【电力预测】基于matlab GUI灰色模型电力负荷预测【含Matlab源码 769期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源: 【电力负荷预测】基于matlab GUI灰色模型电力负荷预测【含Matlab源码 769期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、灰色模型简介
1 灰色系统介绍
灰色系统是由华中科技大学的邓聚龙教授于80年代初创立,该系统作为新兴的横断学科,在短短的二十年里已得到了长足的发展。 其已经成为社会,经济,科教,科技等很多领域进行预测,决策,评估,规划,控制,系统分析和建模的重要方法之一。特别是它对于时间序列短,统计数据少,信息不完全系统的建模与分析,具有非常显著的功效。
灰色预测是一种对含有不确定因素的系统进行预测的方法。灰色预测通过鉴别系统因素之间发展趋势的相异程度,即进行关联分析,并对原始数据进行生成处理来寻找系统变动的规律,生成有较强规律性的数据序列,然后建立相应的微分方程模型,从而预测事物未来发展趋势的状况。其用等时距观测到的反映预测对象特征的一系列数量值构造灰色预测模型,预测未来某一时刻的特征量,或达到某一特征量的时间。

2 灰色系统的基本原理
公理1 差异信息原理
”差异“是信息,凡信息必有差异。
公理2 解的非唯一性原理
信息不完全,不确定的解是非唯一的。该原理是灰色系统理论解决实际问题所遵循的基本法则。
公理3 最少信息原理
灰色系统理论的特点是充分开发利用已占有的”最少信息”。
公理4 认知根据原理
信息是认知的根据。
公理5 新信息优先原理
新信息对认知的作用大于老信息。
公理6 灰性不灭原理
“信息不完全”是绝对的。
3 灰生成技术
3.1 灰色序列生成
是一种通过对原始数据的挖掘,整理来寻求数据变化的现实规律的途径,简称灰生成。
3.2 灰生成特点
在保持原序列形式的前提下,改变序列中的数据的值与性质。一切灰色序列都能通过某种生成弱化其随机性,显现其规律性。
3.3 灰生成的作用
(1)统一序列的目标性质,为灰决策提供基础。
(2)将摆动序列转化为单调增长序列,以利于灰建模。
(3)揭示潜藏在序列中的递增势态,变不可比为可比序列。
4 常见的几种灰色生成类型:
4.1 累加生成算子(AGO)
定义 累加生成算子是对原序列中的数据依次累加得到的数列。

4.2 逆累加生成算子(IAGO)
逆累加生成算子其实就是累减生成,上面是累加,计算步骤跟上面差不多,就是变成了减号罢了。
首先我们先生成序列

4.3 均值生成算子(MEAN)
看到标题大家可能就知道怎么计算了,我们需要将序列中的前后相邻的两数取平均数,以获得生成新的序列。

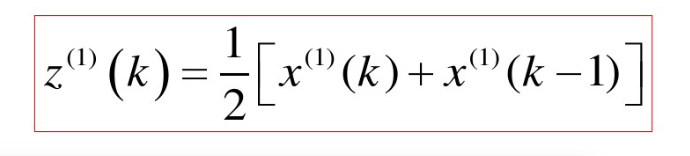
4.4 级比生成算子

5 GM(1,1)模型
我们先简单说明一下模型成立的前提,灰色理论认为一个系统的行为现象虽然是朦胧的,数据是复杂的,但是他一定会包含一定的规律在其中,如果你了解过傅里叶,那么你可以很轻松的理解一个系统暗含规律的情况。灰数的生成就是为了从杂乱的数据中找到规律。因此灰色模型所用的数据是生成数据而非原始数据。




三、部分源代码
function varargout = gmgui(varargin)
% GMGUI MATLAB code for gmgui.fig
% GMGUI, by itself, creates a new GMGUI or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = GMGUI returns the handle to a new GMGUI or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% GMGUI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in GMGUI.M with the given input arguments.
%
% GMGUI('Property','Value',...) creates a new GMGUI or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before gmgui_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to gmgui_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help gmgui
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 10-May-2016 08:02:00
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @gmgui_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @gmgui_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before gmgui is made visible.
function gmgui_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to gmgui (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for gmgui
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes gmgui wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = gmgui_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
global V;
V(1)=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double
global V;
V(2)=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit3 as a double
global V;
V(3)=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit4 as a double
global V;
V(4)=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit5 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit5 as a double
global V;
V(5)=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));
guidata(hObject, handles);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
四、运行结果

五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
[3]周品.MATLAB 神经网络设计与应用[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]陈明.MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[5]方清城.MATLAB R2016a神经网络设计与应用28个案例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2018.
[6]预测模型——灰色模型
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/116504853
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)