Kubernetes资源清单篇:如何创建资源?
在Kubernetes中所有操作的内容,我们都称为“资源对象”,是由API Server基于HTTP/HTTPS接收并响应客户端的操作请求,是一种Restful风格的接口,将各种组件及操作内容都抽象成为标准的REST资源,如Namespace、Pod等,其中操作内容以JSON或yml格式数据进行操作。
本文讲解的是Kubernetes中的最为重要的一节—— 资源清单 ,我们想要在Kubernetes中部署Pod、Service等资源对象,都需要通过资源清单的方式来部署,无论是通过命令 kubectl ,还是可视化控制台,都是离不开资源清单的定义,本文重点讲述资源清单如何定义、如何创建及使用。
1、资源分类
根据资源的功能进行资源分类,Kubernetes资源对象可分为:
- 工作负载(Workload):Pod、ReplicaSet、Deployment、StatefulSet、DaemonSet、Job、CronJob。
- 发现和负载均衡(Discovery & LB):Service 、Ingress。
- 配置和存储(Config & Storage): Volume(存储卷)、CSI(容器存储接口,可以扩展各种各样的第三方存储卷)。
- 集群(Cluster) :Namespace、Node、Role、ClusterRole、RoleBinding(角色绑定)、ClusterRoleBinding(集群角色绑定)。
- 元数据(Metadata) :HPA、PodTemplate(Pod模板,用于让控制器创建Pod时使用的模板)、LimitRange(用来定义硬件资源限制的)。
一个应用通常需要多个资源的支撑,例如,使用Deployment资源管理应用实例(Pod)、使用ConfigMap资源保存应用配置、使用Service或Ingress资源暴露服务、使用Volume资源提供外部存储等。
2.资源清单
资源清单,等同于一个剧本,能够告诉我们每一步应该怎么去做,Kubernetes接收到这么一个剧本,就能够按照这个剧本去执行,以达到我们的预期。
在Kubernetes中,一般都是通过定义资源清单的方式去创建资源。一般使用yaml格式的文件来创建符合我们预期期望的资源,这样的yaml文件我们称为**资源清单** 。(也可以定义为json格式)
如,创建一个Pod资源:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vue-frontend
namespace: test
labels:
app: vue-frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: vue-frontend
image: xcbeyond/vue-frontend:latest
ports:
- name: port
containerPort: 80
hostPort: 8080接下来,以Pod资源定义为例展开对资源清单的详细说明。
2.1 资源清单定义
yaml格式的Pod资源清单定义文件的完整内容如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod # 资源类别
metadata: # 资源元数据
name: string
namespace: string
labels:
- name: string
annotations:
- name: string
spec: # 资源期望的状态
containers: # 容器列表
- name: string # 容器名称,下面的属性均属于对该容器的定义或约束
image: string
imagePullPolicy: [Always|Never|IfNotPresent]
command: [string]
args: [string]
workingDir: string
volumeMounts:
- name: string
mountPath: string
readOnly: boolean
ports:
- name: string
containerPort: int
hostPort: int
protocol: string
env:
- name: string
value: string
resources:
limits:
cpu: string
memory: string
requests:
cpu: string
memory: string
livenssProbe:
exec:
command: [string]
httpGet:
path: string
port: number
host: string
scheme: string
httpHeaders:
- name: string
value: string
tcpSocket:
port: number
initialDelaySeconds: 0
timeoutSeconds: 0
periodSeconds: 0
successThreshold: 0
failureThreshold: 0
……对各属性的详细说明如下表所示:
(必选属性,是必须存在的,否则创建失败。)
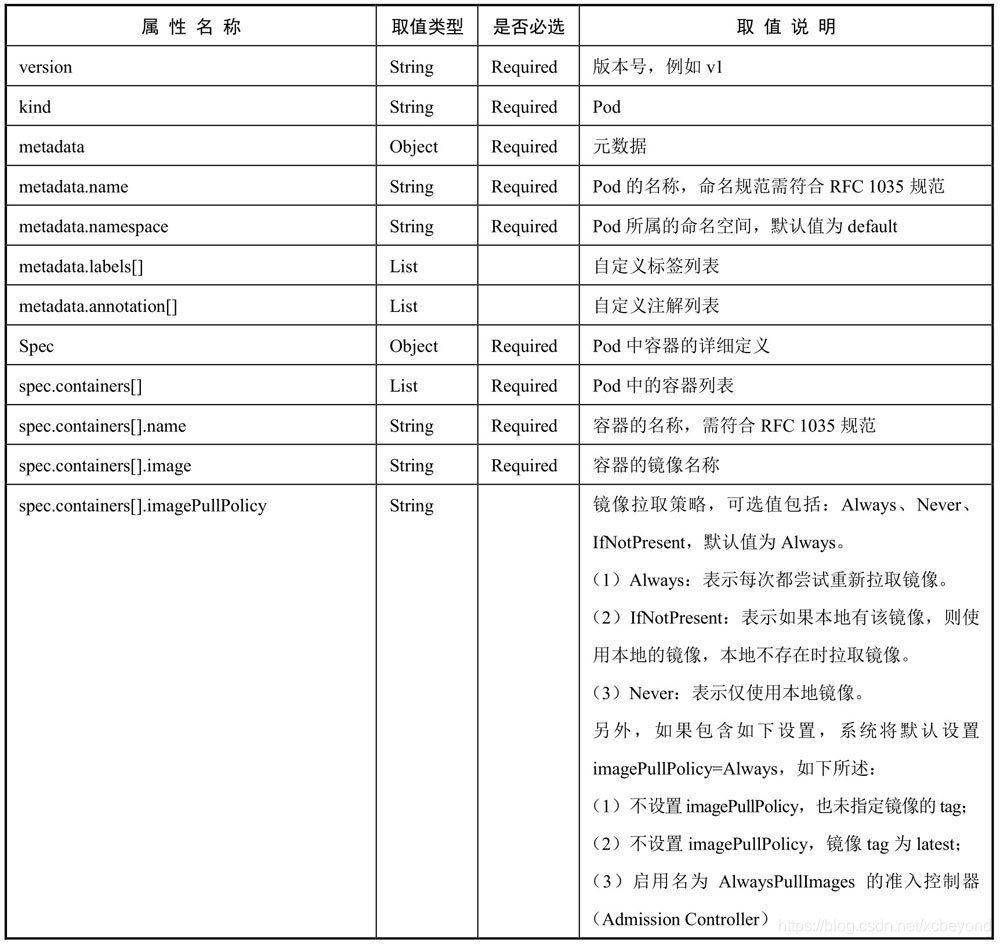
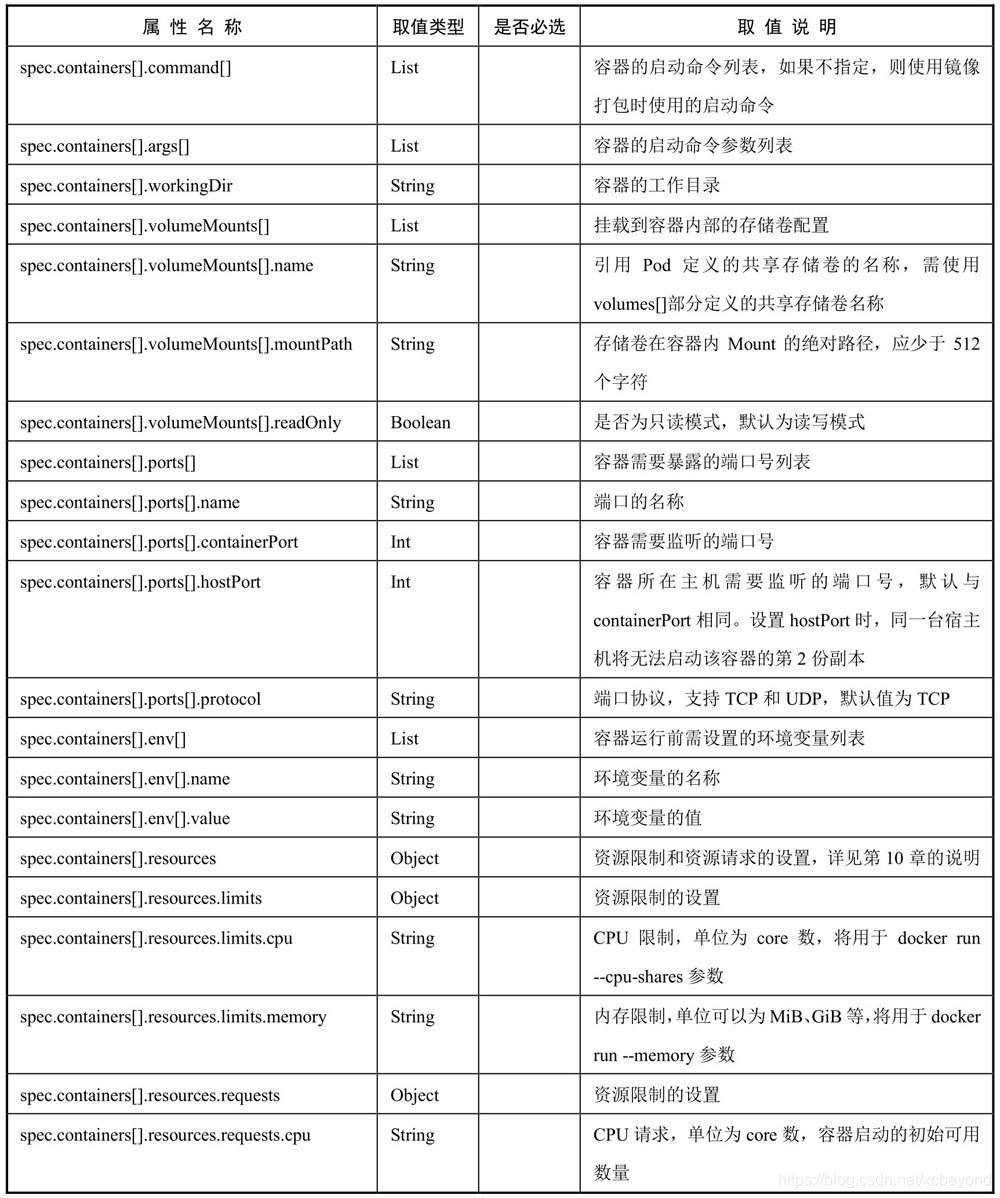
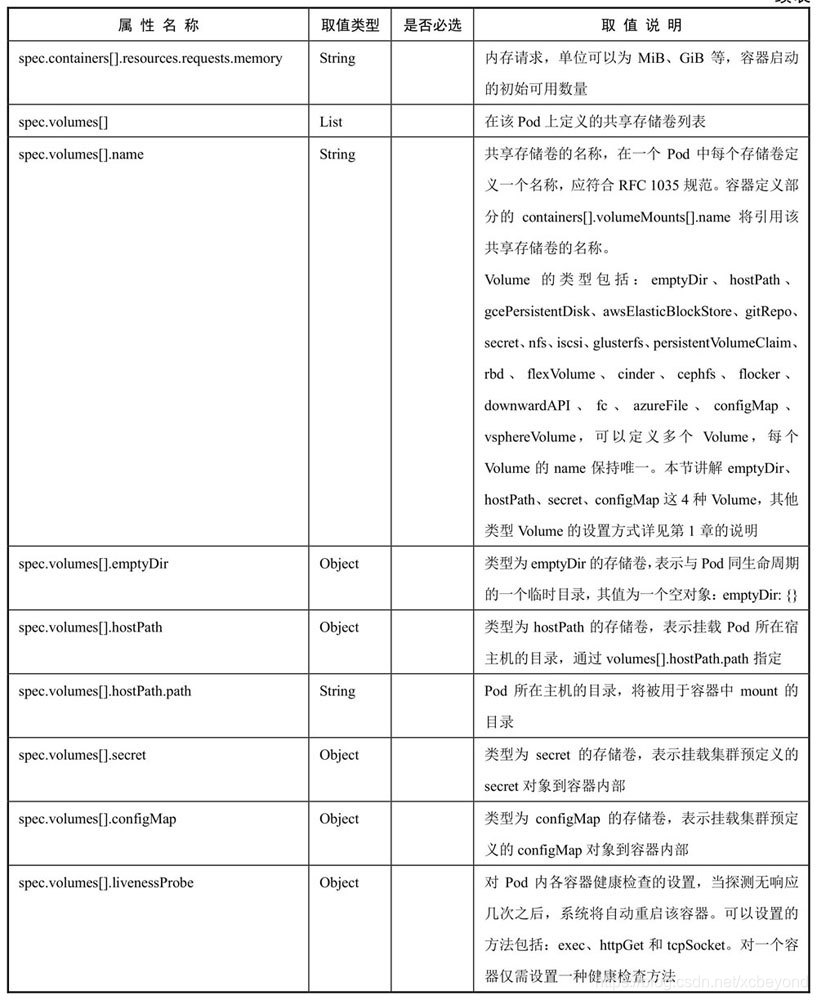
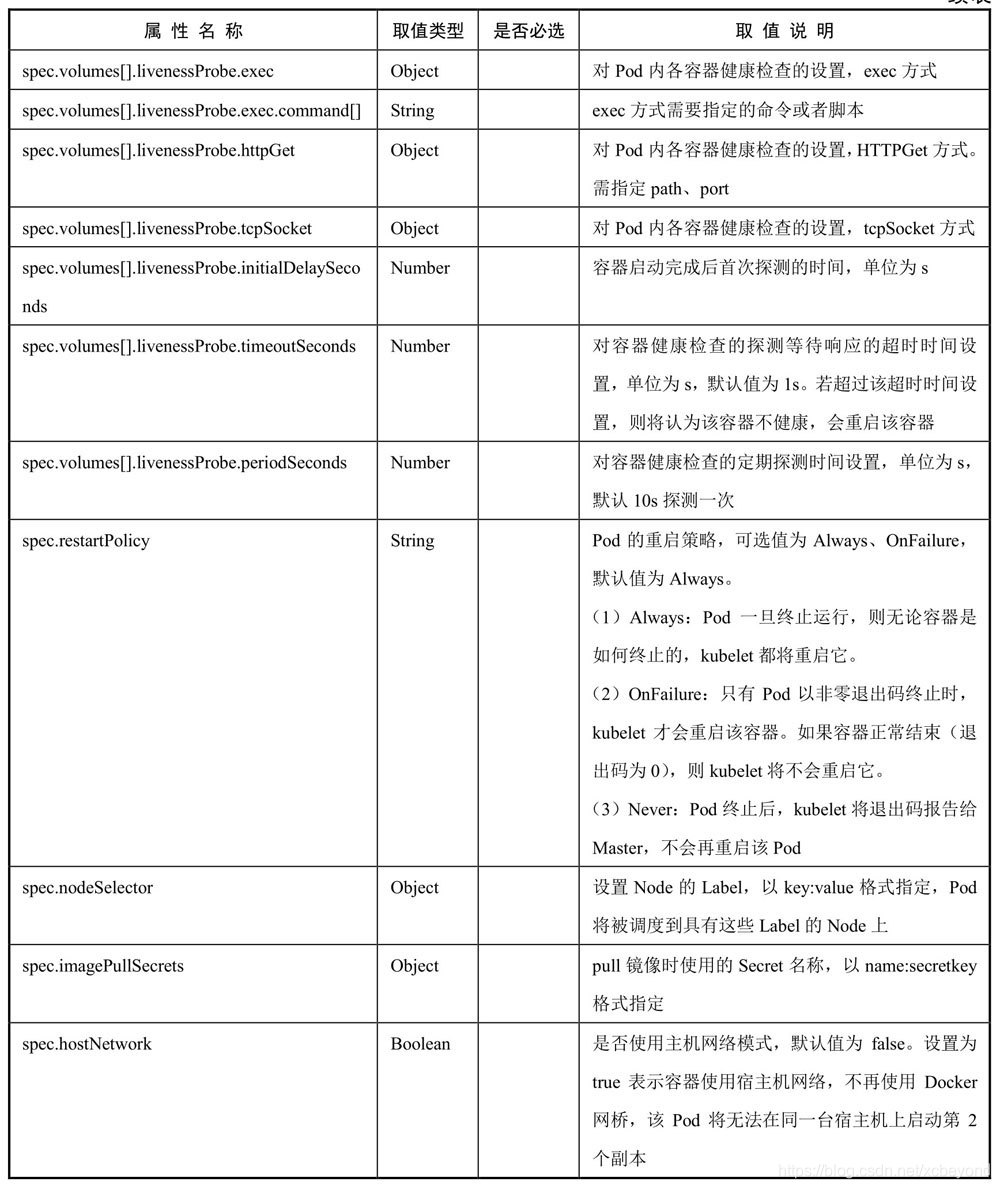
上述列举的是常用的属性,如果想查看全部属性,可以使用命令`kubectl explain pod`:
[xcbeyond@bogon ~]$ kubectl explain pod
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
DESCRIPTION:
Pod is a collection of containers that can run on a host. This resource is
created by clients and scheduled onto hosts.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
spec <Object>
Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
status <Object>
Most recently observed status of the pod. This data may not be up to date.
Populated by the system. Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status查看属性说明,使用如下命令,如:查看pod.spec.containers
[xcbeyond@bogon ~]$ kubectl explain pod.spec.containers
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: containers <[]Object>
DESCRIPTION:
List of containers belonging to the pod. Containers cannot currently be
added or removed. There must be at least one container in a Pod. Cannot be
updated.
A single application container that you want to run within a pod.
FIELDS:
args <[]string>
Arguments to the entrypoint. The docker image's CMD is used if this is not
provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the
container's environment. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in
the input string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped
with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be
expanded, regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be
updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/#running-a-command-in-a-shell
command <[]string>
Entrypoint array. Not executed within a shell. The docker image's
ENTRYPOINT is used if this is not provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME)
are expanded using the container's environment. If a variable cannot be
resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. The
$(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME).
Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless of whether the
variable exists or not. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/#running-a-command-in-a-shell
……2.2 示例
在命名空间test中,定义一个名为frontend的Pod。
(1)定义命名空间
为了便于后期测试,特定义一个新的命名空间test。(如果命名空间test已存在,则无需再建)
命名空间test的资源清单文件test-namespace.yaml如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: test执行 kubectl create 命令创建该Namespace:
[xcbeyond@bogon ~]$ kubectl create -f test-namespace.yaml
namespace/test created(2)定义Pod
定义一个名为frontend的Pod,由一个容器组成,资源清单文件frontend-pod.yaml如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: frontend
namespace: test
labels:
app: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: frontend
image: xcbeyond/vue-frontend:latest
ports:
- name: port
containerPort: 80
hostPort: 8080执行 kubectl create 命令创建该Pod:
[xcbeyond@bogon ~]$ kubectl create -f frontend-pod.yaml
pod/frontend created通过命令 kubectl get pods -n 查看,创建Pod的状态:
[xcbeyond@bogon ~]$ kubectl get pods -n test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
frontend 1/1 Runing 0 79s- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)