【愚公系列】2022年06月 .NET架构班 076-分布式中间件 ScheduleMaster的执行原理
一、ScheduleMaster的执行原理
1.全局架构设计
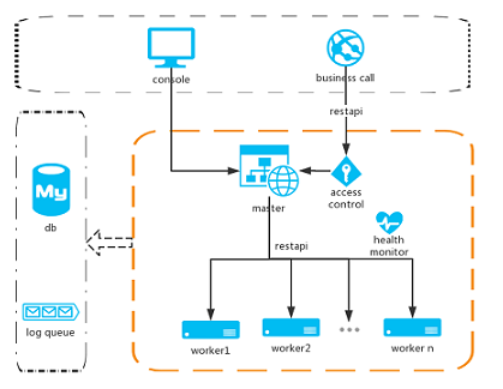
任务全局执行流程:客户端=>master=>work=>调用接口
1、master节点主要做了四件事情
- 选择work节点
- 指定work执行任务
- 对work节点进行健康检查
- 对任务进行故障转移
2、work节点主要做了四件事情
- 取出任务配置信息
- 使用Quartz根据配置运行任务
- 使用反射调用程序集
- 使用httpclient调用http 接口
2.数据库设计
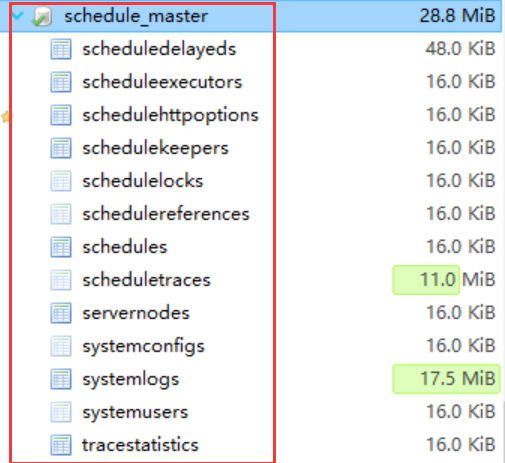
如图所示:
表结构设计为3大块组成
- 任务表 :任务表以schedules表为代表
- 节点表:节点表以servernodes表为代表
- 系统表:系统表以系systemusers为代表
这三个表为主表,这三个表在启动Hos.ScheduleMaster.Web项目的时候,会启动进行创建。记录了任务信息,节点信息,用户信息。
3.添加任务原理
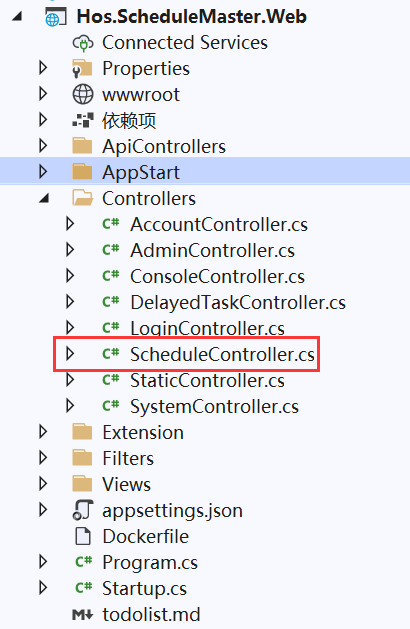
1、进入ScheduleController控制器中,找到Create方法
/// <summary>
/// 创建任务
/// </summary>
/// <param name="task"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ActionResult> Create(ScheduleInfo task)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return this.JsonNet(false, "数据验证失败!");
}
var admin = CurrentAdmin;
ScheduleEntity main = new ScheduleEntity
{
MetaType = task.MetaType,
CronExpression = task.CronExpression,
EndDate = task.EndDate,
Remark = task.Remark,
StartDate = task.StartDate,
Title = task.Title,
Status = (int)ScheduleStatus.Stop,
CustomParamsJson = task.CustomParamsJson,
RunLoop = task.RunLoop,
TotalRunCount = 0,
CreateUserName = admin.UserName
};
if (task.MetaType == (int)ScheduleMetaType.Assembly)
{
main.AssemblyName = task.AssemblyName;
main.ClassName = task.ClassName;
}
ScheduleHttpOptionEntity httpOption = null;
if (task.MetaType == (int)ScheduleMetaType.Http)
{
httpOption = new ScheduleHttpOptionEntity
{
RequestUrl = task.HttpRequestUrl,
Method = task.HttpMethod,
ContentType = task.HttpContentType,
Headers = task.HttpHeaders,
Body = task.HttpBody
};
}
var result = _scheduleService.Add(main, httpOption, task.Keepers, task.Nexts, task.Executors);
if (result.Status == ResultStatus.Success)
{
if (task.RunNow)
{
var start = await _scheduleService.Start(main);
return this.JsonNet(true, "任务创建成功!启动状态为:" + (start.Status == ResultStatus.Success ? "成功" : "失败"), Url.Action("Index"));
}
return this.JsonNet(true, "任务创建成功!", Url.Action("Index"));
}
return this.JsonNet(false, "任务创建失败!");
}
2、进入ScheduleService类中,找到Add方法
/// <summary>
/// 添加一个任务
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model"></param>
/// <param name="httpOption"></param>
/// <param name="keepers"></param>
/// <param name="nexts"></param>
/// <param name="executors"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public ServiceResponseMessage Add(ScheduleEntity model, ScheduleHttpOptionEntity httpOption, List<int> keepers, List<Guid> nexts, List<string> executors = null)
{
if (executors == null || !executors.Any())
{
//没有指定worker就根据权重选择2个
executors = _nodeService.GetAvaliableWorkerByPriority(null, 2).Select(x => x.NodeName).ToList();
}
if (!executors.Any())
{
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "没有可用节点!");
}
model.CreateTime = DateTime.Now;
var user = _repositoryFactory.SystemUsers.FirstOrDefault(x => x.UserName == model.CreateUserName);
if (user != null)
{
model.CreateUserId = user.Id;
}
//保存主信息
_repositoryFactory.Schedules.Add(model);
//创建并保存任务锁
_repositoryFactory.ScheduleLocks.Add(new ScheduleLockEntity { ScheduleId = model.Id, Status = 0 });
//保存http数据
if (httpOption != null)
{
httpOption.ScheduleId = model.Id;
_repositoryFactory.ScheduleHttpOptions.Add(httpOption);
}
//保存运行节点
_repositoryFactory.ScheduleExecutors.AddRange(executors.Select(x => new ScheduleExecutorEntity
{
ScheduleId = model.Id,
WorkerName = x
}));
//保存监护人
if (keepers != null && keepers.Count > 0)
{
_repositoryFactory.ScheduleKeepers.AddRange(keepers.Select(x => new ScheduleKeeperEntity
{
ScheduleId = model.Id,
UserId = x
}));
}
//保存子任务
if (nexts != null && nexts.Count > 0)
{
_repositoryFactory.ScheduleReferences.AddRange(nexts.Select(x => new ScheduleReferenceEntity
{
ScheduleId = model.Id,
ChildId = x
}));
}
//事务提交
if (_unitOfWork.Commit() > 0)
{
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Success, "任务创建成功!", model.Id);
}
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "数据保存失败!");
}
3、进入RepositoryFactory类中,找到

4.任务启动原理
1、进入ScheduleController控制器中,找到_scheduleService.Add()方法
2、然后进入到IScheduleService中,找到Start方法
/// <summary>
/// 启动一个任务
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public async Task<ServiceResponseMessage> Start(ScheduleEntity model)
{
if (model == null) return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "任务信息不能为空!");
if (model.Status != (int)ScheduleStatus.Stop)
{
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "任务在停止状态下才能启动!");
}
if (model.EndDate.HasValue && model.EndDate < DateTime.Now)
{
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "任务结束时间不能小于当前时间!");
}
return await InnerStart(model.Id);
}
3、然后在Start方法中,找到InnerStart方法
private async Task<ServiceResponseMessage> InnerStart(Guid sid)
{
//启动任务
bool success = await _workerDispatcher.ScheduleStart(sid);
if (success)
{
//启动成功后更新任务状态为运行中
_repositoryFactory.Schedules.UpdateBy(m => m.Id == sid, m => new ScheduleEntity
{
Status = (int)ScheduleStatus.Running
});
if (await _unitOfWork.CommitAsync() > 0)
{
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Success, "任务启动成功!");
}
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "更新任务状态失败!");
}
else
{
await _workerDispatcher.ScheduleStop(sid);
_repositoryFactory.Schedules.UpdateBy(m => m.Id == sid, m => new ScheduleEntity
{
Status = (int)ScheduleStatus.Stop,
NextRunTime = null
});
await _unitOfWork.CommitAsync();
return ServiceResult(ResultStatus.Failed, "任务启动失败!");
}
}
4、然后在InnerStart方法中,找到WorkerDispatcher类
5、然后在WorkerDispatcher类中,找到ScheduleStart方法
public async Task<bool> ScheduleStart(Guid sid)
{
return await DispatcherHandler(sid, async (ServerNodeEntity node) =>
{
_scheduleClient.Server = node;
return await _scheduleClient.Start(sid);
});
}
6、然后在ScheduleStart方法中,找到DispatcherHandler
private async Task<bool> DispatcherHandler(Guid sid, RequestDelegate func)
{
var nodeList = _nodeService.GetAvaliableWorkerForSchedule(sid);
if (nodeList.Any())
{
foreach (var item in nodeList)
{
if (!await func(item))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
throw new InvalidOperationException("running worker not found.");
}
7、然后在ScheduleStart方法中,找到ScheduleServiceClient类
8、然后在ScheduleServiceClient类中,找到Start方法
public async Task<bool> Start(Guid sid)
{
return await PostRequest("/api/quartz/start", sid);
}
9、进入到Hos.ScheduleMaster.QuartzHost项目中,找到QuartzController类
10、进入到QuartzController类中,找到Start方法
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Start([FromForm]Guid sid)
{
bool success = await QuartzManager.StartWithRetry(sid);
if (success) return Ok();
return BadRequest();
}
11、进入到Start方法中,找到QuartzManager类
12、进入到QuartzManager类,找到StartWithRetry方法
/// <summary>
/// 启动一个任务,带重试机制
/// </summary>
/// <param name="task"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static async Task<bool> StartWithRetry(Guid sid)
{
var jk = new JobKey(sid.ToString().ToLower());
if (await _scheduler.CheckExists(jk))
{
return true;
}
ScheduleContext context = GetScheduleContext(sid);
IHosSchedule schedule = await HosScheduleFactory.GetHosSchedule(context);
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
try
{
await Start(schedule);
return true;
}
catch (SchedulerException sexp)
{
LogHelper.Error($"任务启动失败!开始第{i + 1}次重试...", sexp, context.Schedule.Id);
}
}
//最后一次尝试
await Start(schedule);
return true;
}
catch (SchedulerException sexp)
{
LogHelper.Error($"任务所有重试都失败了,已放弃启动!", sexp, context.Schedule.Id);
return false;
}
catch (Exception exp)
{
LogHelper.Error($"任务启动失败!", exp, context.Schedule.Id);
return false;
}
}
13、进入到StartWithRetry方法中,找到HosScheduleFactory类
14、进入到HosScheduleFactory类中,找到GetHosSchedule方法
public static async Task<IHosSchedule> GetHosSchedule(ScheduleContext context)
{
IHosSchedule result;
switch ((ScheduleMetaType)context.Schedule.MetaType)
{
case ScheduleMetaType.Assembly:
{
result = new AssemblySchedule();
await LoadPluginFile(context.Schedule);
break;
}
case ScheduleMetaType.Http:
{
result = new HttpSchedule();
break;
}
default: throw new InvalidOperationException("unknown schedule type.");
}
result.Main = context.Schedule;
result.CustomParams = ConvertParamsJson(context.Schedule.CustomParamsJson);
result.Keepers = context.Keepers;
result.Children = context.Children;
result.CancellationTokenSource = new System.Threading.CancellationTokenSource();
result.CreateRunnableInstance(context);
result.RunnableInstance.TaskId = context.Schedule.Id;
result.RunnableInstance.CancellationToken = result.CancellationTokenSource.Token;
result.RunnableInstance.Initialize();
return result;
}
15、进入到QuartzManager类,找到Start方法
private static async Task Start(IHosSchedule schedule)
{
JobDataMap map = new JobDataMap
{
new KeyValuePair<string, object> ("instance",schedule),
};
string jobKey = schedule.Main.Id.ToString();
try
{
IJobDetail job = JobBuilder.Create().OfType(schedule.GetQuartzJobType()).WithIdentity(jobKey).UsingJobData(map).Build();
//添加监听器
var listener = new JobRunListener(jobKey);
listener.OnSuccess += StartedEvent;
_scheduler.ListenerManager.AddJobListener(listener, KeyMatcher<JobKey>.KeyEquals(new JobKey(jobKey)));
ITrigger trigger = GetTrigger(schedule.Main);
await _scheduler.ScheduleJob(job, trigger, schedule.CancellationTokenSource.Token);
using (var scope = new Core.ScopeDbContext())
{
var db = scope.GetDbContext();
var task = db.Schedules.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == schedule.Main.Id);
if (task != null)
{
task.NextRunTime = TimeZoneInfo.ConvertTimeFromUtc(trigger.GetNextFireTimeUtc().Value.UtcDateTime, TimeZoneInfo.Local);
await db.SaveChangesAsync();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new SchedulerException(ex);
}
LogHelper.Info($"任务[{schedule.Main.Title}]启动成功!", schedule.Main.Id);
_ = Task.Run(async () =>
{
while (true)
{
if (schedule.RunnableInstance == null) break;
var log = schedule.RunnableInstance.ReadLog();
if (log != null)
{
LogManager.Queue.Write(new SystemLogEntity
{
Category = log.Category,
Message = log.Message,
ScheduleId = log.ScheduleId,
Node = log.Node,
StackTrace = log.StackTrace,
TraceId = log.TraceId,
CreateTime = log.CreateTime
});
}
else
{
await Task.Delay(3000);
}
}
});
}
16、Start方法为最核心方法。使用Quartz框架进行任务调度
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)