【课程设计|C++】实现两个链表的合并

前言
Hello!
非常感谢您阅读海轰的文章,倘若文中有错误的地方,欢迎您指出~
自我介绍 ଘ(੭ˊᵕˋ)੭
昵称:海轰
标签:程序猿|C++选手|学生
简介:因C语言结识编程,随后转入计算机专业,获得过国家奖学金,有幸在竞赛中拿过一些国奖、省奖…已保研。
学习经验:扎实基础 + 多做笔记 + 多敲代码 + 多思考 + 学好英语!
唯有努力💪
知其然 知其所以然!
1. 实现两个链表的合并
基本功能与要求
(1)建立两个链表A和B,链表元素个数分别为m和n个。
(2)假设元素分别为(x1,x2,…,xm),和(y1,y2,…,yn)。把它们合并成一个线性表C:
当m>=n时,C=x1,y1,x2,y2,…,xn,yn,…,xm
当n>m时, C=y1,x1,y2,x2,…,ym,xm,…,yn;
(3)输出线性表C。
(4)用直接插入排序法对C进行升序排序,生成链表D,并输出链表D。
测试数据
(1) A表(30,41,15,12,56,80)
B表(23,56,78,23,12,33,79,90,55)
(2) A表(30,41,15,12,56,80,23,12,34)
B表(23,56,78,23,12)
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class t>
class node
{
public:
t data;
node<t> *next;
node(node<t> *ptr = NULL) { next = ptr; }
node(t a, node<t> *ptr = NULL)
{
data = a;
next = ptr;
}
};
template <class t>
class linklist
{
public:
void merge(linklist<t> &l1, linklist<t> &l2)
{
int m = l1.length();
int n = l2.length();
node<t> *r;
node<t> *s;
r = first;
node<t> *p = l1.first->next;
cout << p->data << endl;
node<t> *q = l2.first->next;
if (m >= n)
{
while (p != NULL && q != NULL)
{
s = new node<t>(p->data);
r->next = s;
r = s;
s = new node<t>(q->data);
r->next = s;
r = s;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
r->next = p;
}
else
{
while (p != NULL && q != NULL)
{
s = new node<t>(q->data);
r->next = s;
r = s;
s = new node<t>(p->data);
r->next = s;
r = s;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
r->next = q;
}
}
void sort()
{
node<t> *L = first->next;
node<t> *p, *q, *pre;
p = L->next->next;
L->next->next = NULL;
while (p)
{
q = p->next;
pre = L;
while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->data < p->data)
pre = pre->next;
p->next = pre->next;
pre->next = p;
p = q;
}
// first = L
// node<t> *r;
// node<t> *p = l.first->next;
// r = first;
// node<t> *newNode = new node<t>(p->data);
// r->next = newNode;
// r = newNode;
// p = p->next;
// while(p != NULL) {
// t num = r->data;
// newNode = new node<t>(p->data);
// if(p->data > num) {
// // newNode = new node<t>(p->data);
// r->next = newNode;
// r = newNode;
// } else {
// }
// p = p->next;
// }
}
void rel()
{
node<t> *p;
node<t> *s;
p = first->next;
s = p->next;
first->next = NULL;
while (p != NULL)
{
p->next = first->next;
first->next = p;
p = s;
// cout<<"1"<<endl;
if (p != NULL)
{
s = p->next;
}
}
}
linklist() { first = new node<t>; }
linklist(t x) { first = new node<t>(x); }
void creat(t end)
{
node<t> *newnode;
t val;
cin >> val;
while (val != end)
{
newnode = new node<t>(val);
newnode->next = first->next;
first->next = newnode;
cin >> val;
}
}
void creat1(t end)
{
node<t> *r;
node<t> *s;
r = first;
t val;
cin >> val;
while (val != end)
{
s = new node<t>(val);
r->next = s;
r = s;
cin >> val;
}
// first=new node<t>
r->next = NULL;
}
void print()
{
node<t> *p = first->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
cout << p->data << "--->>";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
int length()
{
node<t> *p;
p = first->next;
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
t get(int i)
{
node<t> *p;
int count = 1;
p = first->next;
while (p != NULL && count < i)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL)
throw "位置";
else
return p->data;
}
void insert(t x, int i)
{
node<t> *p;
node<t> *s;
p = first;
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL && count < i - 1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL)
throw "位置";
else
{
s = new node<t>(x);
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
}
}
int locate(t x)
{
node<t> *p;
p = first->next;
int count = 1;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->data == x)
return count;
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return 0;
}
void del(int i)
{
node<t> *p;
node<t> *q;
p = first;
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL && count < i - 1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL || p->next == NULL)
throw "位置";
else
{
q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
delete q;
}
}
~linklist()
{
node<t> *p;
while (first != NULL)
{
p = first;
first = first->next;
delete p;
}
}
// private:
node<t> *first;
};
linklist<int> merge(linklist<int> &l1, linklist<int> &l2)
{
int m = l1.length();
int n = l2.length();
cout << "m =" << m << endl;
linklist<int> ans;
// linklist<int> ans;
// cout << "((" << endl;
node<int> *cur = ans.first;
cout << "((" << endl;
// cout << ans.first->data;
node<int> *p = l1.first;
node<int> *q = l2.first;
if (m >= n)
{
while (p != NULL && q != NULL)
{
cur->next = p;
cur = cur->next;
cur->next = q;
cur = cur->next;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
cur->next = p;
}
else
{
while (p != NULL && q != NULL)
{
cur->next = q;
cur = cur->next;
cur->next = p;
cur = cur->next;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
cur->next = q;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
linklist<int> L;
linklist<int> A;
linklist<int> B;
linklist<int> C;
linklist<int> D;
int key = 1;
int choice;
int choice1;
int choice2;
while (key == 1)
{
cout << "+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++" << endl;
cout << "+ 单链表 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 1.创建单链表(头部插入) +" << endl;
cout << "+ 2. 创建单链表(尾部插入)+" << endl;
cout << "+ 3.查找第i个结点的值 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 4.查找元素x的结点位置 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 5.在第i个位置插入元素x +" << endl;
cout << "+ 6.删除第i个位置的值 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 7.输出单链表各元素 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 8.旋转链表 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 9.新建两个链表 +" << endl;
cout << "+ 10.直接插入排序 +" << endl;
cout << "输入你的选择:(1---10)" << endl;
cin >> choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
{
cout << "输入需要存储的数据 以0结尾 例如 1 2 3 4 0" << endl;
L.creat(0);
cout << "单链表创建完成!" << endl;
}
break;
case 2:
{
cout << "输入需要存储的数据 以0结尾 例如 1 2 3 4 0" << endl;
L.creat1(0);
cout << "单链表创建完成!" << endl;
}
break;
case 3:
{
cout << "输入查找元素的位置i(第i个结点):";
cin >> choice1;
cout << "第" << choice1 << "个结点的值是:";
cout << L.get(choice1) << endl;
}
break;
case 4:
{
cout << "输入查找元素的值:";
cin >> choice1;
cout << "该元素在第" << L.locate(choice1) << "个位置!" << endl;
}
break;
case 5:
{
cout << "输入插入元素的位置(第i个) :";
cin >> choice1;
cout << "输入插入元素的值:";
cin >> choice2;
L.insert(choice2, choice1);
cout << "插入完成!" << endl;
}
break;
case 6:
{
cout << "输入删除元素的位置(第i个):" << endl;
cin >> choice1;
L.del(choice1);
cout << "删除完成!" << endl;
}
break;
case 7:
{
cout << "该链表元素的值是:" << endl;
L.print();
}
break;
case 8:
{
L.rel();
// cout<<"1"<<endl;
}
case 9:
{
cout << "输入需要存储的数据 以0结尾 例如 1 2 3 4 0" << endl;
A.creat1(0);
cout << "单链表创建完成!" << endl;
cout << "输入需要存储的数据 以0结尾 例如 1 2 3 4 0" << endl;
B.creat1(0);
cout << "单链表创建完成!" << endl;
C.merge(A, B);
C.print();
// break;
}
break;
case 10:
{
C.sort();
C.print();
}
break;
}
cout << "是否继续?(1:继续 0:退出)" << endl;
cin >> key;
system("cls");
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
实验截图
菜单

合并两个链表
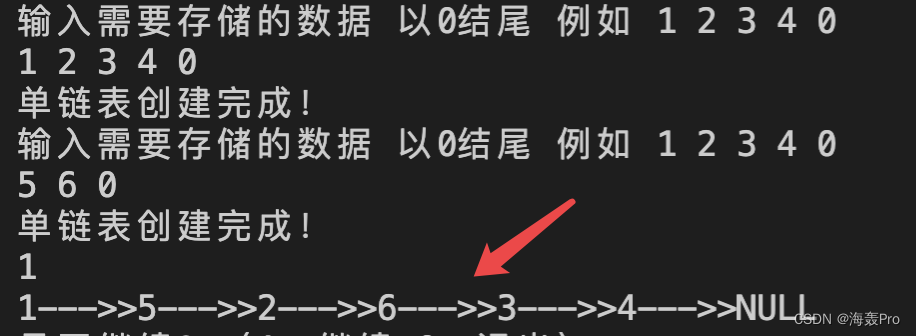
直接插入排序

结语
文章仅作为个人学习笔记记录,记录从0到1的一个过程
希望对您有一点点帮助,如有错误欢迎小伙伴指正

文章来源: haihong.blog.csdn.net,作者:海轰Pro,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:haihong.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125306492
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)