【图像隐写】基于matlab GUI DWT+DCT+PBFO改进图像水印隐藏提取【含Matlab源码 081期】
一、DCT数字水印嵌入与提取简介
1 基本DCT变换
目前,基于DCT域的水印方法已经成为数字水印算法研究的热点,它的核心思想就是通过离散傅立叶变换对图像块进行处理后,再选择变换域中的一些系数值依据一定规则来嵌入水印。
由于图像块中DCT系数频带分布由左上角的直流分量DC往下对应的系数频率由低频升至高频,因此在不影响原图质量的前提下,可将水印信息根据能量大小嵌入相应系数频带中。通过图像块量化与水印嵌入结合的处理方法将水印信息均匀分布在图像的整个空间域,在图像裁剪和滤波方面,变换域的水印比在空间域的更能表现出一定的鲁棒性。
2 水印算法描述
2.1 水印嵌入算法
该算法采用加性嵌入的方式在经过DCT变换后的子图像块的中频域中,选取隐秘位置嵌入水印信息,具体的嵌入流程如下图1所示:
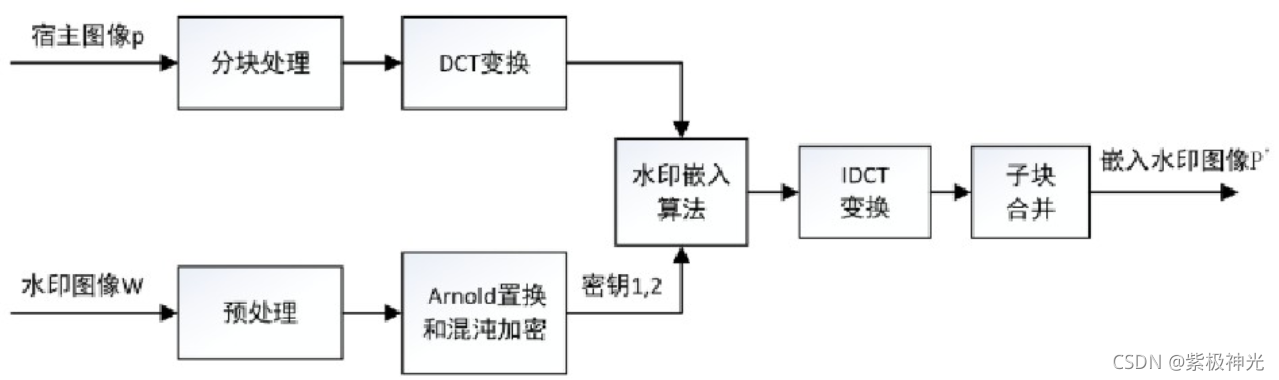
图1 分块水印嵌入流程
(1)分块处理:设宿主图像为P,将其分块处理为8*8的K个子块。
(2)水印预处理:设水印图像为W,对其进行互补变换,变换后的水印图像和变换前的水印图像相互补。
(3)对水印图像进行Arnold置乱变换,并依据混沌映射规则,选取密钥混沌序列并与水印序列异或运算,将置换次数和异或运算处理后的结果分别作为水印嵌入算法的密钥1和密钥2。
(4)DCT变换:对各子块内做DCT变换,利用zig-zag对DCT系数进行扫描,得到第k块子图像块的序列为Zk(i),i=0,1,2,…63.
(5)水印嵌入算法:依据zig-zag排序,在各子块的中、低频段选取特定系数x(m)和x(n),在系数坐标(a,b)和(c,d)处嵌入水印信息图像W,并将其作为密钥3。同理,嵌入互补水印图片W’,并将嵌入的位置作为密钥4。水印嵌入的方法如下:


(6)IDCT变换:将每一个子图像块作二维DCT逆变换。
(7)子块合并:将每一个子块合并成嵌入水印的图像P’。
2.2 水印提取算法
将嵌入水印的图像P’分块处理,并对各子块进行二维DCT变换,由密钥3和4推断所选择的水印系数,若x(m)≤x(n),则水印信息为0,若x(m)>x(n),则水印信息为1,再利用密钥1和2将初步水印的信息解密再进行Arnold逆变换,最终提取出水印信息。
2.3 水印检测算法
本文通过计算峰值信噪比PSNR的值评价嵌入水印的宿主图像的质量,一幅m和n的图像,PSNR度量标准定义为:
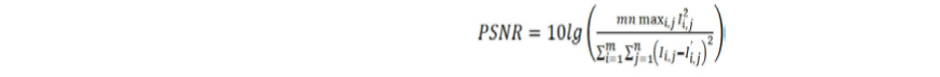
归一化相关系数NC的值判断嵌入水印的图像与宿主图像的相似度,其定义为:


二、部分源代码
close all;
clear all;
clc;
I = imread('pepper.bmp');
J = rgb2gray(I);
K_1 = fft2(J);
L_1 = abs(K_1/256);
K_2 = fftshift(K_1);
L_2 = abs(K_2/256);
figure;
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I); title('原始图像');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(J); title('灰度图像');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(uint8(L_1)); title('灰度图像傅里叶频谱');
subplot(2,2,4);
imshow(uint8(L_2)); title('平移后的频谱');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
其运行结果如下图:
图1 图像傅里叶变换例
2.2 离散余弦变换(DCT)
离散余弦变换(DCT)是一组不同频率和幅值的余弦函数和来近似一副图像,实际上是傅里叶变换的实数部分。由于离散余弦变量对于一副图像,其大部分可视化信息都集中在少数的变换系数上。因此,离散余弦变量是数据压缩常用的一个变换编码方法,它能将高相关数据能量集中,使得它非常适用于图像压缩,例如国际压缩标准的JPEG格式中就采用了离散余弦变换。
在傅立叶变换过程中,如果被展开的函数是实偶函数,那么其傅立叶变换中只包含余弦项,基于傅立叶变换的这一特点,人们提出了离散余弦变换。DCT变换先将图像函数变换成偶函数形式,再对其进行二维离散傅立叶变换,因此DCT变换可以看成是一种简化的傅立叶变换。离散余弦变换叶分为一维离散余弦变换和二维离散余弦变换,在图像处理中用到二维变化,所以介绍下其二维定义,其他定义可查阅《数字图像处理》——冈萨雷斯。其二维离散余弦变换定义如下式:

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
close all;
clear all;
clc;
I = imread ('boats.bmp');
J = dct2(I);
figure('Name','离散余弦变换');
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I); title('原始图像');
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(log(abs(J))); title('离散余弦变换系数图像');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
其运行结果如下图2:
图2 离散余弦变换例
2.3 小波变换(DWT)
小波变化是对傅里叶变换和短时傅里叶变换的一个突破,其改变就在于,将无限长的三角函数基换成了有限长的会衰减的小波。小波变化的理论较多,更多内容可查阅《数字图像处理》——冈萨雷斯相关章节内容,以下从一个叫简单的角度来解释小波变换。
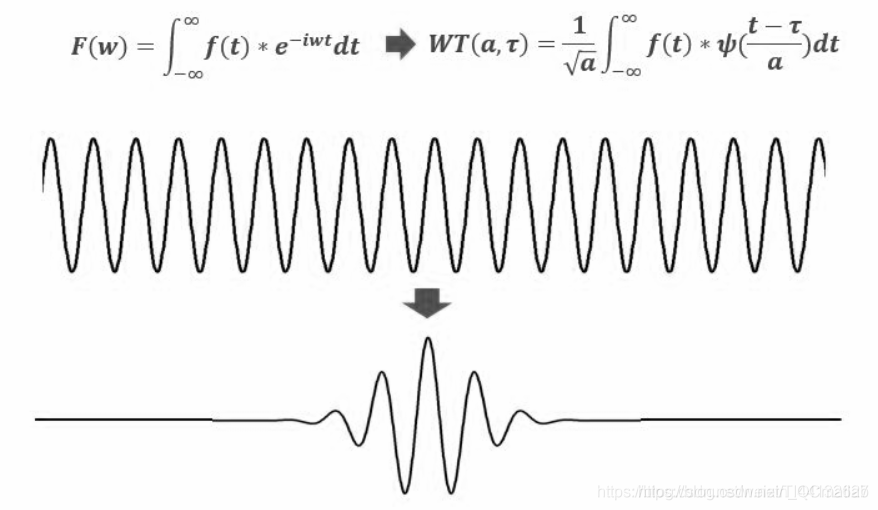
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

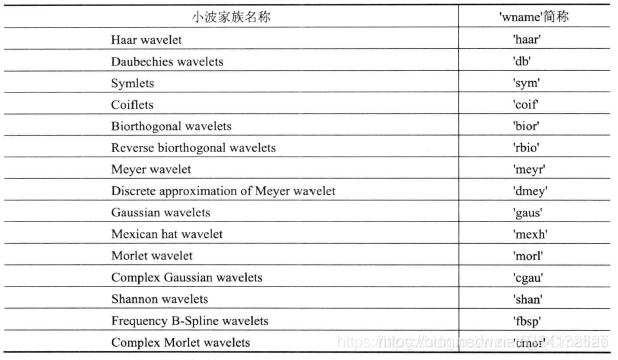
表1 小波变换母小波
function varargout = manit1(varargin)
% MANIT1 M-file for manit1.fig
% MANIT1, by itself, creates a new MANIT1 or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = MANIT1 returns the handle to a new MANIT1 or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% MANIT1('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in MANIT1.M with the given input arguments.
%
% MANIT1('Property','Value',...) creates a new MANIT1 or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before manit1_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to manit1_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help manit1
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 14-Jun-2015 10:32:30
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @manit1_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @manit1_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before manit1 is made visible.
function manit1_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to manit1 (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for manit1
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes manit1 wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = manit1_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in browsecoverimg.
function browsecoverimg_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to browsecoverimg (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename, pathname] = uigetfile({'*.jpg';'*.bmp';'*.gif';'*.*'}, 'Pick an Image File');
S = imread([pathname,filename]);
S=imresize(S,[512,512]);
axes(handles.axes1)
imshow(S)
title('Cover Image')
set(handles.text3,'string',filename)
handles.S=S;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in browsemsg.
function browsemsg_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to browsemsg (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename, pathname] = uigetfile({'*.bmp';'*.jpg';'*.gif';'*.*'}, 'Pick an Image File');
msg = imread([pathname,filename]);
axes(handles.axes2)
imshow(msg)
title('Input Message')
set(handles.text4,'string',filename)
handles.msg=msg;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in DWT.
function DWT_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to DWT (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
message=handles.msg;
cover_object=handles.S;
k=10;
[watermrkd_img,PSNR,IF,NCC,recmessage]=dwt(cover_object,message,k);
axes(handles.axes3)
imshow(watermrkd_img)
title('Watermarked Image')
axes(handles.axes4)
imshow(recmessage)
title('Recovered Message')
a=[PSNR,NCC,IF]';
t=handles.uitable1;
set(t,'Data',a)
handles.a=a;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in DWTDCT.
function DWTDCT_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to DWTDCT (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a=handles.a;
message=handles.msg;
cover_object=handles.S;
k=10;
[watermrkd_img,recmessage,PSNR,IF,NCC1] = dwtdct(cover_object,message,k);
axes(handles.axes3)
imshow(watermrkd_img)
title('DWT+DCT Watermarked Image')
axes(handles.axes4)
imshow(recmessage)
title('DWT+DCT Recovered Message')
b=[PSNR,NCC1,IF]';
t=handles.uitable1;
set(t,'Data',[a b])
handles.b=b;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in DWTDCTBFO.
function DWTDCTBFO_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to DWTDCTBFO (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a=handles.a;
b=handles.b;
message=handles.msg;
cover_object=handles.S;
[watermrkd_img,recmessage,PSNR,IF,NCC,pbest] = BG(cover_object,message);
axes(handles.axes3)
imshow(watermrkd_img)
title('DWT+DCT+BFO Watermarked Image')
axes(handles.axes4)
imshow(recmessage)
title('DWT+DCT+BFO Recovered Message')
c=[PSNR,NCC,IF]';
t=handles.uitable1;
set(t,'Data',[a b c])
handles.c=c;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a=handles.a;
b=handles.b;
c=handles.c;
d=handles.d;
PSNR=[a(1),b(1),c(1),d(1) ];
NCC=[a(2),b(2),c(2),d(2)];
IF=[a(3),b(3),c(3),d(3)];
figure
bar(PSNR)
set(gca,'XTickLabel',' ');
ylabel('PSNR')
text(1,0,'DWT','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
text(2,0,'DWT+DCT','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
text(3,0,'DWT+DCT+BFO','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
text(4,0,'DWT+DCT+PBFO','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
[t]=get(gca,'position');
set(gca,'position',[t(1) 0.31 t(3) 0.65])
title('Bar Graph Comparison of PSNR')
%%%%
figure
bar(NCC)
set(gca,'XTickLabel',' ');
ylabel('NCC')
text(1,0,'DWT','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
text(2,0,'DWT+DCT','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
text(3,0,'DWT+DCT+BFO','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
text(4,0,'DWT+DCT+PBFO','Rotation',260,'Fontsize',8);
[t]=get(gca,'position');
set(gca,'position',[t(1) 0.31 t(3) 0.65])
title('Bar Graph Comparison of NCC')
% --- Executes on button press in DWTDCTPBFO.
function DWTDCTPBFO_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to DWTDCTPBFO (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a=handles.a;
b=handles.b;
c=handles.c;
message=handles.msg;
cover_object=handles.S;
[watermrkd_img,recmessage,PSNR,IF,NCC,pbest] =BG_PSO(cover_object,message);
axes(handles.axes3)
imshow(watermrkd_img)
title('DWT+DCT+PBFO Watermarked Image')
axes(handles.axes4)
imshow(recmessage)
title('DWT+DCT+PBFO Recovered Message')
d=[PSNR,NCC,IF]';
t=handles.uitable1;
set(t,'Data',[a b c d])
handles.d=d;
guidata(hObject,handles)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
三、运行结果

四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[5]万谊丹.基于Arnold和DCT的抗剪切攻击图像水印研究[J].网络安全技术与应用. 2021,(08)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/112424427
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)