【条形码识别】基于matlab GUI二维条形码识别【含Matlab源码 607期】
一、二维条形码识别简介
采用数字图像处理技术对二维条码进行识别, 是二维条形码识别中较常用的方法, 它在处理污损的条形码方面有光电识别方法无法比拟的优势。另外图像式识别方法对识别角度的要求没有光电识别方法那么严格, 对有些二维条形码 (如QR Code码) 可以以任意的角度识别。
1 图像式条形码识别过程
在图像式条形码识别过程中, 首先使用图像采集设备采集二维条形码图像, 然后利用图像处理技术对条形码图像进行去噪和分割处理, 最后调用条码特征读取算法, 读出条码值并显示识别结果, 图3是图像式条形码识别过程, 其中各模块的功能如下:
(1) 图像采集。通过数码相机、扫描仪或专用的图像传感器, 如CCD图像传感器或CMOS图像传感器等设备采集条形码图像。
(2) 图像预处理。图像预处理过程主要包括图像降噪、背景分离、图像校正等环节。由于采集系统或其他原因产生的噪声, 采集的图像有些比较模糊或存在黑白孤立点, 这对条码图像的进一步处理极为不利, 因此要根据条码图像噪声是否严重, 选择一种或多种滤波器进行滤波, 去除噪声。目前采用较多的是中值滤波法。背景分离是将条码区与背景分离, 从而避免在没有有效信息的区域进行特征提取, 提高后续处理的速度。背景分离一般采用标准差阈值跟踪法, 图像条码部分由黑白相间的条块组成, 灰度变化大, 因而标准差较大;而背景部分灰度分布较为平坦, 标准差较小。将条码图像分块, 每个小块的标准差若大于某一阈值, 则该小块中的所有像素点为有效;否则为背景。由于采集进来的图像总会出现一定的倾斜和偏移产生几何畸变, 给快速、正确地识别条码带来困难, 因此必须进行图像校正, 一般方法是:利用行差运算与Hough变换相结合, 快速、准确找到条码图像边界线, 计算出倾斜角度, 通过双线性插值对条码图像进行校正。
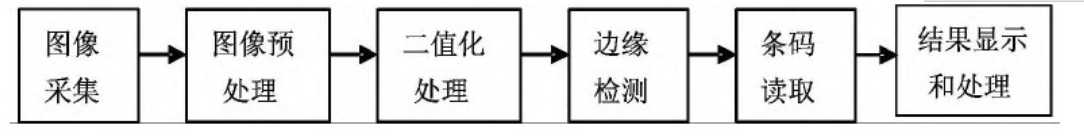
图1 图像式条形码识别过程
(3) 二值化处理。条码识别是以二值图像为基础的, 图像二值化算法很多, 条码图像直方图具有很好的双峰特性, 一般采用大津阈值法[4]就能够对于条码图像进行很好地分割。图像二值化之后, 二值图像中“1”像素代表黑条部分, “0”像素代表白条部分。
(4) 边缘检测。条码识别问题的实质是边缘检测的问题, 传统的条码识别算法是根据二阶导数零交叉来检测条码边缘[2,6]。
(5) 条码读取。根据确定的条码边缘确定条码黑白模块宽度, 利用不同的条码编码规则编制相应的译码程序, 确定条码字符值, 这一算法是非常成熟的。
(6) 结果显示和处理。一般由计算机显示条码识别的结果, 并可根据结果进行实际应用中的处理。
2 图像式条码识别技术难点
在图像式的条形码识别过程中, 若能知道条码条空宽度值, 对于不同的条码都有很成熟的算法来确定条码符号值。因此在图像式条码识别过程中, 图像处理部分的算法是十分重要的, 不同的图像处理方法将影响后续的条码识别结果。图像处理过程中的技术难点如下:
(1) 图像模糊问题。因条码印刷质量差、光照较弱、摄像设备质量等原因, 采集的条形码图像比较模糊, 黑白条块之间的边缘不清晰, 甚至黑白条的边缘几乎融合在一起。针对这一问题, 目前国内的一些处理方法都采用各种经典滤波技术对条码图像进行去噪, 如广泛采用的中值滤波技术。当采集图像非常模糊时, 这种处理方法具有一定局限性, 有时甚至导致条码无法识别。
(2) 边缘检测问题。在传统算法中一般是根据二阶导数零交叉来检测条码边缘。由于图像采集、图像滤波过程中在条码图像边缘处会有一定程度的模糊。又由于在条码图像去噪时, 大都选用经典的中值滤波算法, 该算法对椒盐噪声去噪声效果很明显, 但对高斯噪声去噪效果却较差。而在实际应用中, 图像采集产生的模糊基本上都是高斯噪声, 而中值滤波法对该噪声不能有效地去除。在边缘模糊情况下采用二阶导数零交叉来检测条码边缘会有1~2个像素的偏差, 这对条码的条空宽度的确定会产生影响, 从而影响识别。因此边缘模糊是影响条码识别的重要因素。
3 解决技术难点的方法
要解决边缘模糊问题, 必须对噪声进行分析。我们知道平滑的图像主要集中于中低频部分, 噪声信息或边缘信息主要集中在高频段。通常的滤波方法都是不加区分的滤掉高频信息, 不可避免地也会滤掉边缘信息, 从而造成图像边缘模糊。文献[6]提出了一种基于边缘检测的小波去噪方法, 该方法利用小波变换良好的时频特性, 只要沿着梯度方向检测小波变换系数模值的局部极大值点, 即可得到图像的边缘点, 但小波系数的模值极大值点也可能对应着噪声点。因此在检测出小波系数的极大值后, 还要去除与噪声点对应的小波系数。噪声的Lipschitz指数为负, 信号的Lipschitz指数为正, 它们随着尺度的增大信号系数逐渐变大, 而噪声系数逐渐变小。根据这一特点可除去噪声造成的虚假边缘, 将非噪声点的模值极大点连接起来得到图像的边缘。这种方法既可达到去噪目的又可保持图像的边缘, 这种把去噪和边缘检测结合起来的新思路在一定程度上解决了去噪引起图像边缘模糊的难题。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = untitled(varargin)
% UNTITLED M-file for untitled.fig
% UNTITLED, by itself, creates a new UNTITLED or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = UNTITLED returns the handle to a new UNTITLED or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% UNTITLED('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in UNTITLED.M with the given input arguments.
%
% UNTITLED('Property','Value',...) creates a new UNTITLED or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before untitled_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to untitled_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help untitled
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 03-Nov-2011 13:59:22
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @untitled_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @untitled_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before untitled is made visible.
function untitled_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to untitled (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for untitled
handles.output = hObject;
image1=imread('C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\61602302barcodehcc\barcodehcc\1.bmp');
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(image1);
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes untitled wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = untitled_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on mouse press over axes background.
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global im;
%提取条形码区域构成的矩形的左上角坐标
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
image=im;
l1=rgb2gray(image);
level=graythresh(l1);
l2=im2bw(l1,level);
l3=~l2;
l4=bwareaopen(l3,50);
l5=~l4;
l6=edge(l1,'canny');
l7=imclose(l6,strel('rectangle',[2,19]));
l8=imopen(l7,strel('rectangle',[2,19]));
l9=imopen(l8,strel('rectangle',[2,19]));
[L,num]=bwlabel(l9,8);
STATS=regionprops(L,'all');
a=length(STATS);
%figure,imshow(L);
%hold on;
b=0;
for i=1:a
temp=STATS(i).BoundingBox;
s=temp(3)*temp(4);
if s>b
b=s;
k=i;%记录面积最大的标记区域的索引值
end
end
%rectangle('position',STATS(k).BoundingBox,'edgecolor','r');%绘制最大标记区域的外接矩形
temp=STATS(k).BoundingBox;
Rx=round(temp(1));Ry=round(temp(2));%提取条形码区域左上角的坐标
Rwidth=round(temp(3));Rlength=round(temp(4));
%初始化
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
check_left = [13,25,19,61,35,49,47,59,55,11;... %左边数据编码,奇
39,51,27,33,29,57, 5,17, 9,23]; %左边数据编码,偶
check_right = [114,102,108,66,92,78,80,68,72,116]; %右边数据编码
first_num = [31,20,18,17,12,6,3,10,9,5]; %第一位数据编码
bar = im; %读输入条形码图片
bar_Gray = rgb2gray(bar); %将RGB图片转换灰度图
[a_hist x] = imhist(bar_Gray); %绘制灰度直方图,返回直方图数据向量a_hist,和相应的色彩值向量x
%寻找进行二值化处理的阈值,存放在T中
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
hist_max = [];
if a_hist(1)>a_hist(2)
hist_max = [hist_max 1];
end
x = max(x);
for i=2:x
if a_hist(i)>a_hist(i-1) && a_hist(i)>a_hist(i+1)
hist_max = [hist_max i];
end
end
if a_hist(x)<a_hist(x+1)
hist_max = [hist_max x+1];
end
[m,n] = size(hist_max);
k = 0;
max_1 = 0;
max_2 = 0;
for i=1:n
if k<a_hist(hist_max(i))
k = a_hist(hist_max(i));
max_1 = hist_max(i);
end
end
temp = a_hist(max_1);
a_hist(max_1) = 0;
k = 0;
for i=1:n
if k<a_hist(hist_max(i))
k = a_hist(hist_max(i));
max_2 = hist_max(i);
end
end
a_hist(max_1) = temp;
if max_1>max_2
k = max_1;
max_1 = max_2;
max_2 = k;
end
T = max_1;
k = a_hist(max_1);
for i=max_1:max_2
if k>a_hist(i)
k = a_hist(i);
T = i;
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
[m,n] = size(bar_Gray); %求灰度图的大小
for i=1:m %对图像进行二值化处理
for j=1:n
if bar_Gray(i,j)>T %选择适当的阈值进行二值化处理
bar_10(i,j) = 1;
else
bar_10(i,j) = 0;
end
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[5]赵群礼,周秋平.基于图像的二维条形码识别技术研究[J].合肥师范学院学报. 2010,28(06)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/115107037
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)