【胸片分割】基于matlab GUI最小误差法胸片分割系统【含Matlab源码 1065期】
【摘要】
一、简介
1 最小误差法原理 最小误差阈值分割法是根据图像中背景和目标像素的概率分布密度来实现的,其思想是找到一个阈值,并根据该阈值进行划分,计算出目标点误分为背景的概率和背景点误分为目标点的概率,得出...
一、简介
1 最小误差法原理
最小误差阈值分割法是根据图像中背景和目标像素的概率分布密度来实现的,其思想是找到一个阈值,并根据该阈值进行划分,计算出目标点误分为背景的概率和背景点误分为目标点的概率,得出总的误差划分概率。当总的误差划分概率最小时,便得到所需要的最佳阈值。




2 最小误差法实现步骤
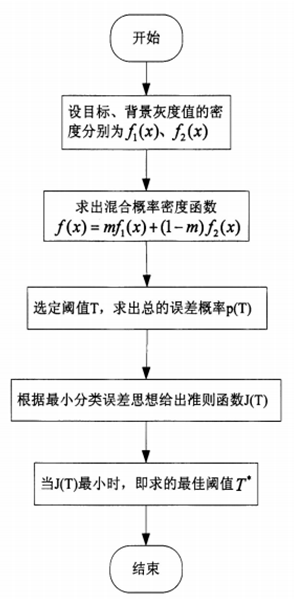
根据图可得最小误差阈值法的算法步骤:
步骤1:假设目标和背景灰度值得密度为,。计算混合概率密度。
步骤2:选定阈值T,计算总的误差概率,对进行求导。
步骤3:根据准则函数,计算使其最小时的T,作为最佳阈值。
二、源代码
function varargout = MainForm(varargin)
% MAINFORM MATLAB code for MainForm.fig
% MAINFORM, by itself, creates a new MAINFORM or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = MAINFORM returns the handle to a new MAINFORM or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% MAINFORM('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in MAINFORM.M with the given input arguments.
%
% MAINFORM('Property','Value',...) creates a new MAINFORM or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before MainForm_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to MainForm_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help MainForm
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 02-May-2021 08:10:18
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @MainForm_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @MainForm_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
function InitAxes(handles)
clc;
axes(handles.axes1); cla reset;
set(handles.axes1, 'XTick', [], 'YTick', [], ...
'XTickLabel', '', 'YTickLabel', '', 'Color', [0.7020 0.7804 1.0000], 'Box', 'On');
axes(handles.axes2); cla reset;
set(handles.axes2, 'XTick', [], 'YTick', [], ...
'XTickLabel', '', 'YTickLabel', '', 'Color', [0.7020 0.7804 1.0000], 'Box', 'On');
function filePath = OpenFile(imgfilePath)
% 打开文件
% 输出参数:
% filePath——文件路径
if nargin < 1
imgfilePath = fullfile(pwd, 'images/test.jpg');
end
[filename, pathname, ~] = uigetfile( ...
{ '*.jpg','All jpg Files';...
'*.png','All png Files';...
'*.*', '所有文件 (*.*)'}, ...
'选择文件', ...
'MultiSelect', 'off', ...
imgfilePath);
filePath = 0;
if isequal(filename, 0) || isequal(pathname, 0)
return;
end
filePath = fullfile(pathname, filename);
% --- Executes just before MainForm is made visible.
function MainForm_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to MainForm (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for MainForm
handles.output = hObject;
InitAxes(handles);
handles.I = 0;
handles.J = 0;
handles.bw_direct = 0;
handles.bw_poly = 0;
handles.bw__kittler = 0;
handles.bw_temp = 0;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes MainForm wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = MainForm_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
filePath = OpenFile();
if isequal(filePath, 0)
return;
end
Img = imread(filePath);
% 灰度化
if ndims(Img) == 3
I = rgb2gray(Img);
else
I = Img;
end
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(I, []);
title('原图像');
handles.I = I;
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
if isequal(handles.I, 0)
return;
end
% 直接二值化
bw_direct = im2bw(handles.I, graythresh(handles.I));
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(bw_direct, []);
title('直接二值化分割');
handles.bw_direct = bw_direct;
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
if isequal(handles.bw_direct, 0)
return;
end
% 圈选胃区域空气
bw_poly = roipoly(handles.bw_direct, c, r);
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(handles.I, []);
hold on;
plot(c, r, 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold off;
title('胃区域空气选择');
handles.bw_poly = bw_poly;
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
if isequal(handles.bw_poly, 0)
return;
end
% 图像归一化
IE = mat2gray(handles.I);
% 对比度增强
IE = imadjust(IE, [0.532 0.72], [0 1]);
IE = im2uint8(mat2gray(IE));
I = im2uint8(mat2gray(handles.I));
% 显示
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(IE, []);
title('图像增强');
figure;
subplot(2, 2, 1); imshow(I); title('原图像');
subplot(2, 2, 2); imshow(IE); title('增强图像');
subplot(2, 2, 3); imhist(I); title('原图像直方图');
subplot(2, 2, 4); imhist(IE); title('增强图像直方图');
JE = IE;
JE(handles.bw_poly) = 255;
handles.JE = JE;
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
if isequal(handles.JE, 0)
return;
end
J = handles.JE;
% 直方图统计
[counts, gray_style] = imhist(J);
% 亮度级别
gray_level = length(gray_style);
% 计算各灰度概率
gray_probability = counts ./ sum(counts);
% 统计像素均值
gray_mean = gray_style' * gray_probability;
% 初始化
gray_vector(1) = realmax;
ks = gray_level-1;
for k = 1 : ks
% 迭代计算
w = w + gray_probability(k+1);
mean_k = mean_k + k * gray_probability(k+1);
% 判断是否收敛
if (w < eps) || (w > 1-eps)
gray_vector(k+1) = realmax;
else
% 计算均值
mean_k1 = mean_k / w;
mean_k2 = (gray_mean-mean_k) / (1-w);
% 计算方差
var_k1 = (((0 : k)'-mean_k1).^2)' * gray_probability(1 : k+1);
var_k1 = var_k1 / w;
var_k2 = (((k+1 : ks)'-mean_k2).^2)' * gray_probability(k+2 : ks+1);
var_k2 = var_k2 / (1-w);
% 计算目标函数
if var_k1 > eps && var_k2 > eps
else
gray_vector(k+1) = realmax;
end
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
三、运行结果







四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118278522
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)