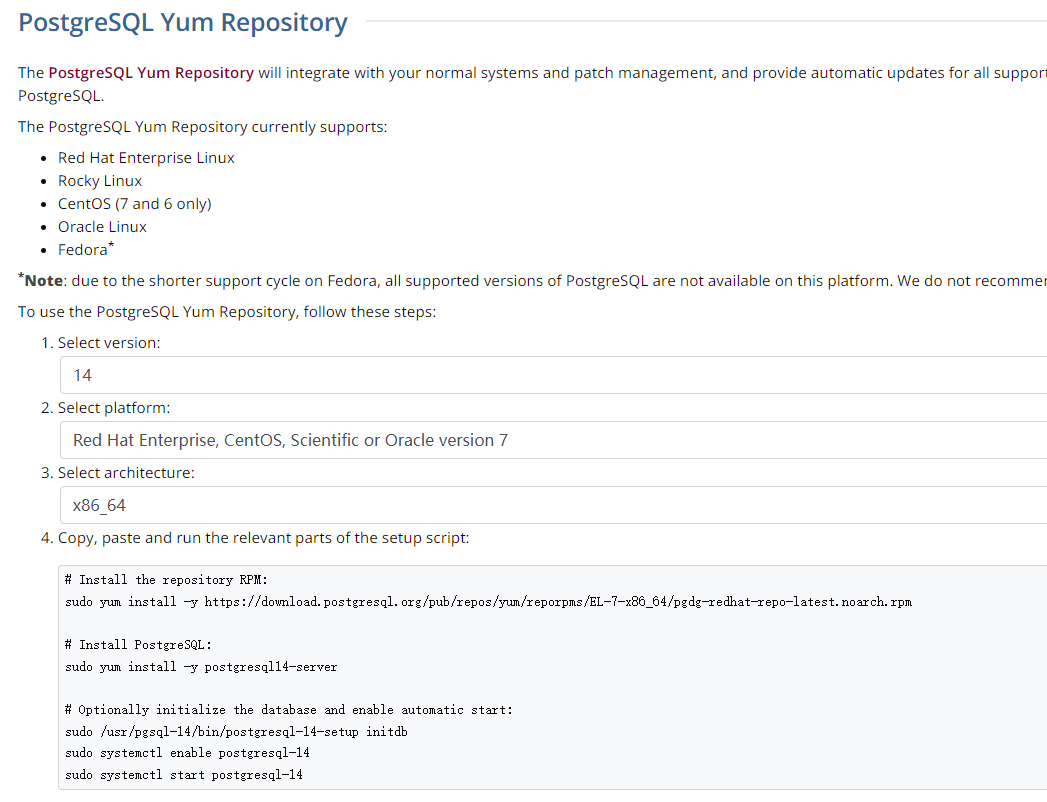
选择上方的Linux后可以看到多种Linux平台,这里我选择Red Hat/Rocky/Centos这个,选择后进入页面可以看到对应的yum语句。
sudo yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install -y postgresql14-server
sudo /usr/pgsql-14/bin/postgresql-14-setup initdb
sudo systemctl enable postgresql-14
sudo systemctl start postgresql-14
Windows 上安装 PostgreSQL
选择Windows版本的下载后,点击链接进入EnterpriseDB网站进行下载https://www.enterprisedb.com/downloads/postgres-postgresql-downloads。
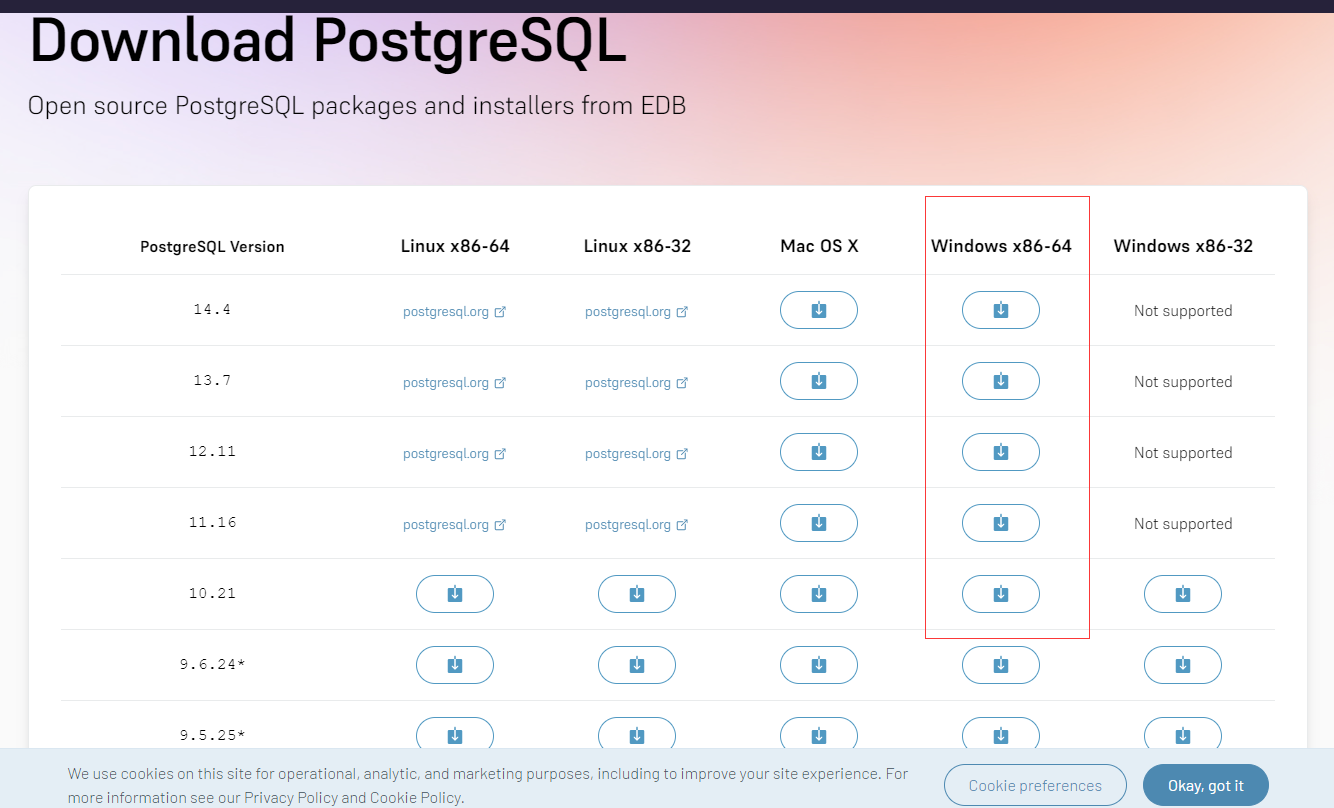
这里我选择64位的Windows系统安装包进行下载。下载完成后点击对应的安装包进行安装。

选择对应的安装位置。
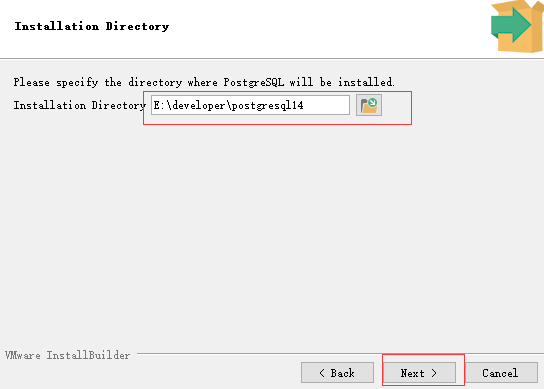
选择需要安装组件。
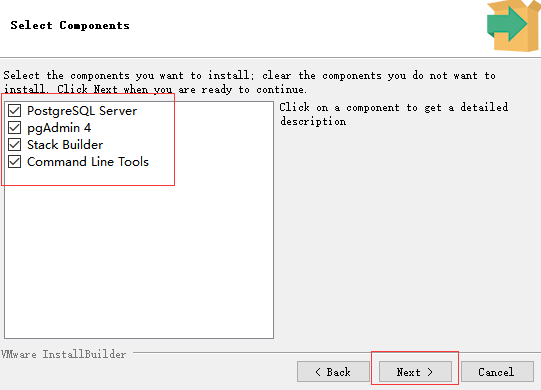
选择数据库路径。
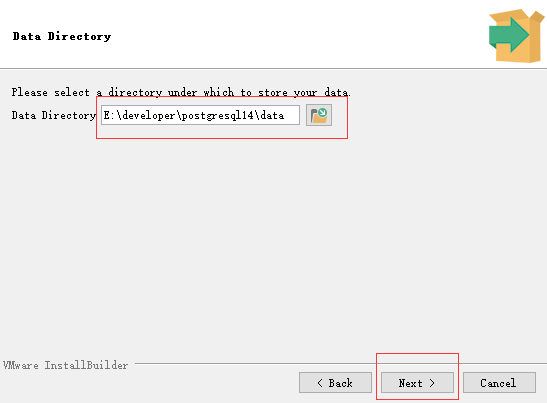
设置超级用户的密码,我这里设置的是zjqzjq。
设置端口号,我这里使用默认的5432。
后续继续next进行安装了。
安装完成后点击取消勾选,点击finish完成安装。
打开pgAdmin4(可以理解成Navicat这种数据库连接工具。)
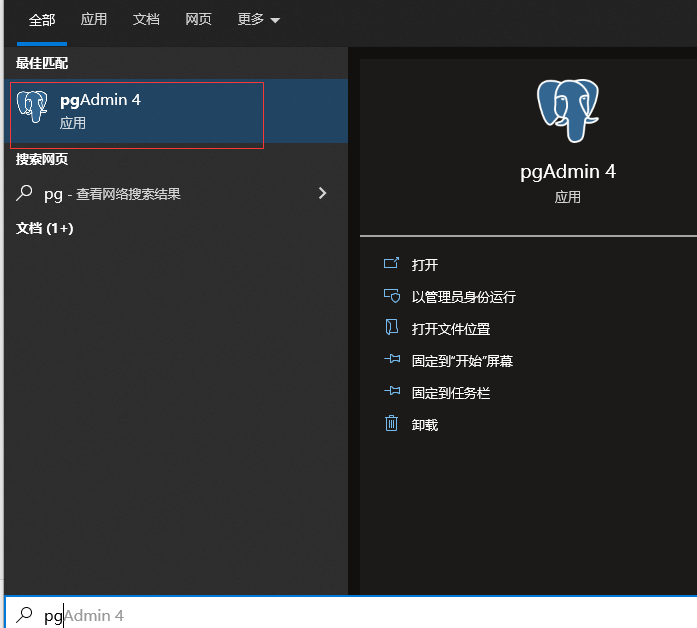
进入界面后,点击左侧servers下面的postgresql 14,输入密码。
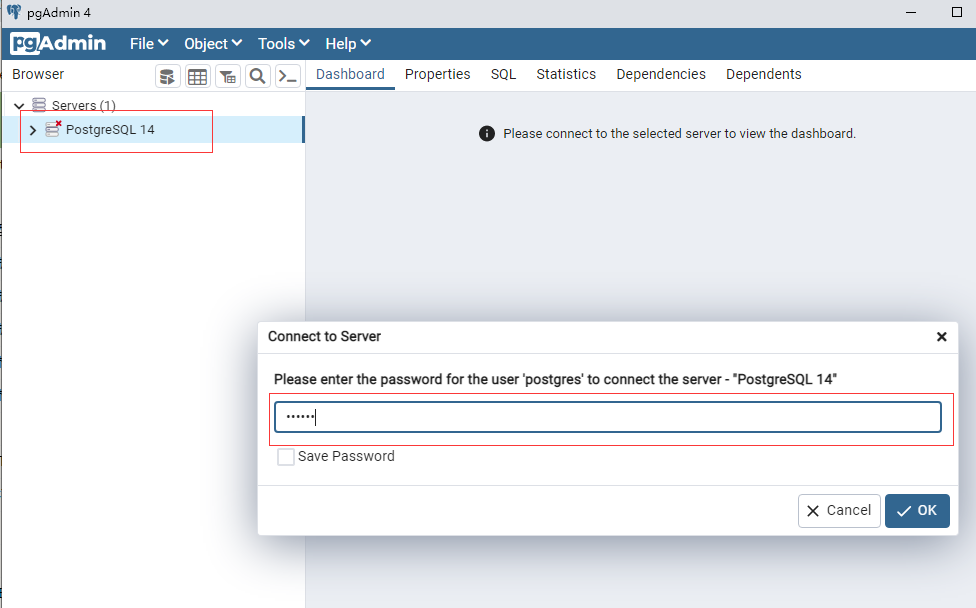
进入后界面如下:
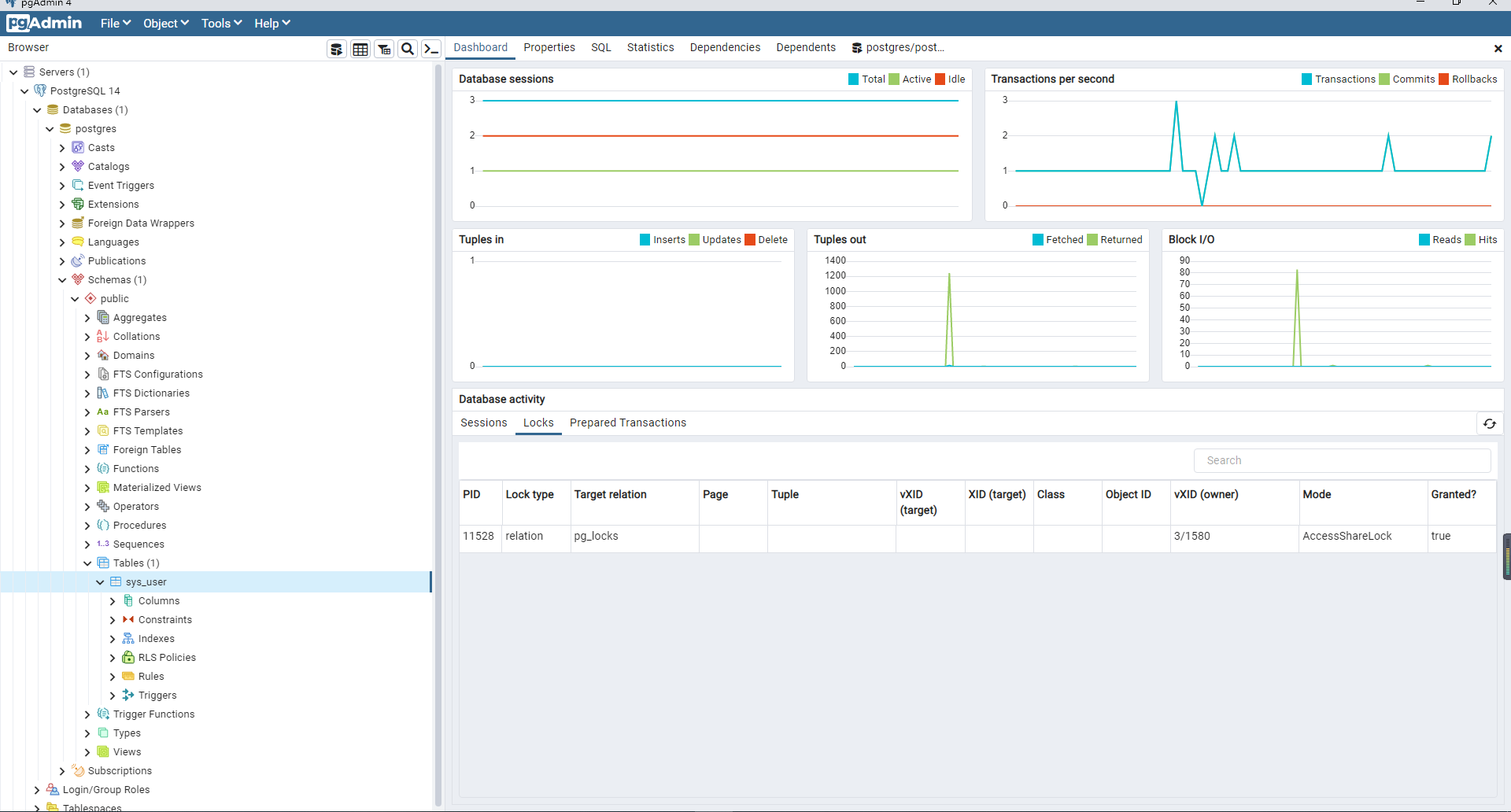
打开SQL shell也可以进入执行相关SQL操作。
前面几个使用默认的,用户口令使用上面设置的密码。
基础使用
增删改查
表操作
创建表:
-- 创建一张表并设置唯一索引和普通索引
create table book(
id serial primary key ,
title text not null ,
meta jsonb default '{}'::jsonb,
price money,
isbn text not null ,
publish_at date not null
);
create unique index on book(isbn);
create index on book using gin(meta);
-- 创建表,含一个自增主键(自增序列底层逻辑:绑定 sequence 对象的表达式默认值),一个content字段保存订单详情,一个时间戳字段记录订单入库时间
create table trade (
id serial primary key,
content text,
created_at timestamp default now()
);
删除表:
数据操作
新增数据:
insert into book(title, price, isbn, publish_at) select 'a book title', 25.4, 'xx-xxxx-xxxx', '2019-12-1'::date;
insert into book(title, price, isbn, publish_at) select 'a other book title', 25.4, 'yy-yyyy-xxxx', '2019-12-1'::date;
更新数据:
create table employee
(
id serial primary key,
name text,
dept text,
salary money
);
-- 修改销售部(dept 字段为 sale)员工 Dora Muk 的工资,将其增加 1000,返回她的工号。
update employee set salary = salary + 1000 where dept = 'sale' and name = 'Dora Muk' returning id;
删除数据:
create table orders
(
id serial primary key,
meta jsonb default '{}'::jsonb,
content jsonb default '{}'::jsonb,
created_at timestamp default now(),
deal boolean
)
-- 删除deal为true的数据并返回id
delete from orders where deal returning id;
查询:
-----------------------------子查询、分组、联合查询
create table employee
(
id serial primary key,
name text,
dept text,
salary money
);
-- 查询出每个部门工资最高的员工的 id, name, dept, salary
select l.id, l.name, l.dept, l.salary
from employee as l
join (select max(salary) as salary, dept
from employee
group by dept) as r
on l.dept = r.dept and l.salary = r.salary
-- 找出比销售部(dept 为 sale)工资最高的员工工资更高的那部分人,查询出他们的完整信息
select id, name, dept, salary
from employee
where salary > (select max(salary)
from employee
where dept = 'sale')
------------------- 分页查询------------------------
create table orders
(
id serial primary key,
product_id integer,
order_date date default now(),
quantity integer,
customer_id integer
);
-- 查询指定的某一天内的数据,并按每一百条一页查询
select id, product_id, order_date, quantity, customer_id
from orders
where date = $1
offset $2 limit 100;
-----------树结构述根---------------------
create table node
(
id serial primary key,
pid integer,
content text
);
-- 其 pid 列引用 id 列,形成一个树结构,根节点的 pid 为 0。写一个查询,找到某一个给定id的记录,其父节点、父节点的父节点,直至根节点的路径。
函数
plsql支持多种函数类型,函数可以用 SQL 写,也可以用 PLPGSQL,还可以用 Python、Perl、LUA等语言。
-
支持数学操作符(除(/)、取模(%)、阶乘(!!)、绝对值(@)等。)
-
支持位串操作符(按位左移(<< )、按位右移(>>)、按位AND(&)等。)
-
支持数学函数(绝对值(abs(x))、0.0到1.0之间的随机数值(random())、余弦(cos(x))等。)
-
支持字符串函数(字串连接(string || string)、合并字符串(concat(串1,串2…))、string中字符的数目(length(string text))等。)
-
支持数据类型格式化函数
| to_char(timestamp, text) | 把时间戳转换成字串 | to_char(current_timestamp, ‘HH12:MI:SS’) | |
| — | — | — | — |
| to_char(interval, text) | 把时间间隔转为字串 | to_char(interval ‘15h 2m 12s’, ‘HH24:MI:SS’) | |
| to_char(int, text) | 把整数转换成字串 | to_char(125, ‘999’) | |
| to_char(double precision, text) | 把实数/双精度数转换成字串 | to_char(125.8::real, ‘999D9’) | |
| to_char(numeric, text) | 把numeric转换成字串 | to_char(-125.8, ‘999D99S’) | |
| to_date(text, text) | 把字串转换成日期 | to_date(‘05 Dec 2000’, ‘DD Mon YYYY’) | |
| to_timestamp(text, text) | 把字串转换成时间戳 | to_timestamp(‘05 Dec 2000’, ‘DD Mon YYYY’) | |
| to_timestamp(double) | 把UNIX纪元转换成时间戳 | to_timestamp(200120400) | |
| to_number(text, text) | 把字串转换成numeric | to_number(‘12,454.8-’, ‘99G999D9S’) | | -
支持日期/时间函数
| age(timestamp, timestamp) | 减去参数,生成一个使用年、月的"符号化"的结果 | age(‘2001-04-10’, timestamp ‘1957-06-13’) | | 43 years 9 mons 27 days |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| age(timestamp) | 从current_date减去得到的数值 | age(timestamp ‘1957-06-13’) | | 43 years 8 mons 3 days |
| current_date | 今天的日期 | | | |
| current_time | 现在的时间 | | | |
| current_timestamp | 日期和时间 | | | |
| date_part(text, timestamp) | 获取子域(等效于extract) | date_part(‘hour’, timestamp ‘2001-02-16 20:38:40’) | | 20 |
| date_part(text, interval) | 获取子域(等效于extract) | date_part(‘month’, interval ‘2 years 3 months’) | | 3 |
| date_trunc(text, timestamp) | 截断成指定的精度 | date_trunc(‘hour’, timestamp ‘2001-02-16 20:38:40’) | | 2001-02-16 20:00:00+00 |
| extract(field from timestamp) | 获取子域 | extract(hour from timestamp ‘2001-02-16 20:38:40’) | | 20 |
| extract(field from interval) | 获取子域 | extract(month from interval ‘2 years 3 months’) | | 3 |
| localtime | 今日的时间 | | | |
| localtimestamp | 日期和时间 | | | |
| now() | 当前的日期和时间(等效于 current_timestamp) | | | |
| timeofday() | 当前日期和时间 | | | | -
系统信息函数
| current_database() | 当前数据库的名字 | | | |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| current_schema() | 当前模式的名字 | | | |
| current_schemas(boolean) | 在搜索路径中的模式名字 | | | |
| current_user | 目前执行环境下的用户名 | | | |
| inet_client_addr() | 连接的远端地址 | | | |
| inet_client_port() | 连接的远端端口 | | | |
| inet_server_addr() | 连接的本地地址 | | | |
| inet_server_port() | 连接的本地端口 | | | |
| session_user | 会话用户名 | | | |
| pg_postmaster_start_time() | postmaster启动的时间 | | | |
| user | current_user | | | |
| version() | PostgreSQL版本信息 | | | |
| has_table_privilege(user,table,privilege) | 用户是否有访问表的权限 | SELECT/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/RULE/REFERENCES/TRIGGER | | 允许用户在程序里查询对象访问权限的函数 |
| has_table_privilege(table,privilege) | 当前用户是否有访问表的权限 | SELECT/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/RULE/REFERENCES/TRIGGER | | |
| has_database_privilege(user,database,privilege) | 用户是否有访问数据库的权限 | CREATE/TEMPORARY | | |
| has_database_privilege(database,privilege) | 当前用户是否有访问数据库的权限 | CREATE/TEMPORARY | | |
| has_function_privilege(user,function,privilege) | 用户是否有访问函数的权限 | EXECUTE | | |
| has_function_privilege(function,privilege) | 当前用户是否有访问函数的权限 | EXECUTE | | |
| has_language_privilege(user,language,privilege) | 用户是否有访问语言的权限 | USAGE | | |
| has_language_privilege(language,privilege) | 当前用户是否有访问语言的权限 | USAGE | | |
| has_schema_privilege(user,schema,privilege) | 用户是否有访问模式的权限 | CREAT/USAGE | | |
| has_schema_privilege(schema,privilege) | 当前用户是否有访问模式的权限 | CREAT/USAGE | | |
| has_tablespace_privilege(user,tablespace,privilege) | 用户是否有访问表空间的权限 | CREATE | | |
上述函数仅部分,更多查看官方:https://www.postgresql.org/docs/
用户和权限
授权:
-- 给用户 fred 授权,允许他查询 emplyee 表
grant select on table employee to fred;
撤销权限:
-- 撤销用户fred 对 trade 表的查询权限
revoke select on trade from fred;
角色授权:
-- Fred、Alice、James、Jone 四位成员,现在你需要给数据分析组授权,允许他们 查询 trade 数据库的 public schema 中的所有表.
create role analysis;
grant analysis to fred, alice, james, jone;
grant select on all tables in schema public to analysis;
索引和约束
索引:
create table book(
id serial primary key ,
title text not null ,
meta jsonb default '{}'::jsonb,
price money,
isbn text not null ,
publish_at date not null
);
create unique index on book(isbn);
create index on book using gin(meta);
有兴趣可以看看我写的mysql相关语句和命令汇总:
长文一次说完MySQL常用语句和命令等汇总
也可以参考菜鸟教程的postgresql教程:https://www.runoob.com/postgresql/postgresql-tutorial.html
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)