SQL第四练:字符串处理函数
【摘要】
1修复表中的名字
1.1题目描述
表: Users
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------...
1修复表中的名字
1.1题目描述
表: Users
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| name | varchar |
+----------------+---------+
user_id 是该表的主键。
该表包含用户的 ID 和名字。名字仅由小写和大写字符组成。
编写一个 SQL 查询来修复名字,使得只有第一个字符是大写的,其余都是小写的。
返回按 user_id 排序的结果表。
查询结果格式示例如下:
输入:
Users table:
+---------+-------+
| user_id | name |
+---------+-------+
| 1 | aLice |
| 2 | bOB |
+---------+-------+
输出:
+---------+-------+
| user_id | name |
+---------+-------+
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
+---------+-------+
1.2求解
第一次我的想法就是直接进行字符串拼接:
select user_id,
concat(upper(left(name,1)) ,lower(SUBSTRING(name,2))) as name
from Users
order by user_id ASC
执行:

1.3知识点
- concat(str1,str2) 连接 拼接两个字符串
- upper(str) 大写 字符串大写
- lower(str) 小写 字符串小写
- LENGTH(str) 长度 字符串长度
- SUBSTRING(str,start,end) 截取 截取字符串,start开始,end结束。
- LEFT(str,len) 截取 从左边开始截取字符串
- RIGHT(str,len) 截取 从右边开始截取字符串
2按日期分组销售产品
2.1题目描述
表 Activities:
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| sell_date | date |
| product | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
此表没有主键,它可能包含重复项。
此表的每一行都包含产品名称和在市场上销售的日期。
编写一个 SQL 查询来查找每个日期、销售的不同产品的数量及其名称。
每个日期的销售产品名称应按词典序排列。
返回按 sell_date 排序的结果表。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
输入:
Activities 表:
+------------+-------------+
| sell_date | product |
+------------+-------------+
| 2020-05-30 | Headphone |
| 2020-06-01 | Pencil |
| 2020-06-02 | Mask |
| 2020-05-30 | Basketball |
| 2020-06-01 | Bible |
| 2020-06-02 | Mask |
| 2020-05-30 | T-Shirt |
+------------+-------------+
输出:
+------------+----------+------------------------------+
| sell_date | num_sold | products |
+------------+----------+------------------------------+
| 2020-05-30 | 3 | Basketball,Headphone,T-shirt |
| 2020-06-01 | 2 | Bible,Pencil |
| 2020-06-02 | 1 | Mask |
+------------+----------+------------------------------+
解释:
对于2020-05-30,出售的物品是 (Headphone, Basketball, T-shirt),按词典序排列,并用逗号 ',' 分隔。
对于2020-06-01,出售的物品是 (Pencil, Bible),按词典序排列,并用逗号分隔。
对于2020-06-02,出售的物品是 (Mask),只需返回该物品名。
2.2求解
重复计算用distinct,count计数,
select
sell_date,
count(distinct product) num_sold,
GROUP_CONCAT(distinct product) products # 默认都好拼接
from
activities
group by sell_date #按照日期分组
order by sell_date; # 按照日期排序
执行:
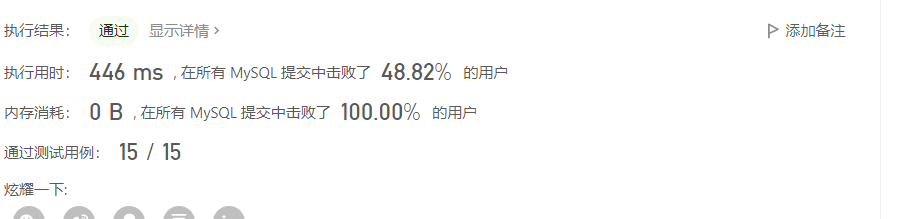
2.3知识点
- GROUP_CONCAT在组中的值之间插入的文字值。如果不指定分隔符,则GROUP_CONCAT函数使用逗号(,)作为默认分隔符
- group by按什么分组
- order by 按什么排序,默认升序。desc降序。
3患某种疾病的患者
3.1题目描述
患者信息表: Patients
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| patient_id | int |
| patient_name | varchar |
| conditions | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
patient_id (患者 ID)是该表的主键。
'conditions' (疾病)包含 0 个或以上的疾病代码,以空格分隔。
这个表包含医院中患者的信息。
写一条 SQL 语句,查询患有 I 类糖尿病的患者 ID (patient_id)、患者姓名(patient_name)以及其患有的所有疾病代码(conditions)。I 类糖尿病的代码总是包含前缀 DIAB1 。
按 任意顺序 返回结果表。
查询结果格式如下示例所示。
输入:
Patients表:
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| 1 | Daniel | YFEV COUGH |
| 2 | Alice | |
| 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
| 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
| 5 | Alain | DIAB201 |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
输出:
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
| 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
解释:Bob 和 George 都患有代码以 DIAB1 开头的疾病。
3.2求解
使用locate(字符,字段名)函数,如果包含,返回>0的数,否则返回0 ,该方法仅仅只能解决包含这个字符,而不是前缀问题,所以会测试有小问题。
select patient_id,patient_name,conditions
from Patients where
locate('DIAB1', conditions)>0;
使用like求解:
select patient_id,patient_name,conditions
from Patients
where conditions like "DIAB1%" # 最前面
or conditions like "% DIAB1%" # 在中间,注意有空格
执行:
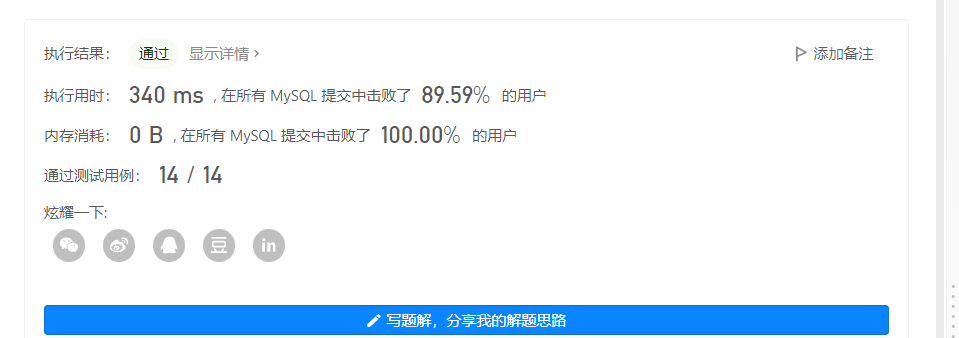
3.4知识点
- like关键词查询
文章来源: chuanchuan.blog.csdn.net,作者:川川菜鸟,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:chuanchuan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125202093
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)