设计模式-行为型模式讲解二(模板、策略、解释器)
一、行为型设计模式
上篇,我们呢讲解了-行为型设计模式的责任链、命令、迭代器模式。
文章地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43692950/article/details/120404903
这篇文章我们来讲解下行为型设计模式的模板方法、策略、解释器模式。
二、模板模式
在模板模式(Template Pattern)中,有些又叫模板方法设计模式,一个抽象类公开定义了执行它的方法的方式/模板。它的子类可以按需要重写方法实现,但调用将以抽象类中定义的方式进行。
它的优点有封装不变扩展可变, 公共代码便于维护,行为由父类控制子类负责具体实现。
举个例子:还是拿常用的画形状的案例来说,比如我们画一个图像之后还要加边框,还要画颜色,如果我们画每个图像都要再考虑怎么加入边框和颜色,就显得有点臃肿,因为加入边框和颜色对所有的图像都是一致的,此时就可以将图形边框和颜色在一个统一的模板中定义规则,具体的实现放在具体的子类中。
下面使用程序演示下上面的例子:
- 定义形状的接口,并定义画图形、加边框、画颜色和生成最终的图形
public interface ShapeInterFace {
void drawShape();
void drawBorder();
void drawColor();
void genShape();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 定义模板
public abstract class ShapeTemplate implements ShapeInterFace {
@Override
public void genShape() {
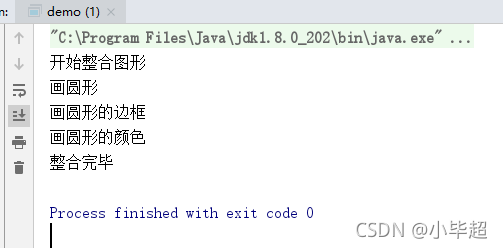
System.out.println("开始整合图形");
drawShape();
drawBorder();
drawColor();
System.out.println("整合完毕");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 定义圆形的实现
public class CircleShapeImpl extends ShapeTemplate {
@Override
public void drawShape() {
System.out.println("画圆形");
}
@Override
public void drawBorder() {
System.out.println("画圆形的边框");
}
@Override
public void drawColor() {
System.out.println("画圆形的颜色");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 演示
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeInterFace shape = new CircleShapeImpl();
shape.genShape();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
三、策略模式
在策略模式(Strategy Pattern)中,一个类的行为或其算法可以在运行时更改。我们创建表示各种策略的对象和一个行为随着策略对象改变而改变的 context 对象。策略对象改变 context 对象的执行算法。
还是采用画图形的例子来说,画不同的图形,通过一个标识来做动作,而不是调用具体的类。
下面使用程序演示下上面的例子:
- 定义形状接口
public interface ShapeInterFace {
void draw();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 定义圆形的实现
public class CricleShape implements ShapeInterFace {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("画圆形!");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 定义矩形的实现
public class RectangleShape implements ShapeInterFace {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("画矩形");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 定义三角形的实现
public class TriangleShape implements ShapeInterFace {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("画三角形");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 定义形状工厂,根据策略拿到不同的实现
public class FactoryStrategy {
private static Map<String, ShapeInterFace> strategys = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ShapeInterFace>();
static {
strategys.put("circle", new CricleShape());
strategys.put("rectangle", new RectangleShape());
strategys.put("triangle", new TriangleShape());
}
public static ShapeInterFace getStrategy(String strategyId) {
return strategys.get(strategyId);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 演示
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FactoryStrategy.getStrategy("circle").draw();
FactoryStrategy.getStrategy("rectangle").draw();
FactoryStrategy.getStrategy("triangle").draw();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

四、解释器模式
解释器模式(Interpreter Pattern)提供了评估语言的语法或表达式的方式,这种模式实现了一个表达式接口,该接口解释一个特定的上下文。这种模式被用在 SQL 解析、符号处理引擎等。
举个例子,拿SQL解析来看,我们写的一般都是SQL指令然后交给数据库就可以拿到我们想要的数据了,数据库是怎么知道我们查那张表的那些数据呢,其实我们将SQL指令交给数据库后,数据库就在对SQL进行解释,检查语法是否正确,并确定查询的表,查询的字段,和条件等。
下面使用程序演示下上面的例子,这里简单的做下SQL 解析,便于理解这种设计模式:
- 定义SQL解析接口
public interface SqlnterFace {
SqlnterFace interpretation(String sql);
void execute();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 定义SELECT查询的实现
public class SelectSqlImpl implements SqlnterFace {
String sql;
String columns;
String table;
String condition;
@Override
public SqlnterFace interpretation(String sql) {
System.out.println("开始解释SQL ");
if (!sql.contains("SELECT")) {
System.out.println("SQL 指令错误!");
return this;
}
this.sql = sql;
this.columns = sql.split("FROM")[0].split(" ")[1].trim();
this.table = sql.split("FROM")[1].split("WHERE")[0].trim();
this.condition = sql.split("WHERE")[1].trim();
System.out.println("解释结果: 查询的表为:" + this.table + " 查询的列为:" + this.columns + " 条件:" + this.condition);
return this;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("执行SQL: " + this.sql);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 演示
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sql = "SELECT name,age FROM user WHERE id=1 ";
SqlnterFace sqlExe = new SelectSqlImpl();
sqlExe.interpretation(sql).execute();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:小毕超,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/qq_43692950/article/details/120405226
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)