【语音去噪】基于matlab GUI LMS+RLS语音去噪【含Matlab源码 528期】
一、LMS+RLS简介
最小均方(LMS, Least Mean Squares)和 递归最小二乘(RLS, Recursive Least Squares)是两种最基本的自适应滤波算法。
1 LMS
LMS算法是自适应滤波器中常用的一种算法与维纳算法不同的是其系统的系数随输入序列而改变。维纳算法中截取输入序列自相关函数的一段构造系统的最佳系数。而LMS算法则是对初始化的滤波器系数依据最小均方误差准则进行不断修正来实现的。因此理论上讲LMS算法的性能在同等条件下要优于维纳。但是LMS是在初始值下逐步调整的,因此在系统稳定前,会有一段调整时间,调整时间受步长因子的控制,一定范围内,步长因子越大,调整时间越小,步长因子的最大取值为R的迹。LMS采用平方误差最小的原则代替均方误差最小的原则,信号基本关系如下:
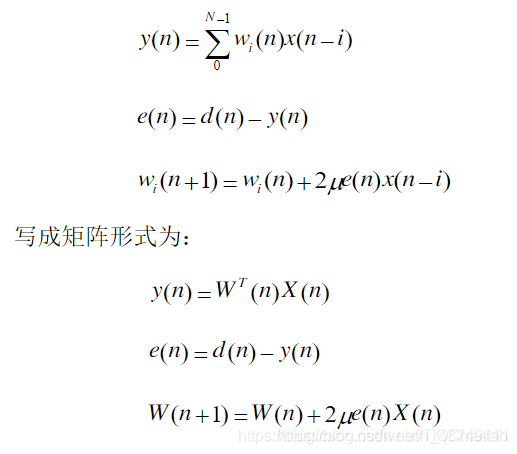
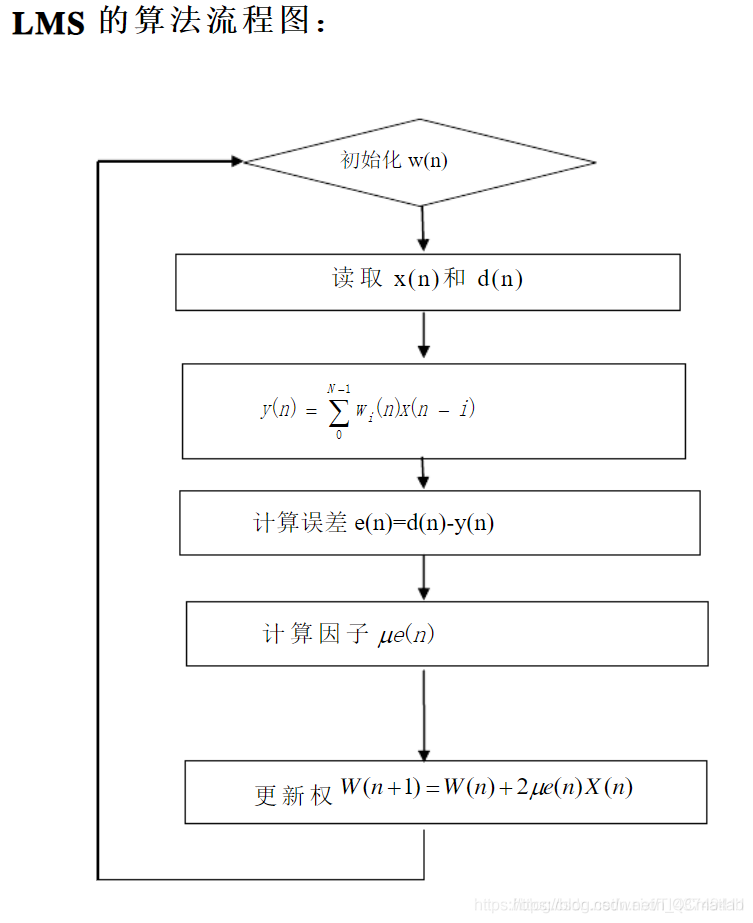
2 RLS



参数递推估计,每取得一次新的观测数据后,就在前次估计结果的基础上,利用新引入的观测数据对前次估计的结果,根据递推算法进行修正,减少估计误差,从而递推地得出新的参数估计值。这样,随着新观测数据的逐次引入,一次接一次地进行参数估计,直到参数估计值达到满意的精确程度为止。
3 RLS算法与LMS对比
由于LMS算法只是用以前各时刻的抽头参量等作该时刻数据块估计时的平方误差均方最小的准则,而未用现时刻的抽头参量等来对以往各时刻的数据块作重新估计后的累计平方误差最小的准则,所以 15 LMS算法对非平稳信号的适应性差。RLS算法的基本思想是力图使在每个时刻对所有已输入信号而言重估的平方误差的加权和最小,这使得RLS算法对非平稳信号的适应性要好。与LMS算法相比,RLS算法采用时间平均,因此,所得出的最优滤波器依赖于用于计算平均值的样本数,而LMS算法是基于集平均而设计的,因此稳定环境下LMS算法在不同计算条件下的结果是一致的。在性能方面,RLS的收敛速率比LMS要快得多,因此,RLS在收敛速率方面有很大优势。 图6分别为RLS算法和LMS算法在处理过程中的误差曲线,它指出了在迭代过程中的误差减少过程。由图可见,RLS算法在迭代过程中产生的误差明显小于LMS算法。由此可见,RLS在提取信号时,收敛速度快,估计精度高而且稳定性好,可以明显抑制振动加速度收敛过程,故对非平稳信号的适应性强,而LMS算法收敛速度慢,估计精度低而且权系数估计值因瞬时梯度估计围绕精确值波动较大,权噪声大,不稳定。
lms滤波器是采用瞬时值对相关矩阵、梯度等进行估计的方法,而rls则是将目标函数固定为最小二乘意义下的指数加权和的形式。换句话说,lms算法的最小化目标函数是瞬时误差信号的平方,而rls算法最小化的目标函数是从0时刻到k时刻为之所有信号在当前系数下的误差信号的加权平方和。由于都使用了当前时刻的系数,因此也可以说是后验误差的加权平方和。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = untitled(varargin)
%UNTITLED M-file for untitled.fig
% UNTITLED, by itself, creates a new UNTITLED or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = UNTITLED returns the handle to a new UNTITLED or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% UNTITLED('Property','Value',...) creates a new UNTITLED using the
% given property value pairs. Unrecognized properties are passed via
% varargin to untitled_OpeningFcn. This calling syntax produces a
% warning when there is an existing singleton*.
%
% UNTITLED('CALLBACK') and UNTITLED('CALLBACK',hObject,...) call the
% local function named CALLBACK in UNTITLED.M with the given input
% arguments.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help untitled
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 09-May-2006 17:38:13
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @untitled_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @untitled_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [], ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before untitled is made visible.
function untitled_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin unrecognized PropertyName/PropertyValue pairs from the
% command line (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for untitled
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes untitled wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = untitled_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in select.
function select_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to select (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename, pathname] = ...
uigetfile({'*.wav'},'File Selector');
if isequal(filename,0)|isequal(pathname,0)
return;
else
str=[pathname,filename];
setappdata(handles.figure1,'str',str);
[Y,FS]=wavread(str); %读取声音信号
SigLength=length(Y); %计算信号长度
t=(0:SigLength-1)/FS;
axes(handles.axes1);
plot(t,Y);
set(gca,'YLim',[-1 1]);
xlabel('t1:时间');
ylabel('Y(原音)');
title('原始语音信号')
end
% --- Executes on button press in test2.
function test2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to test2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
str2= getappdata(handles.figure1,'str');
[Y,FS,NBITS]=wavread(str2); %读取声音信号
sound(Y);
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu1.
function popupmenu1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = get(hObject,'String') returns popupmenu1 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu1
axes(handles.axes2);
popup_sel_index = get(handles.popupmenu1, 'Value');
str2= getappdata(handles.figure1,'str');
[Y,FS]=wavread(str2); %读取声音信号
SigLength=length(Y); %计算信号长度
t=(0:SigLength-1)/FS;
switch popup_sel_index
case 1
case 2
x1=1/2*sin(2*pi*5000*t);
xn=x1+0.02*x1.*randn(size(x1));
xn=xn';
xs=Y+xn;
setappdata(handles.figure1,'xs',xs);
plot(t,xs);
set(gca,'YLim',[-2 2]);
xlabel('t1:时间');
title('加噪后的语音信号')
spPower=sum(abs(Y( : )).^2)/length(Y( : ));
noPower=sum(abs(xn( : )).^2)/length(xn( : ));
spPower=10*log10(spPower);
noPower=10*log10(noPower);
SNR=spPower-noPower;
set(handles.edit4,'string',num2str(SNR));
case 3
xn=sin(2*pi*120*t);
xn=xn';
xs=Y+xn;
setappdata(handles.figure1,'xs',xs);
plot(t,xs);
set(gca,'YLim',[-2 2]);
xlabel('t1:时间');
title('加噪后的语音信号')
spPower=sum(abs(Y( : )).^2)/length(Y( : ));
noPower=sum(abs(xn( : )).^2)/length(xn( : ));
spPower=10*log10(spPower);
noPower=10*log10(noPower);
SNR=spPower-noPower;
set(handles.edit4,'string',num2str(SNR));
case 4
xs=awgn(Y,10);%加入高斯白噪声,信噪比随机产生
setappdata(handles.figure1,'xs',xs);
xn=xs-Y;
plot(t,xs);
set(gca,'YLim',[-2 2]);
xlabel('t1:时间');
title('加噪后的语音信号')
spPower=sum(abs(Y( : )).^2)/length(Y( : ));
noPower=sum(abs(xn( : )).^2)/length(xn( : ));
spPower=10*log10(spPower);
noPower=10*log10(noPower);
SNR=spPower-noPower;
set(handles.edit4,'string',num2str(SNR))
end
% --- Executes on button press in test3.
function test3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to test3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
xs1= getappdata(handles.figure1,'xs');
sound(xs1)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114870881
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)