【语音识别】基于matlab GUI语音识别信号灯图像模拟控制(带面板)【含Matlab源码 757期】
一、简介
1 案例背景
语音识别是一门覆盖面很广泛的交叉学科,它与声学、语音学、语言学、信息理论、模式识别理论及神经生物学等学科都有非常密切的关系"。通过语音信号处理和模式识别理论使得计算机自动识别和理解人类口述的语言,包括两种意义:一是将人类口述的语句逐句地进行识别并转换为文字;二是对口述语言所包括的需求和询问做出合理的分析,执行相关的命令,而不是仅仅转换为书面文字。本案例以语音识别为理论基础,通过与模式识别相结合的方式将其应用到信号灯图像的模拟控制领域,实现对指定语音信号进行自动识别并自动关联信号灯图像的效果,具有一定的使用价值。
2 理论基础
语音信号的端点检测是进行语音识别的一个基本步骤,它是特征训练和识别的基础。端点检测是指在语音信号中查找各种段落(如音素、音节、词素)的始点和终点的位置,并从语音信号中消除无声段,进而实现对语音有效信号段的截取。早期进行端点检测的主要依据是信号能量、振幅和过零率,但经常会出现误检测,效果并不明显。20世纪60年代日本学者Itakura提出了动态时间规整算法(Dynamic Time Warping, DTW) , 该算法的基本思想是把未知量均匀地延长或缩短,并达到与参考模式的长度一致的效果"。在这一过程中,未知语音段的时间轴要不均匀地变化或弯折,以使其特征与模型特征得到对应。因此,一个完整的基于统计的语音识别系统可大致分为以下步骤:
(1)语音信号预处理:
(2)语音信号特征提取;
(3)声学模型选择;
(4)模式匹配选择;
(5)语言模型选择:
(6)语言信息处理。
语音识别研究的第一步为选择识别单元,常用的语音识别单元有单词(句)、音节和音素三种,一般根据具体的研究任务来决定选择哪种识别单元。大部分中小词汇语音识别系统选择单词(句)作为识别单元,大词汇系统的模型库一般规模较大,训练模型步骤较多,模型匹配算法复杂度较高,选择单词(句)作为识别单元难以满足实时性要求。大部分汉语语音识别系统选择音节作为识别单元,其中,汉语是单音节结构的语言,英语是多音节结构的语言,汉语大约1300个音节,如果不考虑声调,则约有408个无调音节,待识别的音节数量相对较少。因此,中、大词汇量汉语语音识别系统一般选择以音节为识别
单元来进行系统设计。英语语音识别系统一般选择音素作为识别单元,中、大词汇量汉语语音识别系统也在越来越多地采用音素作为识别单元。汉语音节仅由声母和韵母构成,其中,零声母有22个,韵母有28个,且二者的声学特性相差很大。在实际应用中,为了提高易混淆音节的区分能力,通常把声母依后续韵母的不同而构成细化声母来进行处理。但是,由于协同发音的影响,音素单元往往具有不稳定的特点,所以如何获得稳定的音素单元依然有待于进一步研究。
选择合理的信号特征参数是语音识别的一个关键因素。为了提高对语音信号进行分析、处理的效率,需要提取特征参数,消除与语音识别无关的冗余信息,保留影响语音识别的重要信息,同时对语音信号进行压缩。因此,在特征参数提取的实际应用中,语音信号的压缩率一般介于10~100.此外,语音信号包含了大量不同种类的信息,需要综合考虑包括成本、性能、响应时间、计算量等在内的各方面因素来决定对哪些信息进行提取,以及选择哪种方式提取。非特定人语音识别系统为了保证一般性,往往侧重于提取反映语义的特征参数,尽量消除说话人的个人信息:特定人语音识别系统为了保证有效性,往往在提取反映语义的特征参数的同时,尽量也保留说话人的个人信息回。
LP(线性预测)分析技术属于特征参数提取技术,具有广泛的应用。许多成熟的语音识别应用系统都采用基于LP的技术来提取Mel倒谱参数作为特征。但LP模型作为一种纯数学模型具有局限性,没有考虑人类听觉系统对语音处理的特点。Mel倒谱参数和PLP(感知线性预测) 分析提取的感知线性预测倒谱, 应用了听觉感知方面的一些研究成果,在一定程度上模拟了人类听觉系统对语音处理的特点。实验证明,采用这种技术能在一定程度上提高语音识别系统的性能。根据目前的使用情况, Mel感知线性预测倒频谱参数充分考虑了人类发声与接收声音的特性并且具有良好的鲁棒性,因此已逐渐取代传统的线性预测编码倒频谱参数。此外,也有部分研究者尝试把小波分析技术应用于语音信号的特征提取,但其应用性能还具有一定的局限性,有待进一步研究。
3 程序实现
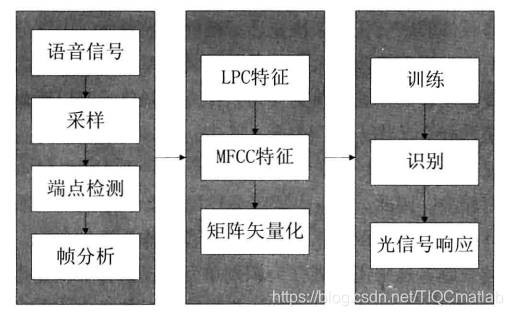
本案例采用MATLAB数学工具通过完成程序实现, 主要采用DTW算法实现语音识别,软件算法设计架构图如图所示。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = EmotionRec(varargin)
% EMOTIONREC M-file for EmotionRec.fig
% EMOTIONREC, by itself, creates a new EMOTIONREC or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = EMOTIONREC returns the handle to a new EMOTIONREC or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% EMOTIONREC('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in EMOTIONREC.M with the given input arguments.
%
% EMOTIONREC('Property','Value',...) creates a new EMOTIONREC or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before EmotionRec_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to EmotionRec_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help EmotionRec
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 12-May-2013 18:24:47
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @EmotionRec_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @EmotionRec_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before EmotionRec is made visible.
function EmotionRec_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to EmotionRec (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for EmotionRec
handles.output = hObject;
addpath(fullfile(pwd, 'voicebox'));
clc;
axes(handles.axes1); cla reset; box on;
set(gca, 'XTick', [], 'YTick', [], ...
'XTickLabel', '', 'YTickLabel', '', 'Color', [0.7020 0.7804 1.0000]);
set(handles.axes2, 'XTick', [], 'YTick', [], ...
'XTickLabel', '', 'YTickLabel', '', 'Color', [0.7020 0.7804 1.0000], ...
'Box', 'On');
handles.dirName = 0;
handles.S = 0;
handles.fileurl = 0;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes EmotionRec wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = EmotionRec_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%% 载入语音库
% 数据库路径
dirName = './wav/Database';
dirName = uigetdir(dirName);
if isequal(dirName, 0)
return;
end
msgbox(sprintf('载入%s成功!', dirName), '提示信息');
handles.dirName = dirName;
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%% 提取特征参数
if isequal(handles.dirName, 0)
msgbox('请选择音频库目录', '提示信息', 'modal');
return;
end
S = GetDatabase(handles.dirName);
handles.S = S;
guidata(hObject, handles);
msgbox('音频信号特征提取完毕', '提示信息', 'modal');
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%% 选择测试文件
file = './wav/Test/1.wav';
[Filename, Pathname] = uigetfile('*.wav', '打开新的语音文件',...
file);
if Filename == 0
return;
end
fileurl = fullfile(Pathname,Filename);
[signal, fs] = audioread(fileurl);
axes(handles.axes1); cla reset; box on;
plot(signal); title('待识别语音信号', 'FontWeight', 'Bold');
msgbox('载入语音文件成功', '提示信息', 'modal');
handles.fileurl = fileurl;
handles.signal = signal;
handles.fs = fs;
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%% 识别
if isequal(handles.fileurl, 0)
msgbox('请选择音频文件', '提示信息', 'modal');
return;
end
if isequal(handles.S, 0)
msgbox('请计算音频库MFCC特征', '提示信息', 'modal');
return;
end
S = handles.S;
[num, MC] = Reco(S, handles.fileurl);
result = S(num).name;
result = result(1:2);
c = 'r';
function MC = GetFeather(file, flag)
if nargin < 2
flag = 0;
end
if nargin < 1
file = '.\wav\Database\关闭\关闭_bsm.wav';
end
[signal, fs] = audioread(file);
framelength = 1024;
framenumber = fix(length(signal)/framelength);
for L = 1:framenumber
for m = 1:framelength
framedata(m) = signal((L-1)*framelength+m);
end
E(L) = sum(framedata.^2);
end
if flag
figure; plot(E);
end
meanE = mean(E);
startflag=0;
startnum=0;
startframe=0;
endframe = 0;
S = [];
for L = 1 : framenumber
if E(L) > meanE
startnum = startnum+1;
if startnum == 2
startframe = L-2;
startflag = 1;
end
end
if E(L) < meanE
if startflag == 1
endframe = L-1;
S = [S; startframe endframe];
startflag = 0;
startnum = 0;
end
end
end
if size(S, 1) > 1
ms = min(S(:, 1));
es = max(S(:, 2));
else
ms = S(1);
es = S(2);
end
MC = [];
snum = 1;
for i = ms : es
si = (i-1)*framelength;
ei = i*framelength;
fi = signal(si:ei);
mc = mfcc(fi,fs);
MC{snum} = mc;
snum = snum + 1;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
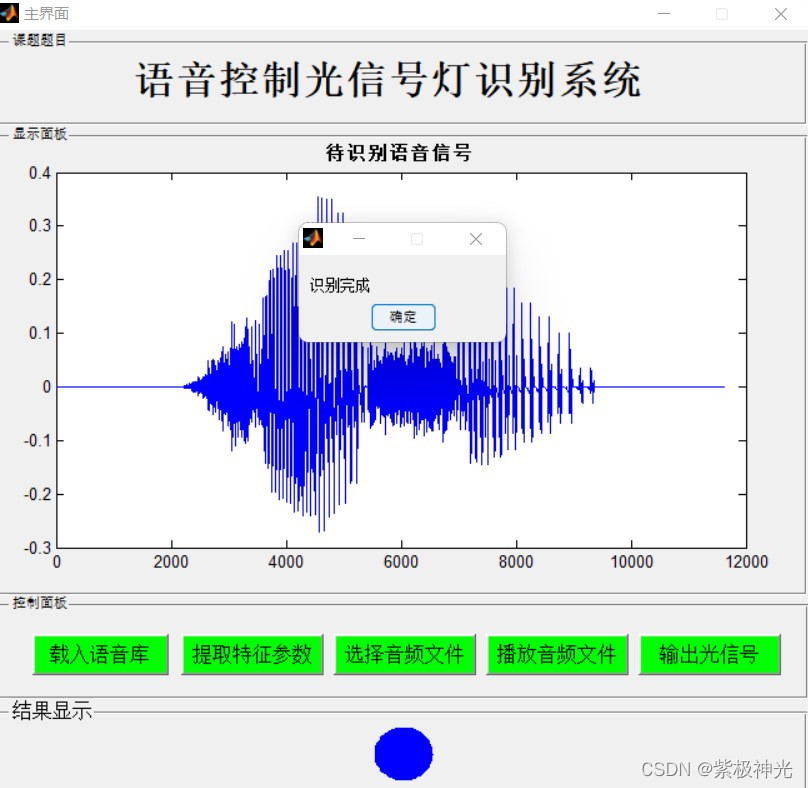
三、运行结果
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 沈再阳.精通MATLAB信号处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[2]高宝建,彭进业,王琳,潘建寿.信号与系统——使用MATLAB分析与实现[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[3]王文光,魏少明,任欣.信号处理与系统分析的MATLAB实现[M].电子工业出版社,2018.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/115587639
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)