【单目标优化求解】基于matlab黑猩猩算法求解单目标问题【含Matlab源码 1413期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
获取代码方式2:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【单目标优化求解】基于matlab黑猩猩算法求解单目标问题【含Matlab源码 1413期】
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、黑猩猩优化算法(ChOA)简介
1 ChOA数学描述
黑猩猩优化算法(ChOA) 是M.Khi she等人于2020年根据黑猩猩群体狩猎行为提出的一种新型元启发式优化算法。ChOA通过模拟攻击黑猩猩、驱赶黑猩猩、拦截黑猩猩和追逐黑猩猩4类黑猩猩协同狩猎行为来达到求解问题的目的。与其他算法相比, ChOA具有收敛速度快、寻优精度高等特点。
(1)驱赶和追逐猎物。
在黑猩猩狩猎过程中,通常根据黑猩猩个体智力和性动机来分配狩猎职责。任何黑猩猩均可随机改变其在猎物周围空间中的位置,数学描述为
d=|cx prey(t) -mx chimp(t) |(1)
x chimp(t+1) =X prey(t) -ad(2)
式中:d为黑猩猩与猎物间距; t为当前迭代次数; X prey(t) 为猎物位置向量; X chimp(t) 为黑猩猩位置向量; a、m、c为系数向量, a=2fr 1-f, c=2r 2, m=Chaotic_value(基于混沌映射的混沌向量) , f为迭代过程中从2.0非线性降至0, r 1、r 2为[0, 1] 范围内的随机向量。
(2)攻击方式。
黑猩猩能够探查猎物位置(通过驱赶、拦截和追逐),然后包围猎物。狩猎过程通常由攻击黑猩猩进行,驱赶黑猩猩、拦截黑猩猩和追逐黑猩猩参与狩猎过程。4类黑猩猩通过下式更新其位置,其他黑猩猩根据最佳黑猩猩位置更新其位置,猎物位置由最佳黑猩猩个体位置估计。数学描述为

式中:dAttacker、dBarrier、dChaser、dDriver分别为当前攻击黑猩猩、拦截黑猩猩、追逐黑猩猩、驱赶黑猩猩与猎物的间距;xAttacker、xBarrier、xChaser、xDriver分别为攻击黑猩猩、拦截黑猩猩、追逐黑猩猩、驱赶黑猩猩相对于猎物的位置向量;a1~a4、m1~m4、c1~c4分别为攻击黑猩猩、拦截黑猩猩、追逐黑猩猩、驱赶黑猩猩系数向量;x1、x2、x3、x4分别为攻击黑猩猩、拦截黑猩猩、追逐黑猩猩和驱赶黑猩猩位置更新向量;x为其他黑猩猩位置向量。
(3)攻击和寻找猎物。
在狩猎最后阶段,一方面黑猩猩根据攻击者、驱赶者、拦截者和追逐者位置更新位置,并攻击猎物;另一方面黑猩猩通过分散寻找猎物显示探查过程,即ChOA全局搜索。
(4)社会动机。
社会动机(性爱和修饰)会导致黑猩猩放弃其狩猎职责,这一行为有助于ChOA在求解高维问题时克服陷入局部最优和收敛速度慢等缺点。在优化过程中,通过50%的概率选择黑猩猩正常位置更新或通过混沌模型进行位置更新。数学模型表示为
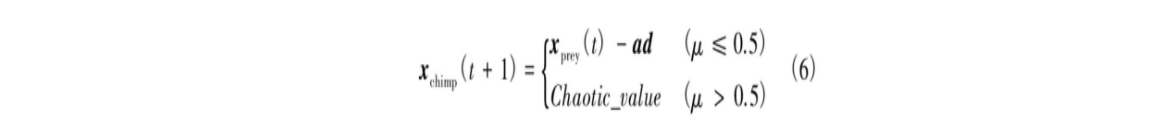
式中:μ为[0,1]范围内的随机数。
三、部分源代码
%___________________________________________________________________%
% You can simply define your cost in a seperate file and load its handle to fobj
% The initial parameters that you need are:
%__________________________________________
% fobj = @YourCostFunction
% dim = number of your variables
% Max_iteration = maximum number of generations
% SearchAgents_no = number of search agents
% lb=[lb1,lb2,...,lbn] where lbn is the lower bound of variable n
% ub=[ub1,ub2,...,ubn] where ubn is the upper bound of variable n
% If all the variables have equal lower bound you can just
% define lb and ub as two single number numbers
%
%__________________________________________
clear all
clc
SearchAgents_no=30; % Number of search agents
N=SearchAgents_no;
Function_name='F2'; % Name of the test function that can be from F1 to F23 (Table 3,4,5 in the paper)
Max_iteration=500; % Maximum numbef of iterations
Max_iter=Max_iteration;
% Load details of the selected benchmark function
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name);
[ABest_scoreChimp,ABest_posChimp,Chimp_curve]=Chimp(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
[PSO_gBestScore,PSO_gBest,PSO_cg_curve]=PSO(N,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
[TACPSO_gBestScore,TACPSO_gBest,TACPSO_cg_curve]=TACPSO(N,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
[MPSO_gBestScore,MPSO_gBest,MPSO_cg_curve]=MPSO(N,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
% PSO_cg_curve=PSO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % run PSO to compare to results
figure('Position',[500 500 660 290])
%Draw search space
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(Function_name);
title('Parameter space')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([Function_name,'( x_1 , x_2 )'])
%Draw objective space
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(MPSO_cg_curve,'Color','g')
hold on
semilogy(PSO_cg_curve,'Color','b')
hold on
semilogy(TACPSO_cg_curve,'Color','y')
hold on
semilogy(Chimp_curve,'--r')
title('Objective space')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
axis tight
grid on
box on
legend('MPSO','PSO','TACPSO','Chimp')
img =gcf; %获取当前画图的句柄
print(img, '-dpng', '-r600', './img.png') %即可得到对应格式和期望dpi的图像
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by TACPSO is : ', num2str(TACPSO_gBestScore)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by PSO is : ', num2str(PSO_gBestScore)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by PSO is : ', num2str(MPSO_gBestScore)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by Chimp is : ', num2str(ABest_scoreChimp)]);
%% % Chimp Optimization Algorithm (ChOA) source codes version 1.0
function O=chaos(index,max_iter,Value)
O=zeros(1,max_iter);
x(1)=0.7;
switch index
%Chebyshev map
case 1
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=cos(i*acos(x(i)));
G(i)=((x(i)+1)*Value)/2;
end
case 2
%Circle map
a=0.5;
b=0.2;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=mod(x(i)+b-(a/(2*pi))*sin(2*pi*x(i)),1);
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 3
%Gauss/mouse map
for i=1:max_iter
if x(i)==0
x(i+1)=0;
else
x(i+1)=mod(1/x(i),1);
end
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 4
%Iterative map
a=0.7;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=sin((a*pi)/x(i));
G(i)=((x(i)+1)*Value)/2;
end
case 5
%Logistic map
a=4;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1)=a*x(i)*(1-x(i));
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 6
%Piecewise map
P=0.4;
for i=1:max_iter
if x(i)>=0 && x(i)<P
x(i+1)=x(i)/P;
end
if x(i)>=P && x(i)<0.5
x(i+1)=(x(i)-P)/(0.5-P);
end
if x(i)>=0.5 && x(i)<1-P
x(i+1)=(1-P-x(i))/(0.5-P);
end
if x(i)>=1-P && x(i)<1
x(i+1)=(1-x(i))/P;
end
G(i)=x(i)*Value;
end
case 7
%Sine map
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1) = sin(pi*x(i));
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
case 8
%Singer map
u=1.07;
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1) = u*(7.86*x(i)-23.31*(x(i)^2)+28.75*(x(i)^3)-13.302875*(x(i)^4));
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
case 9
%Sinusoidal map
for i=1:max_iter
x(i+1) = 2.3*x(i)^2*sin(pi*x(i));
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
case 10
%Tent map
x(1)=0.6;
for i=1:max_iter
if x(i)<0.7
x(i+1)=x(i)/0.7;
end
if x(i)>=0.7
x(i+1)=(10/3)*(1-x(i));
end
G(i)=(x(i))*Value;
end
end
O=G;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
四、运行结果
五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
[3]程国森,崔东文.黑猩猩优化算法-极限学习机模型在富水性分级判定中的应用[J].人民黄河. 2021,43(07)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120858521
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)