【优化算法】正弦余弦算法(SCA)【含Matlab源码 1308期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【优化算法】正弦余弦算法(SCA)【含Matlab源码 1308期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、正弦余弦算法简介
正弦余弦算法(Sine Cosine Algorithm, SCA)是一种新的群体智能优化算法,具有参数少、结构简单以及易实现等特点,因此,利用正弦和余弦函数的波动性和周期性进行迭代寻优。假设种群规模为M,即包含M个个体,每个个体的维度为D,那么,个体i在第j维的空间位置表示为Xij,i∈{1,2,…,M},j∈{1,2,…,D}。首先,在解空间内随机产生M个个体的初始位置,对应种群规模的大小。然后,计算每个个体的适应度值,并记录当前最优个体位置。最后,循环至满足终止条件,输出最优解。在每次迭代中,个体位置的更新表达式为
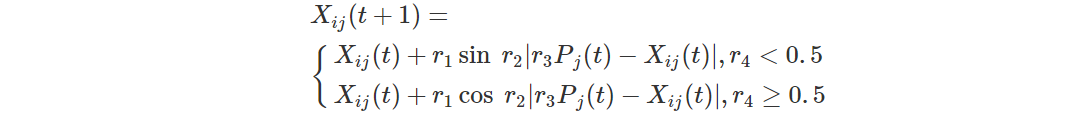
其中:Xij(t)为个体i在第t次迭代时的位置在第j维的分量;Pj(t)为第t次迭代种群当前最优个体在第j维的分量;r2∈[0,2π]、r3∈[0,2]和r4∈[0,1]为3个随机参数;r1为控制参数,随着迭代次数的增加从a递减到0,可表示为
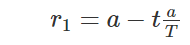
其中:a为常数;t为当前的迭代次数;T为最大迭代次数。
三、部分源代码
clear all
clc
SearchAgents_no=30; % Number of search agents
Function_name='F1'; % Name of the test function that can be from F1 to F23 (Table 1,2,3 in the paper)
Max_iteration=1000; % Maximum numbef of iterations
% Load details of the selected benchmark function
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name);
[Best_score,Best_pos,cg_curve]=SCA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
figure('Position',[284 214 660 290])
%Draw search space
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(Function_name);
title('Test function')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([Function_name,'( x_1 , x_2 )'])
grid off
%Draw objective space
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(cg_curve,'Color','b')
title('Convergence curve')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best flame (score) obtained so far');
axis tight
grid off
box on
legend('SCA')
display(['The best solution obtained by SCA is : ', num2str(Best_pos)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by SCA is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
function [Destination_fitness,Destination_position,Convergence_curve]=SCA(N,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
display('SCA is optimizing your problem');
%Initialize the set of random solutions
X=initialization(N,dim,ub,lb);
Destination_position=zeros(1,dim);
Destination_fitness=inf;
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iteration);
Objective_values = zeros(1,size(X,1));
% Calculate the fitness of the first set and find the best one
for i=1:size(X,1)
Objective_values(1,i)=fobj(X(i,:));
if i==1
Destination_position=X(i,:);
Destination_fitness=Objective_values(1,i);
elseif Objective_values(1,i)<Destination_fitness
Destination_position=X(i,:);
Destination_fitness=Objective_values(1,i);
end
All_objective_values(1,i)=Objective_values(1,i);
end
%Main loop
t=2; % start from the second iteration since the first iteration was dedicated to calculating the fitness
while t<=Max_iteration
% Eq. (3.4)
a = 2;
Max_iteration = Max_iteration;
r1=a-t*((a)/Max_iteration); % r1 decreases linearly from a to 0
% Update the position of solutions with respect to destination
for i=1:size(X,1) % in i-th solution
for j=1:size(X,2) % in j-th dimension
% Update r2, r3, and r4 for Eq. (3.3)
r2=(2*pi)*rand();
r3=2*rand;
r4=rand();
% Eq. (3.3)
if r4<0.5
% Eq. (3.1)
X(i,j)= X(i,j)+(r1*sin(r2)*abs(r3*Destination_position(j)-X(i,j)));
else
% Eq. (3.2)
X(i,j)= X(i,j)+(r1*cos(r2)*abs(r3*Destination_position(j)-X(i,j)));
end
end
end
function func_plot(func_name)
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(func_name);
switch func_name
case 'F1'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F2'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-10,10]
case 'F3'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F4'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F5'
x=-200:2:200; y=x; %[-5,5]
case 'F6'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F7'
x=-1:0.03:1; y=x; %[-1,1]
case 'F8'
x=-500:10:500;y=x; %[-500,500]
case 'F9'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x; %[-5,5]
case 'F10'
x=-20:0.5:20; y=x;%[-500,500]
case 'F11'
x=-500:10:500; y=x;%[-0.5,0.5]
case 'F12'
x=-10:0.1:10; y=x;%[-pi,pi]
case 'F13'
x=-5:0.08:5; y=x;%[-3,1]
case 'F14'
x=-100:2:100; y=x;%[-100,100]
case 'F15'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F16'
x=-1:0.01:1; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F17'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F18'
x=-5:0.06:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F19'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F20'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F21'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F22'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F23'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
end
L=length(x);
f=[];
for i=1:L
for j=1:L
if strcmp(func_name,'F15')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F19')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F20')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F21')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F22')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F23')==0
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j)]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F15')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F19')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F20')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0,0,0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F21')==1 || strcmp(func_name,'F22')==1 ||strcmp(func_name,'F23')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0]);
end
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
四、运行结果

五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120209221
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)