【图像去噪】基于matlab高斯+低通+巴特沃斯滤波虹膜图像滤波【含Matlab源码 501期】
一、图像去噪及滤波简介
1 图像去噪
1.1 图像噪声定义
噪声是干扰图像视觉效果的重要因素,图像去噪是指减少图像中噪声的过程。噪声分类有三种:加性噪声,乘性噪声和量化噪声。我们用f(x,y)表示图像,g(x,y)表示图像信号,n(x,y)表示噪声。
图像去噪是指减少数字图像中噪声的过程。现实中的数字图像在数字化和传输过程中常受到成像设备与外部环境噪声干扰等影响,称为含噪图像或噪声图像。去噪是图像处理研究中的一个重点内容。在图像的获取、传输、发送、接收、复制、输出等过程中,往往都会产生噪声,其中的椒盐噪声是比较常见的一种噪声,它属于加性噪声。
1.2 图像噪声来源
(1)图像获取过程中
图像传感器CCD和CMOS采集图像过程中受传感器材料属性、工作环境、电子元器件和电路结构等影响,会引入各种噪声。
(2)图像信号传输过程中
传输介质和记录设备等的不完善,数字图像在其传输记录过程中往往会受到多种噪声的污染。
1.3 噪声分类
噪声按照不同的分类标准可以有不同的分类形式:
基于产生原因:内部噪声,外部噪声。
基于噪声与信号的关系:
加性噪声:加性噪声和图像信号强度是不相关的,这类带有噪声的图像g可看成为理想无噪声图像f与噪声n之和:
g = f + n;
乘性嗓声:乘性噪声和图像信号是相关的,往往随图像信号的变化而变化,载送每一个象素信息的载体的变化而产生的噪声受信息本身调制。在某些情况下,如信号变化很小,噪声也不大。为了分析处理方便,常常将乘性噪声近似认为是加性噪声,而且总是假定信号和噪声是互相统计独立。
g = f + f*n
按照基于统计后的概率密度函数:
是比较重要的,主要因为引入数学模型这就有助于运用数学手段去除噪声。在不同场景下噪声的施加方式都不同,由于在外界的某种条件下,噪声下图像-原图像(没有噪声时)的概率密度函数(统计结果)服从某种分布函数,那么就把它归类为相应的噪声。下面将具体说明基于统计后的概率密度函数的噪声分类及其消除方式。
1.4 图像去噪算法的分类
(1)空间域滤波
空域滤波是在原图像上直接进行数据运算,对像素的灰度值进行处理。常见的空间域图像去噪算法有邻域平均法、中值滤波、低通滤波等。
(2)变换域滤波
图像变换域去噪方法是对图像进行某种变换,将图像从空间域转换到变换域,再对变换域中的变换系数进行处理,再进行反变换将图像从变换域转换到空间域来达到去除图像嗓声的目的。将图像从空间域转换到变换域的变换方法很多,如傅立叶变换、沃尔什-哈达玛变换、余弦变换、K-L变换以及小波变换等。而傅立叶变换和小波变换则是常见的用于图像去噪的变换方法。
(3)偏微分方程
偏微分方程是近年来兴起的一种图像处理方法,主要针对低层图像处理并取得了很好的效果。偏微分方程具有各向异性的特点,应用在图像去噪中,可以在去除噪声的同时,很好的保持边缘。偏微分方程的应用主要可以分为两类:一种是基本的迭代格式,通过随时间变化的更新,使得图像向所要得到的效果逐渐逼近,这种算法的代表为Perona和Malik的方程,以及对其改进后的后续工作。该方法在确定扩散系数时有很大的选择空间,在前向扩散的同时具有后向扩散的功能,所以,具有平滑图像和将边缘尖锐化的能力。偏微分方程在低噪声密度的图像处理中取得了较好的效果,但是在处理高噪声密度图像时去噪效果不好,而且处理时间明显高出许多。
(4)变分法
另一种利用数学进行图像去噪方法是基于变分法的思想,确定图像的能量函数,通过对能量函数的最小化工作,使得图像达到平滑状态,现在得到广泛应用的全变分TV模型就是这一类。这类方法的关键是找到合适的能量方程,保证演化的稳定性,获得理想的结果。
形态学噪声滤除器将开与闭结合可用来滤除噪声,首先对有噪声图像进行开运算,可选择结构要素矩阵比噪声尺寸大,因而开运算的结果是将背景噪声去除;再对前一步得到的图像进行闭运算,将图像上的噪声去掉。据此可知,此方法适用的图像类型是图像中的对象尺寸都比较大,且没有微小细节,对这类图像除噪效果会较好。
2 频域滤波
2.1 主要步骤:空域(傅里叶变换、卷积)>>>频域(与转移函数相乘、处理、傅里叶反变换)>>>空域
2.2 常用频域增强方法:
巴特沃斯滤波器:阶为n,截断频率为D0的转移函数为:
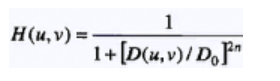
(1)低通滤波:
低通巴特沃斯滤波器在高低频率间的过渡比较光滑,所以得到的输出图其“振铃”现象不明显。
频域低通滤波器能消除虚假轮廓。
(2)高通滤波:
就是利用滤波器的频率特性,让高频的通过,低频的无法通过,就好比在频率域设置阈值,频率域每一个频率分量有一个“幅值”,滤波器就好比在不同的频率分量给这个幅值乘以不同的增益,高通就好比高频部分增益为1,低频部分增益为0,当然这是理想高通。高斯高通滤波器就是频域每一个频率分量的增益的连接而成的曲线是一个高斯曲线
高通巴特沃斯滤波器.
G( x, y ) = g ( x, y ) + c * f( x, y ) c = 0.5,0<=c<=1
(3)带通和带阻滤波
带阻滤波器:阻止一定频率范围内的信号通过而允许其他频率范围内的信号通过。
带通滤波器:允许一定频率范围内的信号通过而阻止其它频率范围内的信号通过。带通和带阻互补。
低通、高通、带通、带阻等线性滤波器可以较好地消除线性叠加在图像上的加性噪声。但实际中,噪声和图像也常常是以非线性的方式结合。例如光源照明成像的情况,其中光的入射和景物的反射是以相乘的形式对成像做出贡献的,这样成像中的噪声与景物也是相乘的关系。
(4)同态滤波:
是一种在频域中同时将图像亮度范围进行压缩和将图像对比度进行增强的方法。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = frequencydem(varargin)
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @frequencydem_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @frequencydem_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin & isstr(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
%----------------------------------------------------------
% --- Executes just before frequencydem is made visible.
function frequencydem_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
movegui(hObject,'onscreen')% To display application onscreen
movegui(hObject,'center') % To display application in the center of screen
image_file = get(handles.nameEdit,'String');
im_original=image_read(char(image_file));
set(handles.Or_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF')
set(handles.filtered_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF');
set(handles.difference_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF');
set(handles.filt3D,'HandleVisibility','OFF');
set(handles.filt2D,'HandleVisibility','OFF');
set(handles.Or_image,'HandleVisibility','ON')
axes(handles.Or_image);
imagesc(im_original);
colormap(gray(256));
axis equal;
axis tight;
axis off;
set(handles.Or_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF')
set(handles.Or_image,'XTickLabel',' ','YTickLabel',' ')
%----------------------------------------------------------
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = frequencydem_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
varargout{1} = handles.output;
%----------------------------------------------------------
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function image_selection_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
if ispc
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
else
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'));
end
%----------------------------------------------------------
% Executes on button press in apply_button.
function apply_button_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
image_file = get(handles.nameEdit,'String'); % to read the image filename selected
im_original=image_read(char(image_file)); % filename
% set(handles.Or_image,'HandleVisibility','ON') % to make plot 1 visible for original image plot
% image(im_original);
% colormap(gray(256));
% axis image;
% axis off;
% set(handles.filtered_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF') % to make plot 2 unvisible to the original image plot
set(handles.Or_image,'XTickLabel',' ','YTickLabel',' ') % to get rid of tick labels
method_number = get(handles.method_selection,'Value'); % selected method
t = get(handles.cutoffEdit,'String');
F_cut = str2num (t);
if F_cut <= 0
msgbox ('Please input meaningful cut off frequency');
return
end;
% For gaussian blur and USM-Filter method
switch method_number
case { 1 } %Ideal Filter
[im_filtered, H] = ideal_low(im_original, F_cut);
case { 2 }
[im_filtered, H] = ideal_high(im_original, F_cut);
case { 3 }
[im_filtered, H] = gaussian_low(im_original,F_cut);
case { 4 }
[im_filtered, H]= gaussian_high(im_original, F_cut);
case { 5 }
t = get(handles.butflyEdit,'String');
n = str2num (t);
if t <= 0
msgbox('Invalid order number!');
return;
end;
[im_filtered, H] = butterworth_low(im_original, F_cut,n);
case { 6 }
t = get(handles.butflyEdit,'String');
n = str2num (t);
if t <= 0
msgbox('Invalid order number!');
return;
end;
[im_filtered, H] = butterworth_high(im_original, F_cut,n);
end;
set(handles.Or_image,'HandleVisibility','ON')
axes(handles.Or_image);
imagesc(im_original);
colormap(gray(256));
axis equal;
axis tight;
axis off;
set(handles.Or_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF')
set(handles.filtered_image,'HandleVisibility','ON') ; % to make plot 2 visible to the filtered image plot
axes(handles.filtered_image);
imagesc(im_filtered) % to plot filtered image
colormap(gray(256));
axis equal;
axis tight;
axis off;
set(handles.filtered_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF')
set(handles.difference_image,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.difference_image);
dif_image = im_filtered- im_original;
imagesc(dif_image);
colormap(gray(256));
axis equal;
axis tight;
axis off;
set(handles.difference_image,'HandleVisibility','OFF')
set(handles.filt2D,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.filt2D);
imagesc(H);
colormap(gray(256));
axis equal;
axis tight;
axis off;
set(handles.filt2D,'HandleVisibility','OFF');
set(handles.filt3D,'HandleVisibility','ON');
axes(handles.filt3D);
[co,ro]=size(H);
surfl(H);
set(handles.filt3D,'HandleVisibility','OFF');
%----------------------------------------------------------
% --- Executes on button press in close_button.
function close_button_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
close all; % to close GUI
%----------------------------------------------------------
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function method_selection_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
if ispc
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
else
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'));
end
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function nameEdit_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to nameEdit
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
else
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'));
end
%Read all kinds of image files
function im_original=image_read(image_file)
lg=length(image_file);
if strcmpi(image_file(lg-2:lg),'mat') | strcmpi(image_file(lg-2:lg),'dat')
im_original=load(image_file);
else
im_original=imread(char(image_file));
end;
im_original = double(im_original);
t=size(im_original,3);
if t==3
imt=floor((im(:,:,1)+im(:,:,2)+im(:,:,3))/3);
clear im_original;
im_original=imt;
clear imt;
end;
t=size(im_original,3);
if t~=1
display('Error in opening the image file!');
end;
% butterworth high pass filter
function [out, H] = butterworth_high (im,fc,n)
[co,ro] = size(im);
cx = round(co/2); % find the center of the image
cy = round (ro/2);
imf=fftshift(fft2(im));
H=zeros(co,ro);
for i = 1 : co
for j =1 : ro
d = (i-cx).^2 + (j-cy).^ 2;
if d ~= 0
H(i,j) = 1/(1+((fc*fc/d).^(2*n)));
end;
end;
end;
outf = imf .* H;
out = abs(ifft2(outf));
% butterworth low pass filter
function [out, H] = butterworth_low (im,fc,n)
[co,ro] = size(im);
cx = round(co/2); % find the center of the image
cy = round (ro/2);
imf=fftshift(fft2(im));
H=zeros(co,ro);
for i = 1 : co
for j =1 : ro
d = (i-cx).^2 + (j-cy).^ 2;
H(i,j) = 1/(1+((d/fc/fc).^(2*n)));
end;
end;
outf = imf .* H;
out = abs(ifft2(outf));
%Gaussian high pass filter
function [out, H] = gaussian_high(im, fc)
imf = fftshift(fft2(im));
[co,ro]=size(im);
H = gaussian_filter(co,ro, fc);
H = 1-H;
out = zeros(co,ro);
outf= imf.*H;
out=abs(ifft2(outf));
%Gaussian lowpass filter
function [out, H] = gaussian_low(im, fc)
imf = fftshift(fft2(im));
[co,ro]=size(im);
out = zeros(co,ro);
H = gaussian_filter(co,ro, fc);
outf= imf.*H;
out=abs(ifft2(outf));
% gaussian filter
function H = gaussian_filter(co,ro, fc)
cx = round(co/2); % find the center of the image
cy = round (ro/2);
H = zeros(co,ro);
for i = 1 : co
for j = 1 : ro
d = (i-cx).^2 + (j-cy).^2;
H(i,j) = exp(-d/2/fc/fc);
end;
end;
三、运行结果






四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[5]基于matlab的传统算法图像去噪的实现原理
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114670687
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)