【多目标优化求解】基于matlab粒子群算法求解配电网抢修优化问题【含Matlab源码 777期】
一、粒子群算法简介
1 粒子群算法的概念
粒子群优化算法(PSO:Particle swarm optimization) 是一种进化计算技术(evolutionary computation)。源于对鸟群捕食的行为研究。粒子群优化算法的基本思想:是通过群体中个体之间的协作和信息共享来寻找最优解.
PSO的优势:在于简单容易实现并且没有许多参数的调节。目前已被广泛应用于函数优化、神经网络训练、模糊系统控制以及其他遗传算法的应用领域。
2 粒子群算法分析
2.1基本思想
粒子群算法通过设计一种无质量的粒子来模拟鸟群中的鸟,粒子仅具有两个属性:速度和位置,速度代表移动的快慢,位置代表移动的方向。每个粒子在搜索空间中单独的搜寻最优解,并将其记为当前个体极值,并将个体极值与整个粒子群里的其他粒子共享,找到最优的那个个体极值作为整个粒子群的当前全局最优解,粒子群中的所有粒子根据自己找到的当前个体极值和整个粒子群共享的当前全局最优解来调整自己的速度和位置。下面的动图很形象地展示了PSO算法的过程:
2 更新规则
PSO初始化为一群随机粒子(随机解)。然后通过迭代找到最优解。在每一次的迭代中,粒子通过跟踪两个“极值”(pbest,gbest)来更新自己。在找到这两个最优值后,粒子通过下面的公式来更新自己的速度和位置。

公式(1)的第一部分称为【记忆项】,表示上次速度大小和方向的影响;公式(1)的第二部分称为【自身认知项】,是从当前点指向粒子自身最好点的一个矢量,表示粒子的动作来源于自己经验的部分;公式(1)的第三部分称为【群体认知项】,是一个从当前点指向种群最好点的矢量,反映了粒子间的协同合作和知识共享。粒子就是通过自己的经验和同伴中最好的经验来决定下一步的运动。以上面两个公式为基础,形成了PSO的标准形式。

公式(2)和 公式(3)被视为标准PSO算法。
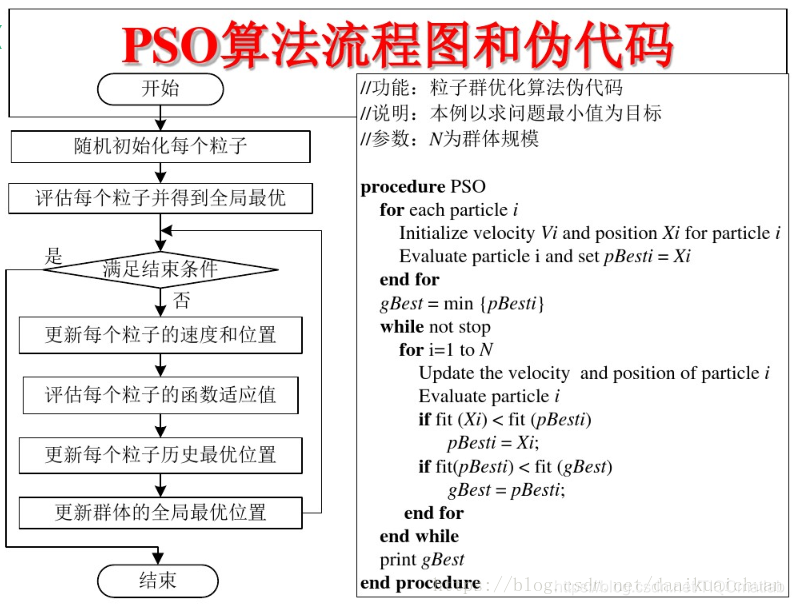
3 PSO算法的流程和伪代码
二、部分源代码
%% optimization + PSO 求解 选址_路径优化问题
%% 时间:2021年4月13日:12:09
clc;clear;close all;
%% 初始化种群
N = 300; % 初始种群个数
d = 6; % 空间维数
ger =60; % 最大迭代次数
limit =zeros(2,2);
limit(:,1)=[-46000 63000 ];
limit(:,2)=[-26000 70000 ] ;
% 设置位置参数限制
vlimit(1) = -10000; % 设置速度限制
vlimit(2)=10000 ;
wmax = 0.8;
wmin = 0.4; % 惯性权重
c1 = 1; % 自我学习因子
c2 = 2; % 群体学习因子
model=CreateModel(); %调用模型函数
for i = 1:d
if mod(i,2)==0
x(:,i) = limit(2,1) + (limit(2,2) - limit(2,1)) * rand(N, 1);%初始种群的位置
else
x(:,i) = limit(1,1) + (limit(1,2) - limit(1,1)) * rand(N, 1);
end
end
v = rand(N, d); % 初始种群的速度
xm = x; % 每个个体的历史最佳位置
ym = zeros(1, d); % 种群的历史最佳位置
fxm = 1./zeros(N,1); % 每个个体的历史最佳适应度
fym = inf; % 种群历史最佳适应度 inf无穷大
%% 群体更新
iter = 1;
record = zeros(ger, 2); % 记录器
average=record;
while iter <= ger
fx=zeros(N,1);
for i=1:N
fx(i)= TourLength(model,x(i,:)) ; % 个体当前适应度
end
intermediate_x=zeros(size(xm));
intermediate_x(1:N,:) = xm;
intermediate_x(N + 1 : N + N,1 : d) = x;
for i=1:N*2
intermediate_x(i,d+3)=150;
intermediate_x(i,d+1:d+2)=Tour(model, intermediate_x(i,:)) ; % 个体当前适应度
end
intermediate_x = ...
non_domination_sort_mod(intermediate_x, 2, d);
intermediate_x = replace_x(intermediate_x, 2, d, N);
record(iter,:) = intermediate_x(1,d+1:d+2);%最小值记
average(iter,1)=sum(intermediate_x(:,d+1))/N;
average(iter,2)=sum(intermediate_x(:,d+2))/N;
ym=intermediate_x(1,1:d);
fym=record(iter,:);
disp(['第',num2str(iter),'次迭代''最小值:',num2str(record(iter,:)),'抢修中心坐标:',num2str(ym)]);
iter = iter+1;
xm=intermediate_x(:,1:d);
w=wmax-(wmax-wmin)*(ger-iter)/ger ;%权重更新
v = v * w + c1 * rand * (xm - x) + c2 * rand * (repmat(ym, N, 1) - x);% 速度更新
% 边界速度处理
for ii=1:N
for jj=1:d
if v(ii,jj)>vlimit(2) v(ii,jj)= vlimit(2);end
if v(ii,jj)<vlimit(1) v(ii,jj)= vlimit(1);end
end
end
x = x + v;% 位置更新
% 边界位置处理
for ii=1:N
for jj=1:d
if mod(jj,2)==0
if x(ii,jj)>limit(2,2) x(ii,jj)= limit(2,2);end
if x(ii,jj)<limit(2,1) x(ii,jj)= limit(2,1);end
else
if x(ii,jj)>limit(1,2) x(ii,jj)= limit(1,2);end
if x(ii,jj)<limit(1,1) x(ii,jj)= limit(1,1);end
end
end
end
end
Schedule = code(x, model); %调用
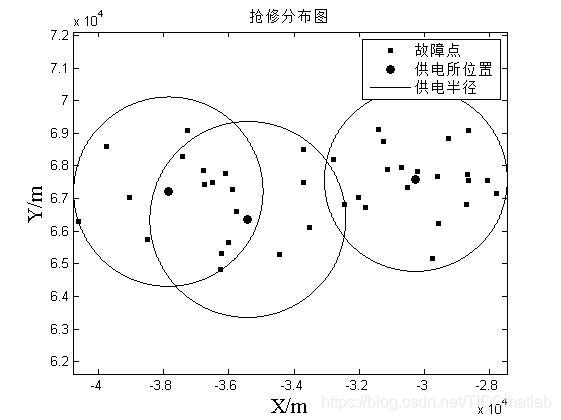
%% 绘制测试结果图
% 故障点
figure(1);
x=model.trouble(1,:);
y=model.trouble(2,:);
for i=1:39
xx=x(i);
yy=y(i);
[ch1]=plot( xx,yy,'ks',...
'MarkerFaceColor','k',...
'MarkerSize',4); hold on
text(xx , yy, num2str(i) ); %带箭头的标注
hold on
end
% 绘制抢修中心
for i=1:3
xx=ym(i*2-1);
yy=ym(i*2);
[ch2]= plot( xx ,yy ,'ko',...
'MarkerFaceColor','k',...
'LineWidth',6);hold on
text(xx , yy, num2str( i) ); %带箭头的标注
hold on
end
%% 规划结果
rand('seed', 0);
C= unifrnd( 0.1, 0.2, model.Num_CenterSletectd , 3) ;%unifrnd可以创建随机的连续均匀分布的数组
for i = 1: model.Num_CenterSletectd
Center = Schedule(i).Center;
Client = Schedule(i).Client ;
xx=model.trouble(1,:);
yy=model.trouble(2,:);
for j= Client
x = [ ym(i*2-1) , xx(j ) ] ;
y = [ ym(i*2) , yy(j ) ] ;
plot( x ,y , '-' ,'color' ,C(i, : ) , 'linewidth' , 1.5 );
hold on
end
end
% 标注
legend([ch1, ch2], {'故障点' ,'供电所位置' }); % 'Location','SouthWestOutside'注释放置位置
xlabel('X/m','fontsize',15,'fontname','Times new roman');
ylabel('Y/m','fontsize',15,'fontname','Times new roman');
title('抢修分布图');
axis on
set(gcf,'color',[1 1 1]); %设置背景颜色
%% 绘制供电半径图
figure(2);
plot(model.trouble(1, : ), model.trouble(2, : ),'ks',...
'MarkerFaceColor','k',...
'MarkerSize',3);hold on
for i=1:3
plot(ym(i*2-1),ym(i*2),'ko',...
'MarkerFaceColor','k',...
'MarkerSize',6);hold on % 抢修中心分布图 ,半径
x=ym(i*2-1);
y=ym(i*2);
r=model.point(3,i)*1000;
theta=0:2*pi/3600:2*pi;
Circle1=x+r*cos(theta);
Circle2=y+r*sin(theta);
plot(Circle1,Circle2,'k-','Linewidth',1);
axis equal
end
legend('故障点' ,'供电所位置', '供电半径');
title('抢修分布图');
xlabel('X/m','fontsize',15,'fontname','Times new roman');
ylabel('Y/m','fontsize',15,'fontname','Times new roman');
for i=1:N
xm(i,d+1:d+2)=Tour(model,xm(i,1:d)) ; % 个体当前适应度
end
xm = non_domination_sort_mod(xm, 2, d);
function f = replace_chromosome(intermediate_chromosome, M, V,pop)
[N, m] = size(intermediate_chromosome);
% Get the index for the population sort based on the rank
[temp,index] = sort(intermediate_chromosome(:,M + V + 1));
clear temp m
% Now sort the individuals based on the index
for i = 1 : N
sorted_chromosome(i,:) = intermediate_chromosome(index(i),:);
end
% Find the maximum rank in the current population
max_rank = max(intermediate_chromosome(:,M + V + 1));
% Start adding each front based on rank and crowing distance until the
% whole population is filled.
previous_index = 0;
for i = 1 : max_rank
% Get the index for current rank i.e the last the last element in the
% sorted_chromosome with rank i.
current_index = max(find(sorted_chromosome(:,M + V + 1) == i));
% Check to see if the population is filled if all the individuals with
% rank i is added to the population.
if current_index > pop
% If so then find the number of individuals with in with current
% rank i.
remaining = pop - previous_index;
% Get information about the individuals in the current rank i.
temp_pop = ...
sorted_chromosome(previous_index + 1 : current_index, :);
% Sort the individuals with rank i in the descending order based on
% the crowding distance.
[temp_sort,temp_sort_index] = ...
sort(temp_pop(:, M + V + 2),'descend');
% Start filling individuals into the population in descending order
% until the population is filled.
for j = 1 : remaining
f(previous_index + j,:) = temp_pop(temp_sort_index(j),:);
end
return;
elseif current_index < pop
% Add all the individuals with rank i into the population.
f(previous_index + 1 : current_index, :) = ...
sorted_chromosome(previous_index + 1 : current_index, :);
else
% Add all the individuals with rank i into the population.
f(previous_index + 1 : current_index, :) = ...
sorted_chromosome(previous_index + 1 : current_index, :);
return;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
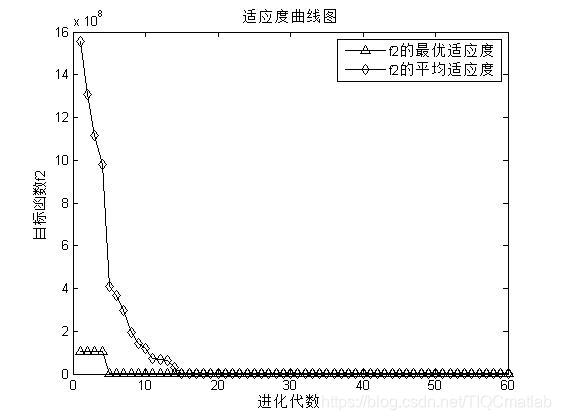
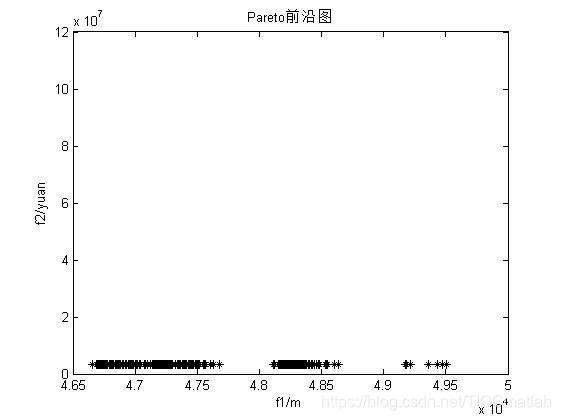
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
[3]周品.MATLAB 神经网络设计与应用[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]陈明.MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[5]方清城.MATLAB R2016a神经网络设计与应用28个案例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2018.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/115690807
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)