【数学建模】基于matlab GUI理发店排队模拟系统【含Matlab源码 1116期】
【摘要】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1: 完整代码已上传我的资源:【数学建模】基于matlab GUI理发店排队模拟系统【含Matlab源码 1116期】
获取代码方式2: 通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭...
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【数学建模】基于matlab GUI理发店排队模拟系统【含Matlab源码 1116期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、部分源代码
function varargout = lifashi_final(varargin)
% LIFASHI_FINAL Application M-file for lifashi_final.fig
% FIG = LIFASHI_FINAL launch lifashi_final GUI.
% LIFASHI_FINAL('callback_name', ...) invoke the named callback.
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.0 15-Aug-2020 00:44:45
if nargin == 0 % LAUNCH GUI
fig = openfig(mfilename,'reuse');
% Use system color scheme for figure:
set(fig,'Color',get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'));
% Generate a structure of handles to pass to callbacks, and store it.
handles = guihandles(fig);
guidata(fig, handles);
if nargout > 0
varargout{1} = fig;
end
elseif ischar(varargin{1}) % INVOKE NAMED SUBFUNCTION OR CALLBACK
try
if (nargout)
[varargout{1:nargout}] = feval(varargin{:}); % FEVAL switchyard
else
feval(varargin{:}); % FEVAL switchyard
end
catch
disp(lasterr);
end
end
%| ABOUT CALLBACKS:
%| GUIDE automatically appends subfunction prototypes to this file, and
%| sets objects' callback properties to call them through the FEVAL
%| switchyard above. This comment describes that mechanism.
%|
%| Each callback subfunction declaration has the following form:
%| <SUBFUNCTION_NAME>(H, EVENTDATA, HANDLES, VARARGIN)
%|
%| The subfunction name is composed using the object's Tag and the
%| callback type separated by '_', e.g. 'slider2_Callback',
%| 'figure1_CloseRequestFcn', 'axis1_ButtondownFcn'.
%|
%| H is the callback object's handle (obtained using GCBO).
%|
%| EVENTDATA is empty, but reserved for future use.
%|
%| HANDLES is a structure containing handles of components in GUI using
%| tags as fieldnames, e.g. handles.figure1, handles.slider2. This
%| structure is created at GUI startup using GUIHANDLES and stored in
%| the figure's application data using GUIDATA. A copy of the structure
%| is passed to each callback. You can store additional information in
%| this structure at GUI startup, and you can change the structure
%| during callbacks. Call guidata(h, handles) after changing your
%| copy to replace the stored original so that subsequent callbacks see
%| the updates. Type "help guihandles" and "help guidata" for more
%| information.
%|
%| VARARGIN contains any extra arguments you have passed to the
%| callback. Specify the extra arguments by editing the callback
%| property in the inspector. By default, GUIDE sets the property to:
%| <MFILENAME>('<SUBFUNCTION_NAME>', gcbo, [], guidata(gcbo))
%| Add any extra arguments after the last argument, before the final
%| closing parenthesis.
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function varargout = lifashi_Callback(h, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function varargout = guke_Callback(h, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function varargout = pushbutton1_Callback(h, eventdata, handles, varargin)
ln=str2double(get(handles.lifashi,'string'));
axes(handles.axes1)
%理发仿真程序
%a(j,i):理发师j在第i分钟正在服务的顾客剩下的时间
%c(i):理发店里的顾客总数
%d(i):理发店等待的顾客数
%S(j) :理发师j的状态,1表示忙,0表示闲
%本程序模拟从第1分钟末到第10分钟末理发店的顾客数目,理发师的状态等情况
%假设理发师对顾客的服务都是从某分钟的末尾开始的
%假设理发师j的工作优先级高于j+1;
c(1)=0;d(1)=0;
for j=1:ln
S(j)=0;
a(j,1)=0;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
三、运行结果
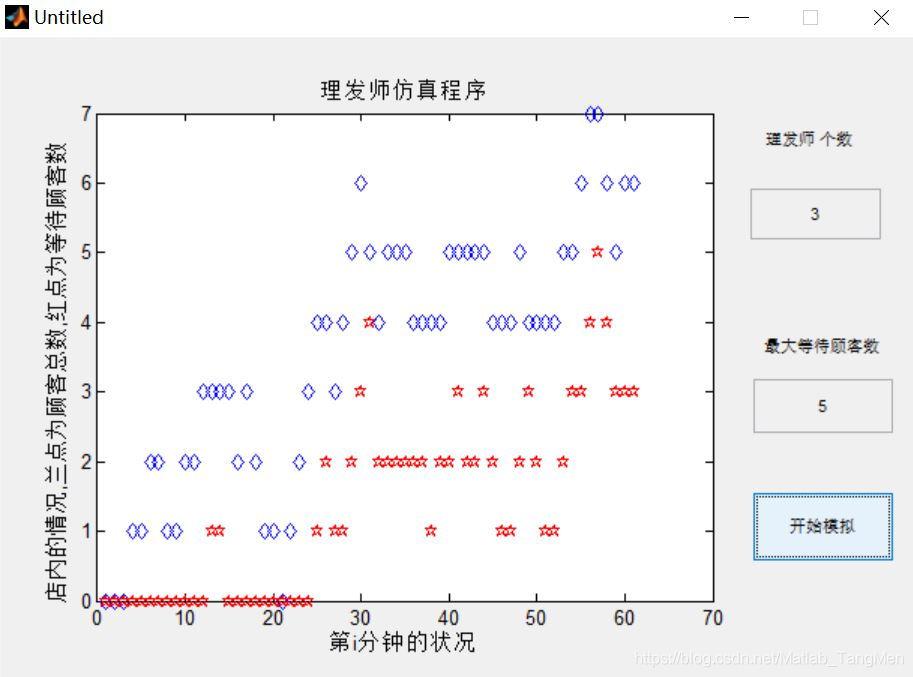
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118771593
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)