【单目标优化求解】基于matlab混沌生物地理算法求解单目标问题【含Matlab源码 1411期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源: 【单目标优化求解】基于matlab混沌生物地理算法求解单目标问题【含Matlab源码 1411期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、生物地理算法简介
1 基本思路
BBO 算法起源于生物地理学,它通过模拟多物种在不同栖息地的分布、迁移、突变等规律求解寻优问题,在多目标规划领域有广泛应用. 栖息地被认为是独立的区域,不同的栖息地拥有不同的适宜指数HSI(Habitat suitability index)。 HSI较高的栖息地物种丰富度较高,随着种群趋于饱和,其迁出率增高,迁入率减少,而HIS较低的栖息地与之相反,迁入率增高,迁出率减少. 当栖息地遭遇灾害或瘟疫等突发事件时,HIS将随之突变,打破动态平衡,为低HIS的栖息地添加了不可预见性,增大了搜索目标解的几率2.2 迁移和突变操作物种的迁移有其具体的物理模型,最常的有线性模型、二次模型、余弦模型等 . 以图 3线性模型为例,当某栖息地物种数目为 0 时迁入率最高,此刻 λ = I,随着迁入物种数目不断增加,受阳光、水、食物等资源限制,迁入率不断降低,迁出率不断增高 . 当栖息地物种数目为 S0时,恰好达到动态平衡,此时迁出率与迁入率相同 . 而栖息地达到饱和状态时,物种数量达到最大值Smax ,此刻不再有物种迁入,迁出率 μ = E.突变操作基于生物地理学统计公式完成:
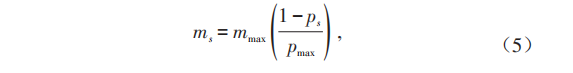

式中:ms为栖息地发生突变的概率,mmax为最大突变率,用户可自行设定 . ps为栖息地容纳s种物种的概率, pmax代表容纳最大种群的概率。
三、部分源代码
clear all
clc
nMonte = 100; % Number of Monte Carlo runs
DisplayFlag = true; % Whether or not to display results during run
GenFlag = true; % whether or not to exit BBO after population becomes uniform
PopSize = 30; % Population sizes for which to run SBBO
% Choose the test function
% ProblemFunction=@Sphere;
% ProblemFunction=@Ackley;
% ProblemFunction=@Fletcher;
% ProblemFunction=@Griewank;
% ProblemFunction=@Penalty1;
% ProblemFunction=@Penalty2;
ProblemFunction=@Quartic;
% ProblemFunction=@Rastrigin;
% ProblemFunction=@Rosenbrock;
% ProblemFunction=@Schwefel;
% or you objective function
% ProblemFunction=@YourObjectiveFunction;
%Chaotic_map_no=1; %Chebyshev
%Chaotic_map_no=2; %Circle
Chaotic_map_no=3; %Gauss/mouse
%Chaotic_map_no=4; %Iterative
%Chaotic_map_no=5; %Logistic
%Chaotic_map_no=6; %Piecewise
%Chaotic_map_no=7; %Sine
%Chaotic_map_no=8; %Singer
%Chaotic_map_no=9; %Sinusoidal
%Chaotic_map_no=10; %Tent
%You can define the number of search agents and iterations in the Init.m file
Max_iterations=10000;% This should be equal or greater than OPTIONS.Maxgen in Init.m file
ChaosVec=zeros(10,Max_iterations);
%Calculate chaos vector
for i=1:10
ChaosVec(i,:)=chaos(i,Max_iterations,1);
end
% BBO algorithm
[cg_curve0] = BBO(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, PopSize, GenFlag);
% BBO with chaotic selection operator
[cg_curve1] = CBBO1_10(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, PopSize, GenFlag,ChaosVec(Chaotic_map_no,:));
% BBO with chaotic migration operator
[cg_curve2] = CBBO11_20(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, PopSize, GenFlag,ChaosVec(Chaotic_map_no,:));
% BBO with chaotic mutation operator
[cg_curve3] = CBBO21_30(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, PopSize, GenFlag,ChaosVec(Chaotic_map_no,:));
% BBO with chaotic selection/migration operators combined
[cg_curve4] = CBBO31_40(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, PopSize, GenFlag,ChaosVec(Chaotic_map_no,:));
% BBO with chaotic selection/migration/mutation operators combined
[cg_curve5] = CBBO41_50(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, PopSize, GenFlag,ChaosVec(Chaotic_map_no,:));
semilogy(cg_curve0,'Color','y')
hold on
semilogy(cg_curve1,'Color','k')
semilogy(cg_curve2,'Color','b')
semilogy(cg_curve3,'Color','g')
semilogy(cg_curve4,'Color','r')
semilogy(cg_curve5,'Color','c')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
axis tight
grid on
box on
legend('BBO' , ['CBBO' num2str(Chaotic_map_no)] , ['CBBO' num2str(Chaotic_map_no+10)] ,['CBBO' num2str(Chaotic_map_no+20)] ,['CBBO' num2str(Chaotic_map_no+30)] ,['CBBO' num2str(Chaotic_map_no+40)] )
function [OPTIONS, MinCost, AvgCost, InitFunction, CostFunction, FeasibleFunction, ...
MaxParValue, MinParValue, Population] = Init(DisplayFlag, ProblemFunction, RandSeed)
% Initialize population-based optimization software.
% WARNING: some of the optimization routines will not work if population size is odd.
OPTIONS.popsize = 30; % total population size
OPTIONS.Maxgen = 499; % generation count limit
OPTIONS.numVar = 30; % number of genes in each population member
OPTIONS.pmutate = 0; % mutation probability
if ~exist('RandSeed', 'var')
RandSeed = round(sum(100*clock));
end
%rand('state', RandSeed); % initialize random number generator
if DisplayFlag
disp(['random # seed = ', num2str(RandSeed)]);
end
% Get the addresses of the initialization, cost, and feasibility functions.
[InitFunction, CostFunction, FeasibleFunction] = ProblemFunction();
% Initialize the population.
[MaxParValue, MinParValue, Population, OPTIONS] = InitFunction(OPTIONS);
% Make sure the population does not have duplicates.
Population = ClearDups(Population, MaxParValue, MinParValue);
% Compute cost of each individual
Population = CostFunction(OPTIONS, Population);
% Sort the population from most fit to least fit
Population = PopSort(Population);
% Compute the average cost
AverageCost = ComputeAveCost(Population);
% Display info to screen
MinCost = [Population(1).cost];
AvgCost = [AverageCost];
if DisplayFlag
disp(['The best and mean of Generation # 0 are ', num2str(MinCost(end)), ' and ', num2str(AvgCost(end))]);
end
return;
function O=chaos(index,max_iter,Value)
O=zeros(1,max_iter);
x(1)=0.7;
switch index
%Chebyshev map
case 1
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=cos(i*acos(x(i)));
G(i)=((x(i)+1)*Value)/2;
end
case 2
%Circle map
a=0.5;
b=0.2;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=mod(x(i)+b-(a/(2*pi))*sin(2*pi*x(i)),1);
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 3
%Gauss/mouse map
for i=1:max_iter
if x(i)==0
x(i+1)=0;
else
x(i+1)=mod(1/x(i),1);
end
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 4
%Iterative map
a=0.7;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=sin((a*pi)/x(i));
G(i)=((x(i)+1)*Value)/2;
end
case 5
%Logistic map
a=4;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=a*x(i)*(1-x(i));
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 6
%Piecewise map
P=0.4;
for i=1:max_iter
if x(i)>=0 && x(i)<P
x(i+1)=x(i)/P;
end
if x(i)>=P && x(i)<0.5
x(i+1)=(x(i)-P)/(0.5-P);
end
if x(i)>=0.5 && x(i)<1-P
x(i+1)=(1-P-x(i))/(0.5-P);
end
if x(i)>=1-P && x(i)<1
x(i+1)=(1-x(i))/P;
end
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 7
%Sine map
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1) = sin(pi*x(i));
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
case 8
%Singer map
u=1.07;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1) = u*(7.86*x(i)-23.31*(x(i)^2)+28.75*(x(i)^3)-13.302875*(x(i)^4));
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
case 9
%Sinusoidal map
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1) = 2.3*x(i)^2*sin(pi*x(i));
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
case 10
%Tent map
x(1)=0.6;
for i=1:max_iter
if x(i)<0.7
x(i+1)=x(i)/0.7;
end
if x(i)>=0.7
x(i+1)=(10/3)*(1-x(i));
end
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
end
O=G;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
四、运行结果

五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120858482
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)