【路径规划】基于matlab GUI多种蚁群算法栅格地图最短路径规划【含Matlab源码 650期】
一、蚁群算法及栅格地图简介
1 蚁群算法
1.1 蚁群算法的提出
蚁群算法(ant colony optimization, ACO),又称蚂蚁算法,是一种用来寻找优化路径的机率型算法。它由Marco Dorigo于1992年在他的博士论文中提出,其灵感来源于蚂蚁在寻找食物过程中发现路径的行为。遗传算法在模式识别、神经网络、机器学习、工业优化控制、自适应控制、生物科学、社会科学等方面都得到应用。
1.2 蚁群算法基本原理
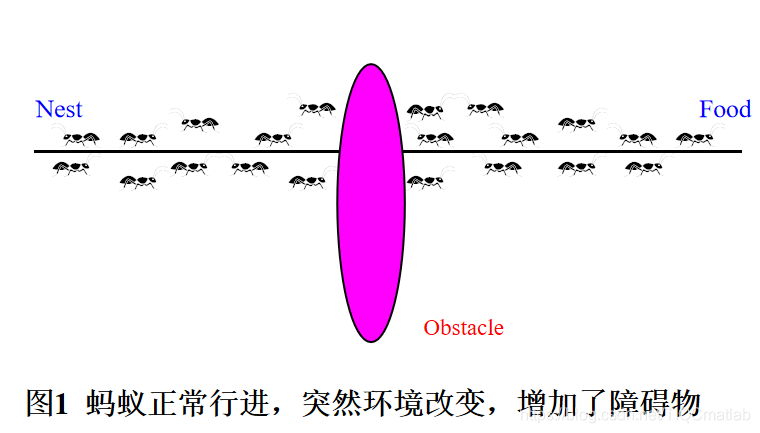
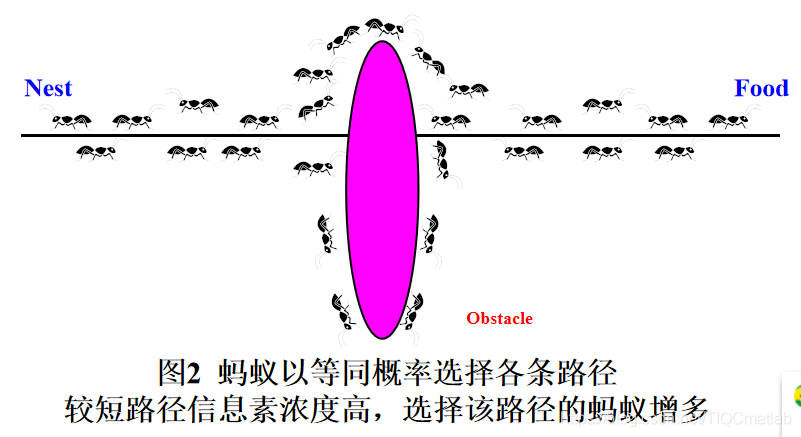
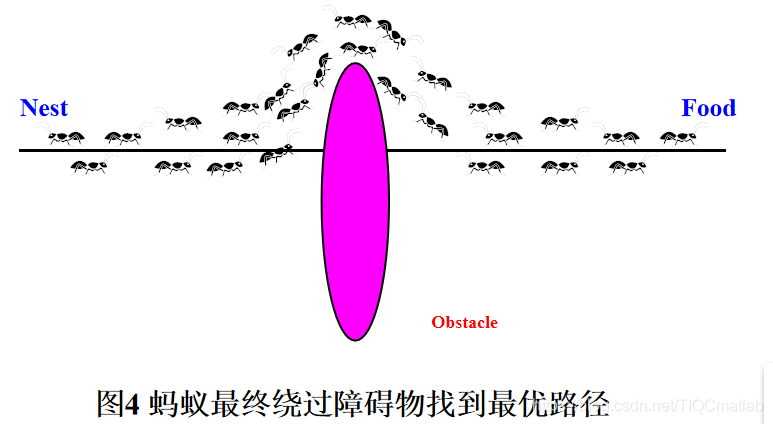
2 栅格地图
2.1 栅格法应用背景
路径规划时首先要获取环境信息, 建立环境地图, 合理的环境表示有利于建立规划方法和选择合适的搜索算法,最终实现较少的时间开销而规划出较为满意的路径。一般使用栅格法在静态环境下建立环境地图。
2.2 栅格法实质
将AGV的工作环境进行单元分割, 将其用大小相等的方块表示出来,这样栅格大小的选取是影响规划算法性能的一个很重要的因素。栅格较小的话,由栅格地图所表示的环境信息将会非常清晰,但由于需要存储较多的信息,会增大存储开销,同时干扰信号也会随之增加,规划速度会相应降低,实时性得不到保证;反之,由于信息存储量少,抗干扰能力有所增强,规划速随之增快,但环境信息划分会变得较为模糊,不利于有效路径的规划。在描述环境信息时障碍物所在区域在栅格地图中呈现为黑色,地图矩阵中标为1,可自由通行区域在栅格地图中呈现为白色,地图矩阵中标为0。路径规划的目的就是在建立好的环境地图中找到一条最优的可通行路径,所以使用栅格法建立环境地图时,栅格大小的合理设定非常关键。
2.3 10乘10的静态环境地图
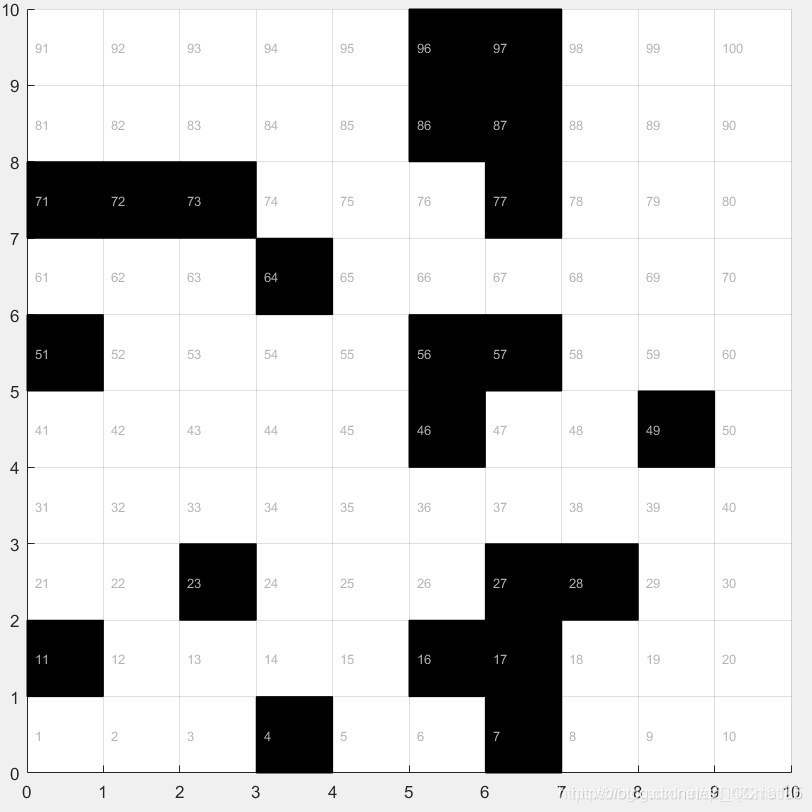
10乘10的静态环境地图代码
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%建立环境地图%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function DrawMap(map)
n = size(map);
step = 1;
a = 0 : step :n(1);
b = 0 : step :n(2);
figure(1)
axis([0 n(2) 0 n(1)]); %设置地图横纵尺寸
set(gca,'xtick',b,'ytick',a,'GridLineStyle','-',...
'xGrid','on','yGrid','on');
hold on
r = 1;
for(i=1:n(1)) %设置障碍物的左下角点的x,y坐标
for(j=1:n(2))
if(map(i,j)==1)
p(r,1)=j-1;
p(r,2)=i-1;
fill([p(r,1) p(r,1) + step p(r,1) + step p(r,1)],...
[p(r,2) p(r,2) p(r,2) + step p(r,2) + step ],'k');
r=r+1;
hold on
end
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%栅格数字标识%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
x_text = 1:1:n(1)*n(2); %产生所需数值.
for i = 1:1:n(1)*n(2)
[row,col] = ind2sub([n(2),n(1)],i);
text(row-0.9,col-0.5,num2str(x_text(i)),'FontSize',8,'Color','0.7 0.7 0.7');
end
hold on
axis square
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
建立环境矩阵,1代表黑色栅格,0代表白色栅格,调用以上程序,即可得到上述环境地图。
map=[0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0;
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0;
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0;
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;];
DrawMap(map); %得到环境地图
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2.4 栅格地图中障碍栅格处路径约束
移动体栅格环境中多采用八方向的移动方式,此移动方式在完全可通行区域不存在运行安全问题,当
移动体周围存在障碍栅格时此移动方式可能会发生与障碍物栅格的碰撞问题,为解决此问题加入约束
条件,当在分别与障碍物栅格水平方向和垂直方向的可行栅格两栅格之间通行时,禁止移动体采用对
角式移动方式。
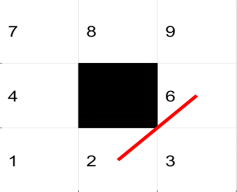
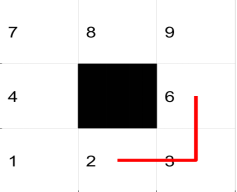
约束条件的加入,实质是改变栅格地图的邻接矩阵,将障碍栅格(数字为“1”的矩阵元素)的对角栅格
设为不可达, 即将对角栅格的距离值改为无穷大。其实现MATLAB代码如下:
代码:
%约束移动体在障碍栅格对角运动
%通过优化邻接矩阵实现
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 约束移动体移动方式 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function W=OPW(map,W)
% map 地图矩阵 % W 邻接矩阵
n = size(map);
num = n(1)*n(2);
for(j=1:n(1))
for(z=1:n(2))
if(map(j,z)==1)
if(j==1) %若障碍物在第一行
if(z==1) %若障碍物为第一行的第一个
W(j+1,j+n(2)*j)=Inf;
W(j+n(2)*j,j+1)=Inf;
else
if(z==n(2)) %若障碍物为第一行的最后一个
W(n(2)-1,n(2)+n(1)*j)=Inf;
W(n(2)+n(1)*j,n(2)-1)=Inf;
else %若障碍物为第一行的其他
W(z-1,z+j*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+j*n(2),z-1)=Inf;
W(z+1,z+j*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+j*n(2),z+1)=Inf;
end
end
end
if(j==n(1)) %若障碍物在最后一行
if(z==1) %若障碍物为最后一行的第一个
W(z+n(2)*(j-2),z+n(2)*(j-1)+1)=Inf;
W(z+n(2)*(j-1)+1,z+n(2)*(j-2))=Inf;
else
if(z==n(2)) %若障碍物为最后一行的最后一个
W(n(1)*n(2)-1,(n(1)-1)*n(2))=Inf;
W((n(1)-1)*n(2),n(1)*n(2)-1)=Inf;
else %若障碍物为最后一行的其他
W((j-2)*n(2)+z,(j-1)*n(2)+z-1)=Inf;
W((j-1)*n(2)+z-1,(j-2)*n(2)+z)=Inf;
W((j-2)*n(2)+z,(j-1)*n(2)+z+1)=Inf;
W((j-1)*n(2)+z+1,(j-2)*n(2)+z)=Inf;
end
end
end
if(z==1)
if(j~=1&&j~=n(1)) %若障碍物在第一列非边缘位置
W(z+(j-2)*n(2),z+1+(j-1)*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+1+(j-1)*n(2),z+(j-2)*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+1+(j-1)*n(2),z+j*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+j*n(2),z+1+(j-1)*n(2))=Inf;
end
end
if(z==n(2))
if(j~=1&&j~=n(1)) %若障碍物在最后一列非边缘位置
W((j+1)*n(2),j*n(2)-1)=Inf;
W(j*n(2)-1,(j+1)*n(2))=Inf;
W(j*n(2)-1,(j-1)*n(2))=Inf;
W((j-1)*n(2),j*n(2)-1)=Inf;
end
end
if(j~=1&&j~=n(1)&&z~=1&&z~=n(2)) %若障碍物在非边缘位置
W(z+(j-1)*n(2)-1,z+j*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+j*n(2),z+(j-1)*n(2)-1)=Inf;
W(z+j*n(2),z+(j-1)*n(2)+1)=Inf;
W(z+(j-1)*n(2)+1,z+j*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+(j-1)*n(2)-1,z+(j-2)*n(2))=Inf;
W(z+(j-2)*n(2),z+(j-1)*n(2)-1)=Inf;
W(z+(j-2)*n(2),z+(j-1)*n(2)+1)=Inf;
W(z+(j-1)*n(2)+1,z+(j-2)*n(2))=Inf;
end
end
end
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
6 栅格法案例
下面以Djkstra算法为例, 其实现如下:
map=[0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0;
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0;
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0;
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;];
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%建立环境矩阵map%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
DrawMap(map); %得到环境地图
W=G2D(map); %得到环境地图的邻接矩阵
W(W==0)=Inf; %邻接矩阵数值处理
W=OPW(map,W); %优化邻接矩阵
[distance,path]=dijkstra(W,1,100);%设置起始栅格,得到最短路径距离以及栅格路径
[x,y]=Get_xy(distance,path,map); %得到栅格相应的x,y坐标
Plot(distance,x,y); %画出路径
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行结果如下:
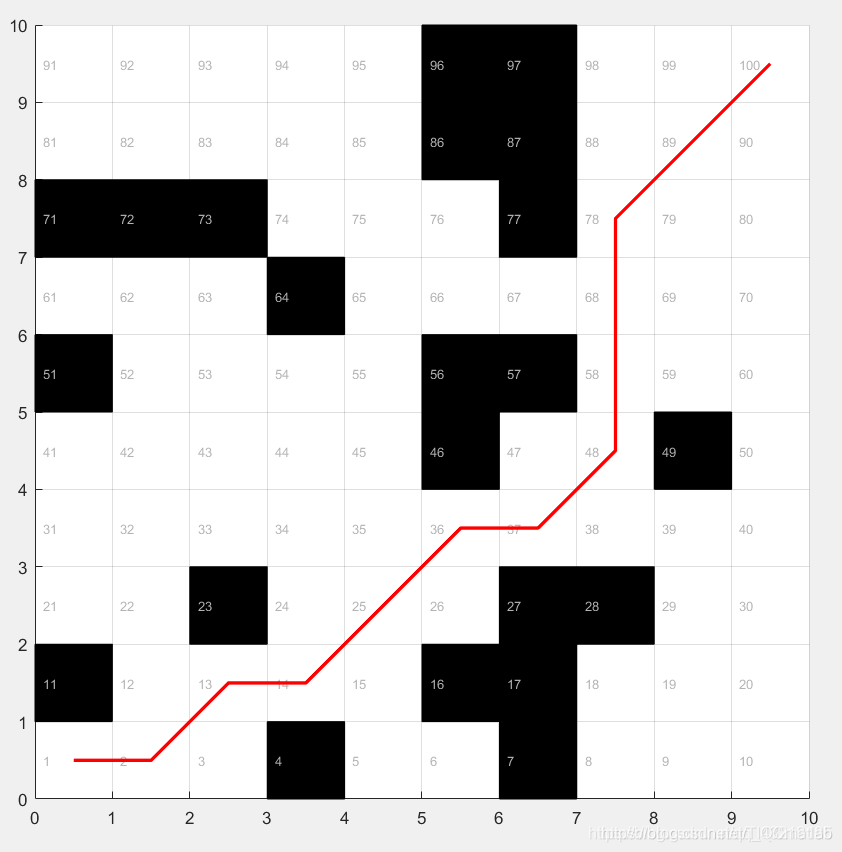
其中函数程序:
DrawMap(map) 详见建立栅格地图
W=G2D(map) ; 详见建立邻接矩阵
[distance, path] =dijkstra(W, 1, 100) 详见Djk stra算法
[x, y] =Get_xy(distance, path, map) ;
Plot(distance, x, y) ;
二、部分源代码
function varargout = main_GUI_xu(varargin)
% MAIN_GUI_XU MATLAB code for main_GUI_xu.fig
% MAIN_GUI_XU, by itself, creates a new MAIN_GUI_XU or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = MAIN_GUI_XU returns the handle to a new MAIN_GUI_XU or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% MAIN_GUI_XU('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in MAIN_GUI_XU.M with the given input arguments.
%
% MAIN_GUI_XU('Property','Value',...) creates a new MAIN_GUI_XU or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before main_GUI_xu_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to main_GUI_xu_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help main_GUI_xu
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 22-Mar-2017 15:58:57
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @main_GUI_xu_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @main_GUI_xu_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before main_GUI_xu is made visible.
function main_GUI_xu_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to main_GUI_xu (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for main_GUI_xu
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes main_GUI_xu wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
init_all(handles)
set(handles.edit38,'string','先选择实验目的,默认选择目的一,即运行一种算法');
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = main_GUI_xu_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on selection change in listbox1.
function listbox1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to listbox1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = cellstr(get(hObject,'String')) returns listbox1 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from listbox1
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function listbox1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to listbox1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: listbox controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% 绘制栅格线和调用figure的屏幕回调函数
global barrier pushbutton1_userdata
pushbutton1_userdata = 1; % 控制设计障碍物按钮是否能够使用
set(handles.edit38,'string','障碍物设计完成后,请点击输出障碍物按钮,否则容易出错');
axes(handles.axes1)
cla reset
n_barrier = str2double(get(handles.edit1,'string'));
barrier = zeros(n_barrier,n_barrier);
axes(handles.axes1);
s.hf = get(handles.axes1,'parent');
% 绘制栅格边线
for i=0:1:n_barrier
plot([0,n_barrier],[i,i],'color','k');
hold on
axis([0,n_barrier,0,n_barrier])
for j=0:1:n_barrier
plot([i,i],[0,n_barrier],'color','k') ;
hold on
axis([0,n_barrier,0,n_barrier])
end
end
% 设置figure的WindowButtonDownFcn属性
set(s.hf,'WindowButtonDownFcn',@figure1_windowbuttondownfcn)
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu1.
function popupmenu1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = cellstr(get(hObject,'String')) returns popupmenu1 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu1
global barrier_select start_select goal_select pushbutton1_userdata barrier start goal
barrier_value = get(handles.popupmenu1,'value');
cd('barrier')
if barrier_value==2
barrier_select = xlsread('e_barrier');
start_select = 20;
goal_select = 295;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==3
barrier_select = xlsread('simple_e');
start_select = 20;
goal_select = 295;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==4
barrier_select = xlsread('u_barrier');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 400;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==5
barrier_select = xlsread('light_u_barrier');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 400;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==6
barrier_select = xlsread('right_u_barrier');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 400;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==7
barrier_select = xlsread('z_barrier');
start_select = 49;
goal_select = 369;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==8
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_z');
start_select = 47;
goal_select = 367;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==9
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_1');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 400;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==10
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_2');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 400;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==11
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_30');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 890;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==12
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_50_1');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 2500;
elseif barrier_value==13
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_50_2');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 2500;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==14
barrier_select = xlsread('complex_50_3');
start_select = 1;
goal_select = 2500;
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
elseif barrier_value==15
barrier_select = xlsread('barrier_tmp');
set(handles.edit18,'string','请选择起点和终点')
pushbutton1_userdata = 0;
start = 0;
goal = 0;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/115314598
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)