【物理应用】基于matlab PIC模型太阳风粒子模拟【含Matlab源码 493期】
【摘要】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1: 通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
获取代码方式2: 完整代码已上传我的资源:【物理应用】基于matlab PIC模型太阳风粒子模拟...
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
获取代码方式2:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【物理应用】基于matlab PIC模型太阳风粒子模拟【含Matlab源码 493期】
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、部分源代码
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Si
%
% For more,
% and
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%reset variables
clear variables
%identify globals needed by the potential solver
global EPS0 QE den A n0 phi0 phi_p Te box
%setup constants
EPS0 = 8.854e-12; %permittivity of free space
QE = 1.602e-19; %elementary charge
K = 1.381e-23; %boltzmann constant
AMU = 1.661e-27; %atomic mass unit
M = 32*AMU; %ion mass (molecular oxygen)
%input settings
n0 = 1e12; %density in #/m^3
phi0 = 0; %reference potential
Te = 1; %electron temperature in eV
Ti = 0.1; %ion velocity in eV
v_drift = 7000; %ion injection velocity, 7km/s
phi_p = -5; %wall potential
%calculate plasma parameters
lD = sqrt(EPS0*Te/(n0*QE)); %Debye length
vth = sqrt(2*QE*Ti/M); %thermal velocity with Ti in eV
%set simulation domain
nx = 16; %number of nodes in x direction
ny = 10; %number of nodes in y direction
ts = 200; %number of time steps
dh = lD; %cell size
np_insert = (ny-1)*15; %insert 15 particles per cell
%compute some other values
nn = nx*ny; %total number of nodes
dt = 0.1*dh/v_drift; %time step, at vdrift move 0.10dx
Lx = (nx-1)*dh; %domain length in x direction
Ly = (ny-1)*dh; %domain length in y direction
%specify plate dimensions
box(1,:) = [floor(nx/3) floor(nx/3)+2]; %x range
box(2,:) = [1 floor(ny/2)]; %y range
%create an object domain for visualization
object = zeros(nx,ny);
for j=box(2,1):box(2,2)
object(box(1,1):box(1,2),j)=ones(box(1,2)-box(1,1)+1,1);
end
%calculate specific weight
flux = n0*v_drift*Ly; %flux of entering particles
npt = flux*dt; %number of real particles created per timestep
spwt = npt/np_insert; %specific weight, real particles per macroparticle
mp_q = 1; %macroparticle charge
max_part=20000; %buffer size
%allocate particle array
part_x = zeros(max_part,2); %particle positions
part_v = zeros(max_part,2); %particle velocities
%set up multiplication matrix for potential solver
%here we are setting up the Finite Difference stencil
A = zeros(nn); %allocate empty nn * nn matrix
%set regular stencil on internal nodes
for j=2:ny-1 %only internal nodes
for i=2:nx-1
u = (j-1)*nx+i; %unknown (row index)
A(u,u) = -4/(dh*dh); %phi(i,j)
A(u,u-1)=1/(dh*dh); %phi(i-1,j)
A(u,u+1)=1/(dh*dh); %phi(i+1,j)
A(u,u-nx)=1/(dh*dh); %phi(i,j-1)
A(u,u+nx)=1/(dh*dh); %phi(i,j+1)
end
end
%neumann boundary on y=0
for i=1:nx
u=i;
A(u,u) = -1/dh; %phi(i,j)
A(u,u+nx) = 1/dh; %phi(i,j+1)
end
%neumann boundary on y=Ly
for i=1:nx
u=(ny-1)*nx+i;
A(u,u-nx) = 1/dh; %phi(i,j-1)
A(u,u) = -1/dh; %phi(i,j)
end
%neumann boundary on x=Lx
for j=1:ny
u=(j-1)*nx+nx;
A(u,:)=zeros(1,nn); %clear row
A(u,u-1) = 1/dh; %phi(i-1,j)
A(u,u) = -1/dh; %phi(i,j)
end
%dirichlet boundary on x=0
for j=1:ny
u=(j-1)*nx+1;
A(u,:)=zeros(1,nn); %clear row
A(u,u) = 1; %phi(i,j)
end
%dirichlet boundary on nodes corresponding to the plate
for j=box(2,1):box(2,2)
for i=box(1,1):box(1,2)
u=(j-1)*nx+i;
A(u,:)=zeros(1,nn); %clear row
A(u,u)=1; %phi(i,j)
end
end
%initialize
phi = ones(nx,ny)*phi0; %set initial potential to phi0
np = 0; %clear number of particles
disp(['Solving potential for the first time. Please be patient, this could take a while.']);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% MAIN LOOP
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for it=1:ts %iterate for ts time steps
%reset field quantities
den = zeros(nx,ny); %number density
efx = zeros(nx,ny); %electric field, x-component
efy = zeros(nx,ny); %electric field, y-component
chg = zeros(nx,ny); %charge distribution
%*** 1. CALCULATE CHARGE DENSITY ***
% deposit charge to nodes
for p=1:np %loop over particles
fi = 1+part_x(p,1)/dh; %real i index of particle's cell
i = floor(fi); %integral part
hx = fi-i; %the remainder
fj = 1+part_x(p,2)/dh; %real j index of particle's cell
j = floor(fj); %integral part
hy = fj-j; %the remainder
%interpolate charge to nodes
chg(i,j) = chg(i,j) + (1-hx)*(1-hy);
chg(i+1,j) = chg(i+1,j) + hx*(1-hy);
chg(i,j+1) = chg(i,j+1) + (1-hx)*hy;
chg(i+1,j+1) = chg(i+1,j+1) + hx*hy;
end
%calculate density
den = spwt*mp_q*chg/(dh*dh);
%apply boundaries
den(1,:) = 2*den(1,:); %double density since only half volume contributing
den(nx,:) = 2*den(nx,:);
den(:,1) = 2*den(:,1);
den(:,ny) = 2*den(:,ny);
%add density floor for plotting and to help the solver
den = den + 1e4;
%*** 2. CALCULATE POTENTIAL ***
phi = eval_2dpot_GS(phi);
%*** 3. CALCULATE ELECTRIC FIELD ***
efx(2:nx-1,:) = phi(1:nx-2,:) - phi(3:nx,:); %central difference on internal nodes
efy(:,2:ny-1) = phi(:,1:ny-2) - phi(:,3:ny); %central difference on internal nodes
efx(1,:) = 2*(phi(1,:) - phi(2,:)); %forward difference on x=0
efx(nx,:) = 2*(phi(nx-1,:) - phi(nx,:)); %backward difference on x=Lx
efy(:,1) = 2*(phi(:,1) - phi(:,2)); %forward difference on y=0
efy(:,ny) = 2*(phi(:,ny-1) - phi(:,ny)); %forward difference on y=Ly
efx = efx / (2*dh); %divide by dominator
efy = efy / (2*dh);
%*** 4. GENERATE NEW PARTICLE ***
if (np+np_insert>=max_part) %make sure we don't exceed array limits
% np_insert=max_part-np;
end
%insert particles randomly distributed in y and in the first cell
part_x(np+1:np+np_insert,1)=rand(np_insert,1)*dh; %x position
part_x(np+1:np+np_insert,2)=rand(np_insert,1)*Ly; %y position
%sample Maxwellian in x and y, add drift velocity in x
part_v(np+1:np+np_insert,1)=v_drift+(-1.5+rand(np_insert,1)+rand(np_insert,1)+rand(np_insert,1))*vth;
part_v(np+1:np+np_insert,2)=0.5*(-1.5+rand(np_insert,1)+rand(np_insert,1)+rand(np_insert,1))*vth;
np=np+np_insert; %increment particle counter
%*** 5. MOVE PARTICLES ***
p=1;
while(p<=np) %loop over particles
fi = 1+part_x(p)/dh; %i index of particle's cell
i = floor(fi);
hx = fi-i; %fractional x position in cell
fj = 1+part_x(p,2)/dh; %j index of particle' cell
j = floor(fj);
hy = fj-j; %fractional y position in cell
%gather electric field
E=[0 0];
E = [efx(i,j) efy(i,j)]*(1-hx)*(1-hy); %contribution from (i,j)
E = E+ [efx(i+1,j) efy(i+1,j)]*hx*(1-hy); %(i+1,j)
E = E + [efx(i,j+1) efy(i+1,j)]*(1-hx)*hy; %(i,j+1)
E = E + [efx(i+1,j+1) efy(i+1,j+1)]*hx*hy; %(i+1,j+1)
%update velocity and position
F = QE*E; %Lorentz force, F=qE
a = F/M; %acceleration
part_v(p,:) = part_v(p,:)+a*dt; %update velocity
part_x(p,:) = part_x(p,:)+part_v(p,:)*dt; %update position
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
三、运行结果
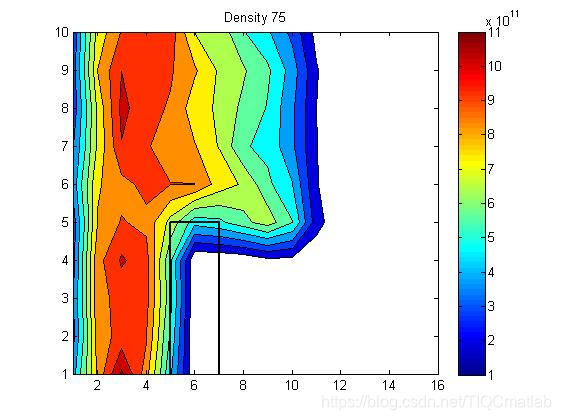
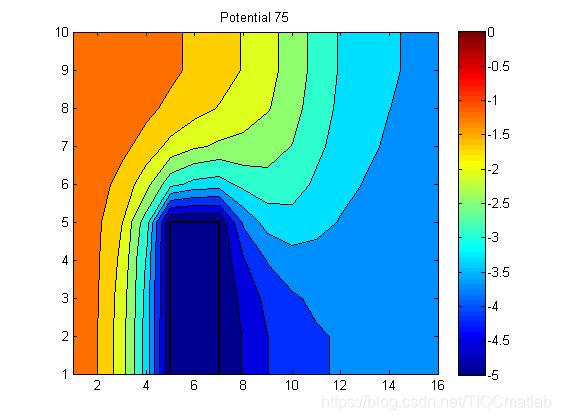
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 门云阁.MATLAB物理计算与可视化[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114643928
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)