【运动学】基于matlab GUI地球自转模拟【含Matlab源码 1115期】
【摘要】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1: 完整代码已上传我的资源:【运动学】基于matlab GUI地球自转模拟【含Matlab源码 1115期】
获取代码方式2: 通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证...
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【运动学】基于matlab GUI地球自转模拟【含Matlab源码 1115期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、部分源代码
function varargout = globegui(varargin)
% GLOBEGUI M-file for globegui.fig created with GUIDE
%
% Creates a GUI for viewing a spinning Earth globe
%
% GLOBEGUI, by itself, creates a new GLOBEGUI or raises the existing
% one.
%
% H = GLOBEGUI returns the handle to a new GLOBEGUI or the handle to
% the existing one.
%
% GLOBEGUI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in GLOBEGUI.M with the given input arguments.
%
% GLOBEGUI('Property','Value',...) creates a new GLOBEGUI or raises the
% existing one. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before globegui_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to globegui_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 10-Mar-2021 09:50:13
%
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @globegui_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @globegui_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before globegui is made visible.
function globegui_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to globegui (see VARARGIN)
% Check whether initialization has been done in case this GUI
% is a singleton and has already been opened.
% if isfield(handles,'running')
% disp('No initialization this time.')
% else
% handles.running = true;
% guidata(hObject,handles)
% disp('Initializing...')
% end
% Choose default command line output for globegui
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes globegui wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = globegui_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in spinstopbutton.
function spinstopbutton_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% Spins the globe in the axes or stops it, renaming the button
% from "Spin" to "Stop" and back again. When its label is "Stop"
% this callback is executing an endless loop and is re-entered;
% thus it must have properties set as follows (which is the
% default behavior of a GUIDE GUI):
% Interruptible: 'on', BusyAction: 'queue'
%
% hObject handle to spinstopbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
str = get(hObject,'String'); % get the current pushbutton string
% Determine which string the label matches
state = find(strcmp(str,handles.Strings));
% Toggle the button label to other string
set(hObject,'String',handles.Strings{3-state});
% If the index when entering was 1, start to spin the object
if (state == 1)
% globe = struct;
filming = handles.movie;
az = handles.azimuth;
hgrotate = handles.tform;
% Spin globe as long as the figure exists or until user
% interrupts by pressing the button a second time
while ishandle(handles.axes1)
% If button label changed since last iteration, stop now
if find(strcmp(get(hObject,'String'),...
handles.Strings)) == 1
% Save rotation state to restart at this orientation
handles.azimuth = az;
guidata(hObject,handles);
break
end
az = az + 0.01745329252; % Increment azimuth (in radians)
% to rotate east one degree
% Modify the hgtransform controling the two surface objects
set(hgrotate,'Matrix',makehgtform('zrotate',az));
drawnow % Refresh the screen
% If the Make movie button is checked, save frames
% but don't store more than one revolution
% NOTE: filming slows down the animation
% Need to test whether axes exists because user can quit
% during filming, destroying axes and figure
if ishandle(handles.axes1) && filming > 0 && filming < 361
globeframes(filming) = getframe(handles.axes1);
filming = filming + 1;
end
end
% Write captured frames to MAT-file if in movie mode
if (filming)
filename = sprintf('globe%i.mat',filming-1);
disp(['Writing movie to file ' filename]);
save (filename, 'globeframes')
end
end
% --- Executes on button press in quitbutton.
function quitbutton_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to quitbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%handles = guidata(hObject);
% Get the figure's handle, then destroy it
fig = handles.figure1;
close(fig)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function spinstopbutton_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to spinstopbutton (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Creates the handles structure and places into it label strings
% to test button's current name against
handles.Strings = {'Spin';'Stop'};
% Commit the new struct element to appdata
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function axes1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to axes1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: place code in OpeningFcn to populate axes1
% Generate a colormap appropriate for terrain display
cmap = [0 0 0.2000; 0 0 0.2471;...
0 0 0.2941; 0 0 0.3412;...
0 0 0.3882; 0 0 0.4353;...
0 0 0.4824; 0 0 0.5294;...
0 0 0.5765; 0 0 0.6235;...
0 0 0.6706; 0 0 0.7176;...
0 0 0.7647; 0 0 0.8118;...
0 0 0.8588; 0 0 0.9059;...
0 0 0.9529; 0 0 1.0000;...
0 0.0556 1.0000; 0 0.1111 1.0000;...
0 0.1667 1.0000; 0 0.2222 1.0000;...
0 0.2778 1.0000; 0 0.3333 1.0000;...
0 0.3889 1.0000; 0 0.4444 1.0000;...
0 0.5000 1.0000; 0 0.5556 1.0000;...
0 0.6111 1.0000; 0 0.6667 1.0000;...
0 0.7222 1.0000; 0 0.7778 1.0000;...
0 0.8333 1.0000; 0 0.8889 1.0000;...
0 0.9444 1.0000; 0 1.0000 1.0000;...
0 0.4000 0.2000; 0.0253 0.4429 0.2043;...
0.0555 0.4857 0.2092; 0.0906 0.5286 0.2157;...
0.1306 0.5714 0.2251; 0.1755 0.6143 0.2382;...
0.2253 0.6571 0.2562; 0.2800 0.7000 0.2800;...
0.3684 0.7429 0.3396; 0.4586 0.7857 0.4041;...
0.5496 0.8286 0.4735; 0.6402 0.8714 0.5478;...
0.7296 0.9143 0.6269; 0.8165 0.9571 0.7110;...
0.9000 1.0000 0.8000; 0.8499 0.9538 0.7044;...
0.8099 0.9077 0.6144; 0.7787 0.8615 0.5302;...
0.7548 0.8154 0.4516; 0.7367 0.7692 0.3787;...
0.7231 0.7231 0.3115; 0.6769 0.6413 0.2499;...
0.6308 0.5580 0.1941; 0.5846 0.4744 0.1439;...
0.5385 0.3921 0.0994; 0.4923 0.3124 0.0606;...
0.4462 0.2368 0.0275; 0.4000 0.1667 0];
load topo % Get 1x1 degree terrain grid
% Make axes a slightly oversized unit box centered on 0,0,0
set(hObject,'xlim',[-1.02 1.02],...
'ylim',[-1.02 1.02],...
'zlim',[-1.02 1.02]);
% Create a spherical structure
[x,y,z] = sphere(50);
hgttilt = hgtransform;
hgrotate = hgtransform('parent',hgttilt);
% Set display properties
props.FaceColor= 'texture';
props.EdgeColor = 'none';
props.FaceLighting = 'gouraud';
props.Cdata = topo; % Use topo grid as a texturemap
props.Parent = hgrotate; % Make hgtransform surface parent
hsurf = surface(x,y,z,props); % Draw 3-D view
colormap(cmap) % Use special terrain colormap defined above
% Rotate the surface by 23.44 deg (0.4091 radians) around x-axis;
% this is the earth's tilt from normal to the ecliptic.
% To learn about geometric operations, type "doc hgtransform".
set(hgttilt,'Matrix',makehgtform('xrotate',0.4091));
% Create another mesh to be the graticule
[gx,gy,gz] = sphere(15);
% Decimate every other row to make mesh elements square
for j = 2:9
gx(j,:) = [];
gy(j,:) = [];
gz(j,:) = [];
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
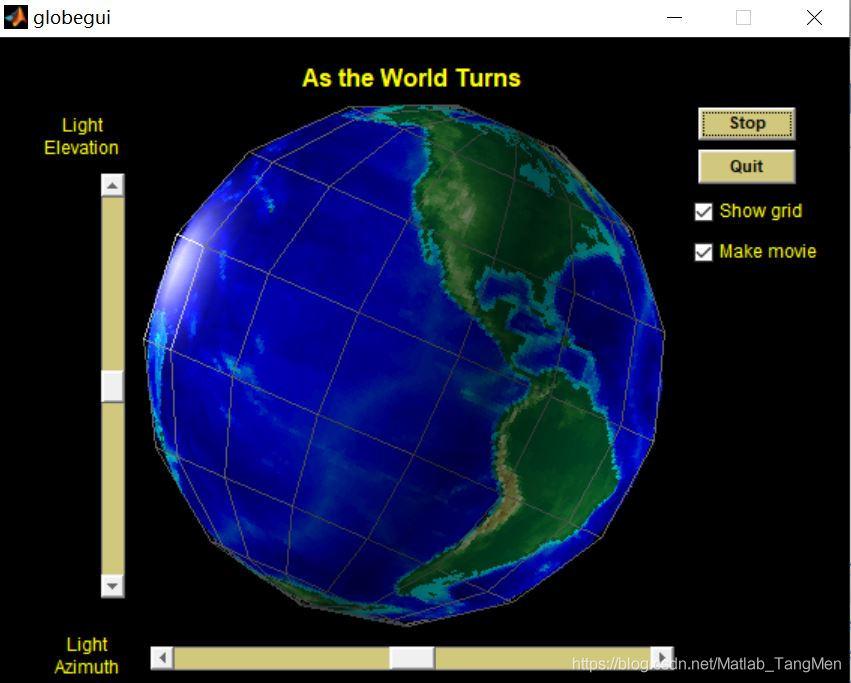
三、运行结果
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 门云阁.MATLAB物理计算与可视化[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118771584
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)