数据结构与算法之双链表
⭐️前面的话⭐️
本篇文章带大家认识数据结构与算法之双链表,链表是一种在逻辑结构连续,物理结构不连续的数据结构,可以分为单链表与双链表两类,正文将介绍双链表的增删查改,对于链表的概念已经在《数据结构与算法之单链表》一文中已经介绍过了,所以本文对于链表理论概念方面不再赘述,上次实现了不带头结点的单链表,这次就介绍一个带头的双链表吧!描述代码:Java。
📒博客主页:未见花闻的博客主页
🎉欢迎关注🔎点赞👍收藏⭐️留言📝
📌本文由未见花闻原创!
📆华为云首发时间:🌴2022年5月31日🌴
✉️坚持和努力一定能换来诗与远方!
💭参考书籍:📚《Java核心技术卷1》,📚《数据结构》,📚《Java编程思想》
💬参考在线编程网站:🌐牛客网🌐力扣
博主的码云gitee,平常博主写的程序代码都在里面。
博主的github,平常博主写的程序代码都在里面。
🍭作者水平很有限,如果发现错误,一定要及时告知作者哦!感谢感谢!
1.双链表理论基础
1.1双链表的基本结构
我们知道链表在实际当中有8种,根据是否带头结点,是否循环,引用指向这三点派生出来许许多多类型的链表,但是本质上都是一样的,它始终在物理结构是离散的,逻辑结构上是连续的。本文将介绍的是带头结点非循环的双链表,下文都以双链表简称。
首先,无论是什么类型的链表,它结点的基本结构是一样的,都是数据域+引用(指针)域,单链表引用域只有一个方向的指向,而双链表引用域有前后双向的指向。
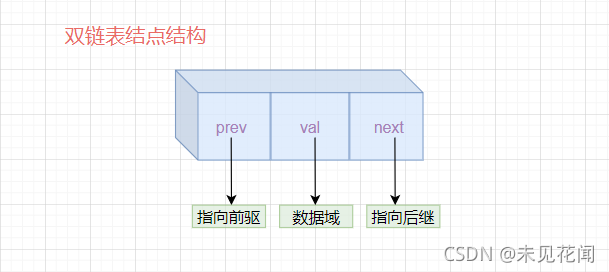
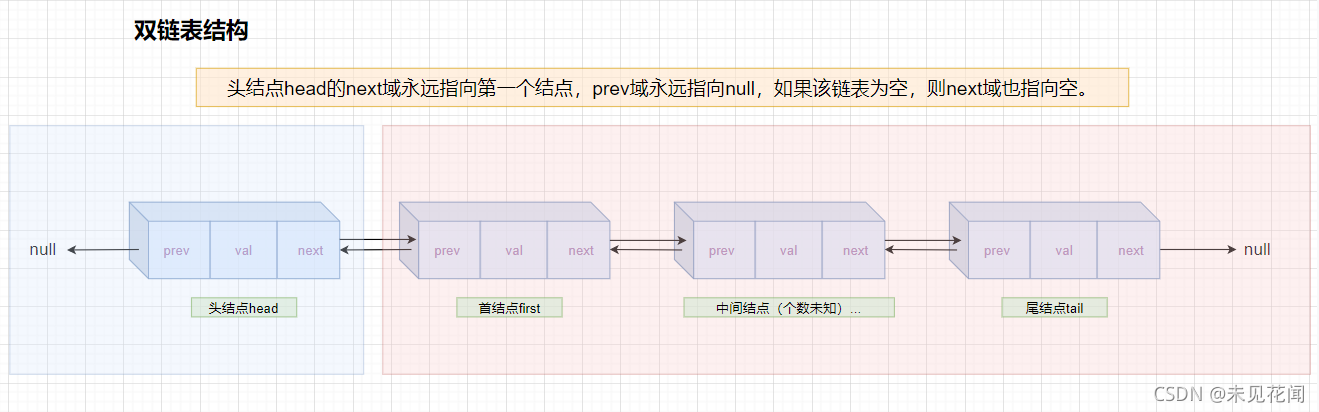
对于带头(傀儡)结点的双链表:头结点head的next域永远指向第一个结点,prev域永远指向null,如果该链表为空,则next域也指向空。
1.2双链表的与单链表的区别
单链表与双链表最大的区别就是方向,单链表是单向的,只能向一个方向“生长”,双链表是双向的,能够向双向进行“生长”。
在遍历链表时,单链表只能找到后继结点,找不到前驱结点,而双链表既能找到后继结点,也能找到前驱结点。
在对一目标结点进行删除时,单链表必须知道目标结点的前驱才能删除目标结点,而双链表不必知道目标结点的前驱,就能删除目标结点。
2.双链表从理论到实践
2.1双链表结点
class DoubleLinkedListNode {
public int val;//数据域
public DoubleLinkedListNode next;//指向后继
public DoubleLinkedListNode prev;//指向前驱
public DoubleLinkedListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;//构造方法
}
}
2.2双链表(带头结点)类
public class DoubleLinkedList {
public DoubleLinkedListNode head;//头结点
public DoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = new DoubleLinkedListNode(0);
}
//功能实现方法
}
2.3双链表增删查改实现
2.3.1双链表的打印
这个很简单,就是遍历一遍双链表。
public void display(){
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
2.3.2头插法
如果链表不为空,先让新结点指向后结点,再让头结点指向新结点。
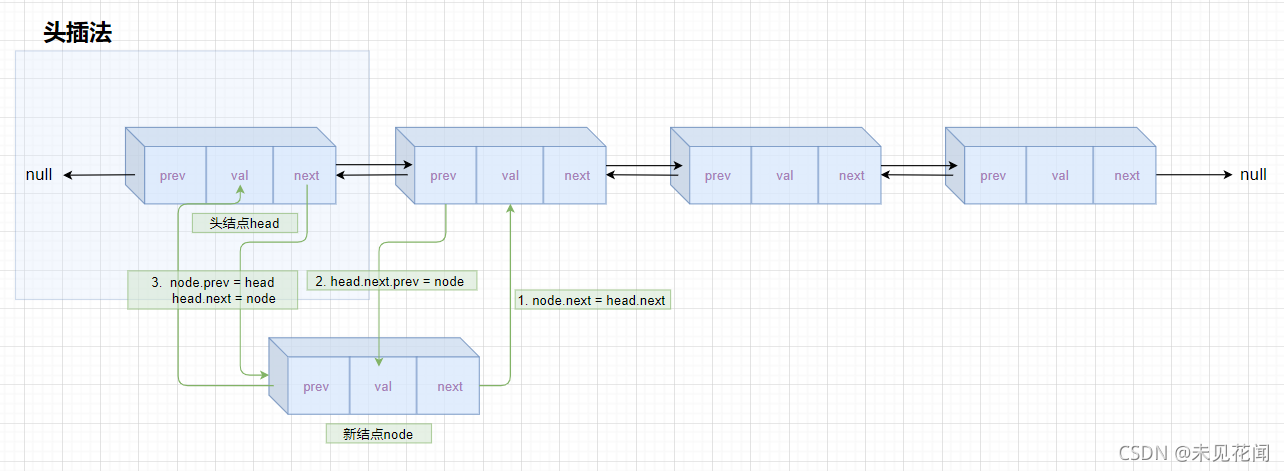
如果链表为空,则不需要完成图中的步骤2(即不需要将head.next.prev指向新结点node)。
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
DoubleLinkedListNode node = new DoubleLinkedListNode(data);
node.next = head.next;
if (head.next != null) {
head.next.prev = node;
}
head.next = node;
node.prev = head;
}
2.3.3尾插法
找到链表最后一个结点,插入最后一个结点后即可,链表为空时,最后一个结点可能为头结点。
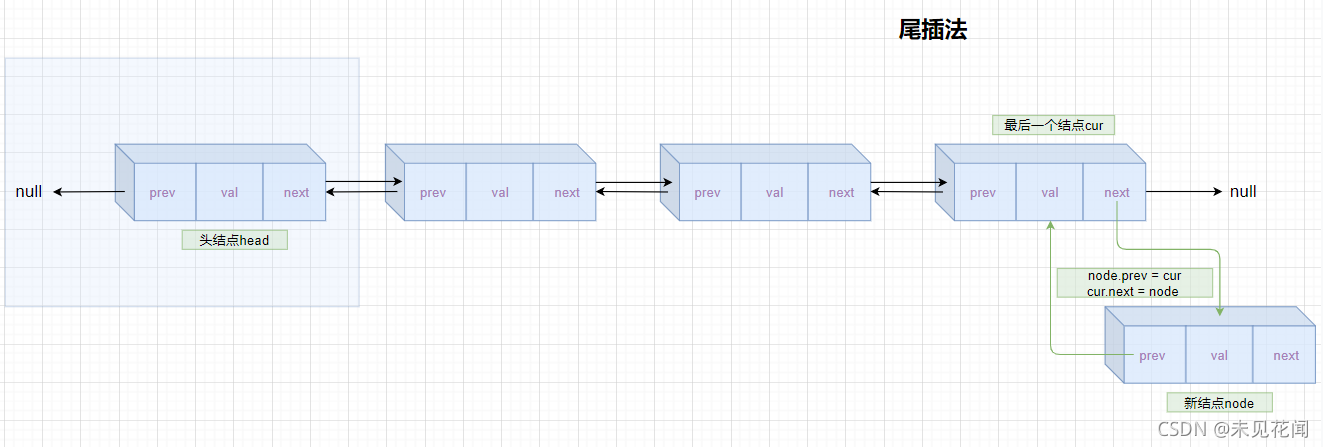
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
DoubleLinkedListNode node = new DoubleLinkedListNode(data);
cur.next = node;
node.prev = cur;
}
2.3.4链表长度获取
遍历就好。
//得到双链表的长度
public int size(){
int cnt = 0;
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
2.3.5在任意位置插入
分为3种情况:
- 在下标为0的位置插入,也就是头结点后,采用头插法。
- 在下标为链表长度size的位置插入,采用尾插法。
- 其他情况,按如图方式插入。
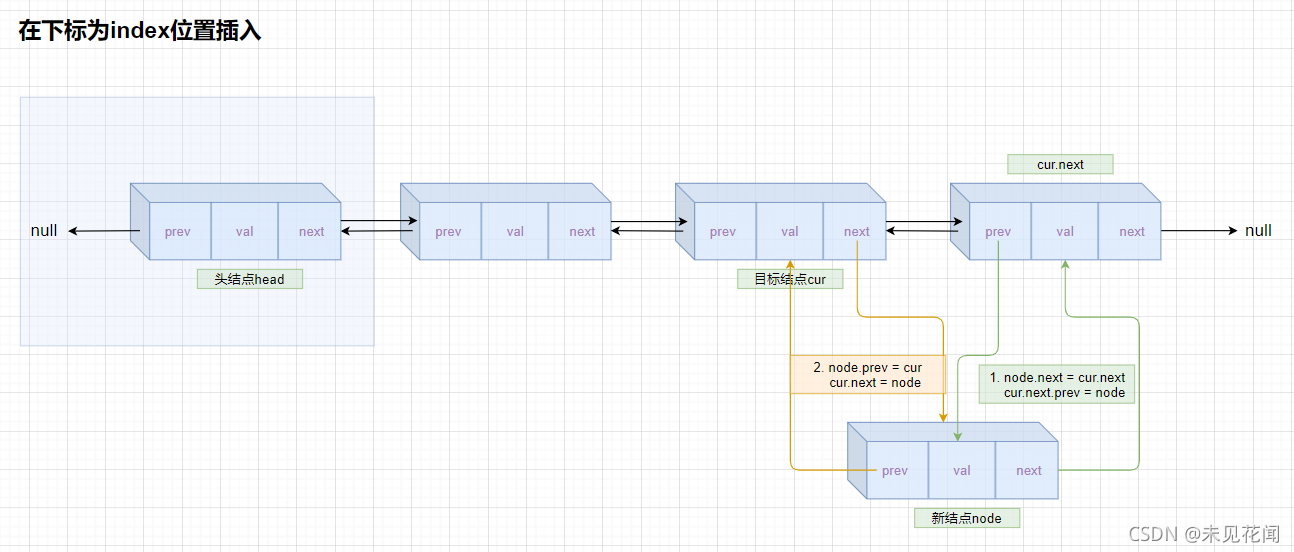
如果插入位置非法,直接返回或者抛异常,单链表实现中我们采用了直接返回的方法,这次采用抛异常。异常自定义,需要继承RuntimeException或Exception,前者时运行时异常的父类,会在运行时检查,后者为各类异常的父类,会在编译时检查。在这里,只有运行后才能知道传入的下标值是否合法,所以我们自定义异常时需继承RuntimeException类。
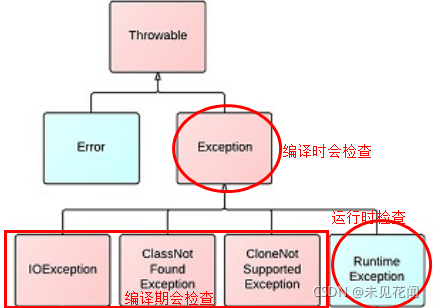
抛出的异常可以使用try…catch…语句捕获,这里就简单演示一下,如果不会直接返回就行,异常在后续博客会详细介绍。
try{
//可能会有异常的语句;
dls.addIndex(20, 10);//可能存在下标非法
}catch (IndexExcept(捕获异常类) e(引用变量)) {
//捕获异常
e.printStackTrace();//打印异常信息
}
class IndexExcept extends RuntimeException{
public IndexExcept(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws IndexExcept{
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexExcept(index + "位置非法!");
}
if (size() == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (size() == index) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
DoubleLinkedListNode node = new DoubleLinkedListNode(data);
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = node;
node.prev = cur;
cur.next = node;
}
2.3.6判断一个数据是否在链表中
遍历查找。
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
if (this.head.next == null) {
return false;
}
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
2.3.7删除双链表的结点
如果cur.next=null,直接让cur.prev = cur.next就可以了,其他情况将目标结点的前一个结点的next指向目标结点后一个结点,目标结点的后一个结点的prev指向目标结点的前一个结点。当链表为空的时候可以直接返回,也可以抛出一个异常,上次实现单链表采用了返回的方法,这次尝试抛一个自定义异常。
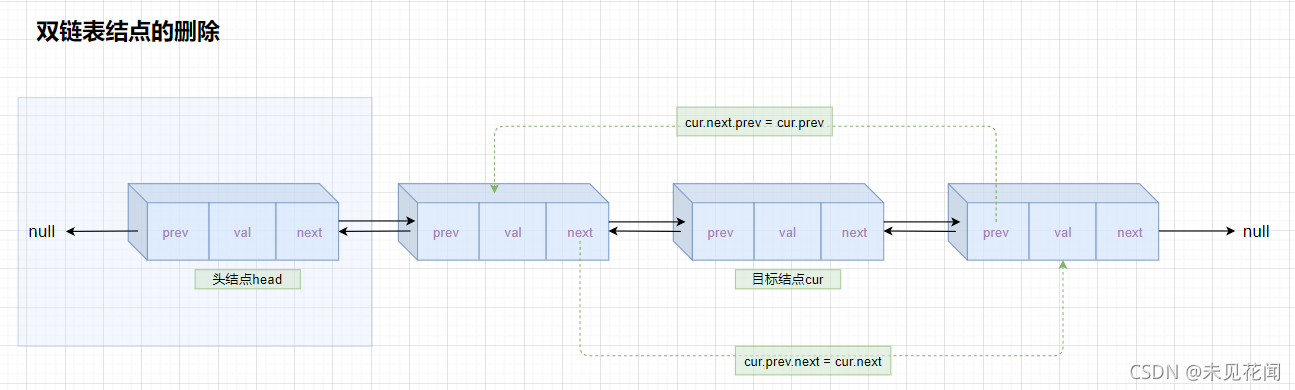
异常自定义,需要继承RuntimeException或Exception,前者时运行时异常的父类,会在运行时检查,后者为各类异常的父类,会在编译时检查。在这里,只有运行后才能知道链表是否为空,所以我们自定义异常时需继承RuntimeException类。
class LinkedListElemNull extends RuntimeException{
public LinkedListElemNull(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
删除链表中值为key的第一个结点
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if (this.head.next == null) {
throw new LinkedListElemNull("LinkedList is null");
}
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("没有找到目标结点!");
}
删除链表中值为key的所有结点
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if (this.head.next == null) {
throw new LinkedListElemNull("LinkedList is null");
}
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
2.3.8双链表的销毁
与单链表一样,先保存后一个结点,再将当前结点的引用域置空。
public void clear(){
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
DoubleLinkedListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur.prev = null;
cur = next;
}
this.head.next = null;
}
3.源代码
3.1实现类
class IndexExcept extends RuntimeException{
public IndexExcept(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
class LinkedListElemNull extends RuntimeException{
public LinkedListElemNull(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
class DoubleLinkedListNode {
public int val;
public DoubleLinkedListNode next;
public DoubleLinkedListNode prev;
public DoubleLinkedListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class DoubleLinkedList {
public DoubleLinkedListNode head;//头结点
public DoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = new DoubleLinkedListNode(0);
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
DoubleLinkedListNode node = new DoubleLinkedListNode(data);
node.next = head.next;
if (head.next != null) {
head.next.prev = node;
}
head.next = node;
node.prev = head;
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
DoubleLinkedListNode node = new DoubleLinkedListNode(data);
cur.next = node;
node.prev = cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws IndexExcept{
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexExcept(index + "位置非法!");
}
if (size() == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (size() == index) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
DoubleLinkedListNode node = new DoubleLinkedListNode(data);
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = node;
node.prev = cur;
cur.next = node;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
if (this.head.next == null) {
return false;
}
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if (this.head.next == null) {
throw new LinkedListElemNull("LinkedList is null");
}
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("没有找到目标结点!");
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if (this.head.next == null) {
throw new LinkedListElemNull("LinkedList is null");
}
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//得到双链表的长度
public int size(){
int cnt = 0;
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
public void display(){
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear(){
DoubleLinkedListNode cur = this.head.next;
DoubleLinkedListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur.prev = null;
cur = next;
}
this.head.next = null;
}
}
3.2测试代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkedList dls = new DoubleLinkedList();
dls.addLast(1);
dls.addLast(2);
dls.addFirst(3);
dls.display();
System.out.println("============");
dls.addIndex(0, 4);
dls.addIndex(4, 5);
dls.addIndex(2,6);
dls.display();
System.out.println(dls.contains(4));
System.out.println(dls.contains(99));
System.out.println("=========");
try{
dls.addIndex(20, 10);
}catch (IndexExcept e) {
e.printStackTrace();
dls.display();
}
System.out.println("============");
dls.remove(5);
dls.remove(6);
dls.remove(4);
dls.display();
System.out.println("===========");
dls.addIndex(0,7);
dls.addIndex(3,7);
dls.addIndex(3,7);
dls.addIndex(3,7);
dls.addIndex(7,7);
dls.display();
dls.removeAllKey(7);
dls.display();
System.out.println("=============");
dls.clear();
dls.display();
}
}

3.3项目文件
途径1:
博主的码云gitee,平常博主写的程序代码都在里面。
途径2:
博主的github,平常博主写的程序代码都在里面。
途径3:
联系我!
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)