【雷达通信】基于matlab无人机FMCW毫米波高度计雷达仿真【含Matlab源码 1261期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源: 【雷达通信】基于matlab无人机FMCW毫米波高度计雷达仿真【含Matlab源码 1261期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、FMCW毫米波简介
0 概念
FMCW(Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave),即调频连续波。FMCW技术和脉冲雷达技术是两种在高精度雷达测距中使用的技术。其基本原理为发射波为高频连续波,其频率随时间按照三角波规律变化。
1 基础知识
FMCW雷达的核心是一种叫做线性调频脉冲的信号,线性调频脉冲是频率随时间以线性的方式增长的正弦波,在下图中

信号以fc的正弦波开始,然后他的频率不断增大,chirp信号的起始频率为 fc,带宽为B,信号的持续时间为Tc,则频率变化率(斜率)为:S=B/Tc

上图是简单的雷达示意图,有单个TX天线和单个RX天线,雷达工作过程大致为:1处的合成器生成一个线性调频脉冲,TX将脉冲传播出去,当脉冲遇到物体时会反射回来,RX接收反射的调频脉冲,TX和RX信号混在一起,最终在4处生成一种叫做IF(中频)的信号。下面详细了解以下关键元件4(混频器)。

混频器有两个输入一个输出,如果向混频器的两个输入端口输入两个正弦波,那么混频器将输出有以下两条性质的正弦波:
性质1:输出正弦波的瞬时频率等于两个输入正弦波的瞬时频率差值;
性质2:输出正弦波的起始相位等于两个输入正弦波的起始相位差值。

如上图, 被物体反射后的信号可以简单的看做是发射信号的延时,用t(时间差值)来表示,t=2d/c,接收信号与发射信号混频后的输出信号频率恒定,假设IF的频率为f,那么f=St=S2d/c (S为调频连续波的斜率),其中d为物体的距离,c 为光速。对混频后的信号做FFT变换,可以得到单峰值频谱图。从上图中可以看出,为了避免产生距离判别模糊,t需要满足τ<Tc ,因此可得出系统所能探测的最远距离与Tc 有关。
三、部分源代码
%
%
% 1T1R Simulation.
% Senario: UAV radar to horizontal ground/slope ground , height measurement.
clc;clear
%% Radar Parameters
fc = 24e9;
c = physconst('LightSpeed');
lambda = c/fc;
tm = 5e-4; % Chirp Cycle
bw = 300e6; % FMCW Bandwidth
range_max = 5; % Max detection Range 1~100 meters
v_max = 2.5; % Max Velocity
%
range_res = c/2/bw;
sweep_slope = bw/tm;
fr_max = range2beat(range_max,sweep_slope,c);
fd_max = speed2dop(2*v_max,lambda);
fb_max = fr_max+fd_max;
fs = max(2*fb_max,bw);
%%
%% Use Phased Array System Toolbox to generate an FMCW waveform
waveform = phased.FMCWWaveform('SweepTime',tm,'SweepBandwidth',bw,...
'SampleRate',fs);
%%
tx_antenna = phased.IsotropicAntennaElement('FrequencyRange',[23.8e9 24.4e9],'BackBaffled',true);
rx_antenna = phased.IsotropicAntennaElement('FrequencyRange',[23.8e9 24.4e9],'BackBaffled',true);
%%
transmitter = phased.Transmitter('PeakPower',0.001,'Gain',20);
receiver = phased.ReceiverPreamp('Gain',20,'NoiseFigure',8.5,'SampleRate',fs);
txradiator = phased.Radiator('Sensor',tx_antenna,'OperatingFrequency',fc,...
'PropagationSpeed',c);
rxcollector = phased.Collector('Sensor',rx_antenna,'OperatingFrequency',fc,...
'PropagationSpeed',c);
rng(2020);
fs_d = 2500000;
Dn = fix(fs/fs_d);
%%
%% --------------Radar Motion Platform-------------- %%
radar_s = phased.Platform('InitialPosition',[0;0;0],...
'Velocity',[0.05;2.3;-0.04]); %% *********** Set Radar Velocity Here **************
%% Targets ------------- Ground -------------------- %%
target_ypos = -6:0.15:6;
target_num = size(target_ypos,2);
target_xpos = 1.3*ones(1,target_num) + 0*1.1*target_ypos; %% *********** Set Ground Shape Here **************
target_zpos = zeros(1,target_num);
target_pos = [[target_xpos,target_xpos,target_xpos];
[target_ypos,target_ypos,target_ypos];
[target_zpos-0.15,target_zpos,target_zpos+0.155]];
target_num = target_num*3;
target_rcs = 0.02*ones(1,target_num);
targets_vel = [zeros(1,target_num);zeros(1,target_num);zeros(1,target_num)];
targets = phased.RadarTarget('MeanRCS',target_rcs,'PropagationSpeed',c,'OperatingFrequency',fc);
targetmotion = phased.Platform('InitialPosition',target_pos,...
'Velocity',targets_vel);
%%
%% Signal Propogation
% simulation of free space propagtion
channel = phased.FreeSpace('PropagationSpeed',c,...
'OperatingFrequency',fc,'SampleRate',fs,'TwoWayPropagation',true);
%%
%%
% Generate Time Domain Waveforms of Chirps
% xr is the data received at rx array
Nsweep = 32; % Number of Chirps (IF signal) of this simulation
chirp_len = fix(fs_d*waveform.SweepTime);
xr = complex(zeros(chirp_len,1,Nsweep));
disp('The simulation will take some time. Please wait...')
for m = 1:Nsweep
if mod(m,1)==0
disp([num2str(m),'/',num2str(Nsweep)])
end
% Update radar and target positions
[radar_pos,radar_vel] = radar_s(waveform.SweepTime);
[tgt_pos,tgt_vel] = targetmotion(waveform.SweepTime);
[~,tgt_ang] = rangeangle(tgt_pos,radar_pos);
% Transmit FMCW waveform
sig = waveform();
txsig = transmitter(sig);
% Toggle transmit element
txsig = txradiator(txsig,tgt_ang);
% Propagate the signal and reflect off the target
txsig = channel(txsig,radar_pos,tgt_pos,radar_vel,tgt_vel);
txsig = targets(txsig);
% Dechirp the received radar return
rxsig = rxcollector(txsig,tgt_ang);
rxsig = receiver(rxsig);
dechirpsig = dechirp(rxsig,sig);
% Decimate the return to reduce computation requirements
for n = size(xr,2):-1:1
xr(:,n,m) = decimate(dechirpsig(1:chirp_len*Dn,n),Dn,'FIR');
end
end
range_res = range_res*size(dechirpsig,1)/Dn/size(xr,1);
%%
xrv = squeeze(xr);
save('vrv.mat',...
'xrv','fc','fs_d','c','tm','bw','waveform','range_res',...
'Nsweep','chirp_len','Dn','fb_max','lambda',...
'v_max','range_max')
%%
%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Part II: Signal Processing %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%
if ~exist('xrv')
load('vrv.mat');
end
% FFT points
nfft_r = 2^nextpow2(size(xrv,1));
nfft_d = 2^nextpow2(size(xrv,2));
nfft_mul = 2;
ra_res = range_res*size(xrv,1)/nfft_mul/nfft_r;
% RDM Algorithm
rngdop = phased.RangeDopplerResponse('PropagationSpeed',c,...
'DopplerOutput','Speed','OperatingFrequency',fc,'SampleRate',fs_d,...
'RangeMethod','FFT','PRFSource','Property',...
'RangeWindow','Hann','PRF',1/waveform.SweepTime,...
'SweepSlope',waveform.SweepBandwidth/waveform.SweepTime,...
'RangeFFTLengthSource','Property','RangeFFTLength',nfft_r*nfft_mul,...
'DopplerFFTLengthSource','Property','DopplerFFTLength',nfft_d*nfft_mul,...
'DopplerWindow','Hann');
% RD Map
[resp,r,sp] = rngdop(xrv);
% % Range-Energy Calibration
% for k=size(resp,1)/2+1:size(resp,1)
% resp(k,:,:) = resp(k,:,:) * (k-size(resp,1)/2)^3;
% end
subplot(221);plotResponse(rngdop,squeeze(xrv));axis([-2*v_max 2*v_max 0 range_max-0.05])
%respmap = mag2db(abs(resp));
respmap = abs(resp);
respmap = avg_filter_2D(respmap,1);
subplot(222);mesh(respmap(nfft_r*nfft_mul/2+1:nfft_r*nfft_mul/2+1+30*nfft_mul,...
:))
%nfft_d*nfft_mul/2-12*nfft_mul:nfft_d*nfft_mul/2+12*nfft_mul))
subplot(413);plot(sum(respmap(nfft_r*nfft_mul/2+1:nfft_r*nfft_mul/2+1+30*nfft_mul,...
nfft_d*nfft_mul/2-1:nfft_d*nfft_mul/2+2),2))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
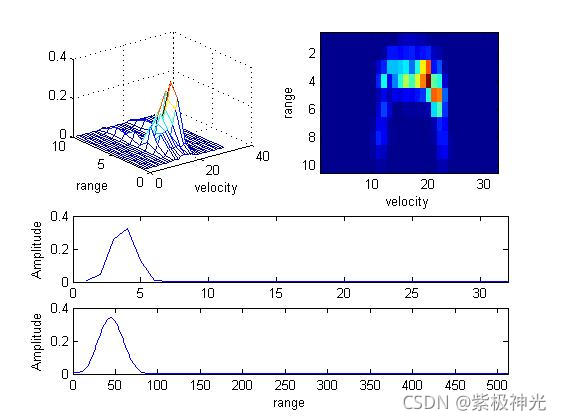
四、运行结果
五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 沈再阳.精通MATLAB信号处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[2]高宝建,彭进业,王琳,潘建寿.信号与系统——使用MATLAB分析与实现[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[3]王文光,魏少明,任欣.信号处理与系统分析的MATLAB实现[M].电子工业出版社,2018.
[4]李树锋.基于完全互补序列的MIMO雷达与5G MIMO通信[M].清华大学出版社.2021
[5]何友,关键.雷达目标检测与恒虚警处理(第二版)[M].清华大学出版社.2011
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/119951190
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)