【语音分离】基于matlab FASTICA语音分离【含Matlab源码 1023期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【语音分离】基于matlab FASTICA语音分离【含Matlab源码 1023期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、FASTICA简介
1 基础概念
FastICA算法,又称不动点(Fixed-Point)算法,是由芬兰赫尔辛基大学Hyvärinen等人提出来的。是一种快速寻优迭代算法,与普通的神经网络算法不同的是这种算法采用了批处理的方式,即在每一步迭代中有大量的样本数据参与运算。但是从分布式并行处理的观点看该算法仍可称之为是一种神经网络算法。
FastICA算法有基于峭度、基于似然最大、基于负熵最大等形式,这里,我们介绍基于负熵最大的FastICA算法(可以有效地把不动点迭代所带来的优良算法特性与负熵所带来的更好统计特性结合起来)。它以负熵最大作为一个搜寻方向,可以实现顺序地提取独立源,充分体现了投影追踪(Projection Pursuit)这种传统线性变换的思想。此外,该算法采用了定点迭代的优化算法,使得收敛更加快速、稳健。
因为FastICA算法以负熵最大作为一个搜寻方向,因此先讨论一下负熵判决准则。由信息论理论可知:在所有等方差的随机变量中,高斯变量的熵最大,因而我们可以利用熵来度量非高斯性,常用熵的修正形式,即负熵。根据中心极限定理,若一随机变量由许多相互独立的随机变量之和组成,只要具有有限的均值和方差,则不论其为何种分布,随机变量较更接近高斯分布。换言之,较的非高斯性更强。因此,在分离过程中,可通过对分离结果的非高斯性度量来表示分离结果间的相互独立性,当非高斯性度量达到最大时,则表明已完成对各独立分量的分离。
2 负熵的定义


3 算法原理










4 算法步骤

三、部分源代码
clc
clear all
%% --------------------------------- Set Parameters
N = 1; %The number of observed mixtures
Ns = 2; %The number of independent sources
Ls = 1000; %Sample size, i.e.: number of observations
finalTime = 40*pi; %Final sample time (s)
initialTime = 0; %Initial sample time (s)
%% --------------------------------- Generating Data for SSA-ICA
Amix = rand(N,Ns); %Amix is a random N x Ns mixing matrix
timeVector = initialTime:(finalTime-initialTime)/(Ls-1):finalTime; %Vector of time coordinates
source1 = sin(1.1*timeVector); %Independent source component 1, sin(a * t)
source2 = cos(0.25*timeVector); %Independent source component 2, cos(b * t)
S = [source1;source2]; %Source Matrix
figure
plot(timeVector,source1) %Plotting the N independent sources vs. time
xlabel('time (s)')
ylabel('Signal Amplitude')
legend('source 1')
figure
plot(timeVector,source2) %Plotting the N independent sources vs. time
xlabel('time (s)')
ylabel('Signal Amplitude')
legend('source 2')
Yobs = Amix*S; %Matrix consisting of M samples of N observed mixtures
figure
plot(timeVector,Yobs) %Plotting the observed signal vs. time
xlabel('time (s)')
ylabel('Signal Amplitude')
legend('observed signal')
function [Sest] = Fast_ICA(Xobs,C)
%% Preprocessing, Centering
SX = size(Xobs);
N = SX(1);
M = SX(2);
X = Xobs'; %X is the transpose of the matrix of M samples of N mixtures, used in subsequent calculations
Xmean = mean(X); %Xmean is the mean vector of the matrix X
for i = 1:N
X(:,i) = X(:,i) - Xmean(i); %The matrix X is centered by subtracting each of the N mixtures by their corresponding sample averages
end
%% Preprocessing, Whitening
ExxT = cov(X); %The covariance matrix of X is computed and stored in ExxT
[E,D] = eig(ExxT); %Eigenvalue decomposition is applied on the covariance matrix of X, ExxT
Z = E*1/sqrt(D)*E'*X'; %The matrix X is whitened to Z
%% FastICA algorithm
W = 0.5*ones(C,N); %Initializing W, a matrix consisting of columns corresponding with the inverse of the (transformed) mixing Amix
iterations = 100; %The amount of iterations used in the fastICA algorithm
for p = 1:C
wp = ones(N,1)*0.5;
wp = wp / sqrt(wp'*wp);
for i = 1:iterations
G = tanh(wp'*Z);
Gder = 1-tanh(wp'*Z).^2;
wp = 1/M*Z*G' - 1/M*Gder*ones(M,1)*wp;
dumsum = zeros(C,1);
for j = 1:p-1
dumsum = dumsum + wp'*W(:,j)*W(:,j);
end
wp = wp - dumsum;
wp = wp / sqrt(wp'*wp);
end
W(:,p) = wp;
end
%% Output Results
W = W/sqrt(2); %The factor sqrt(2) is an emirical constant added to make the predictions fit the data properly. The source of the factor has yet to be determined.
Sest = W'*Z;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
四、运行结果

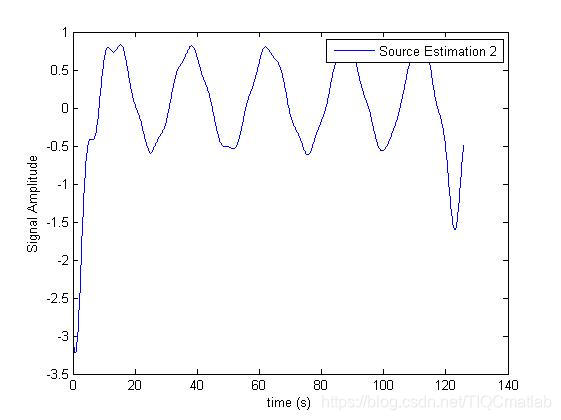
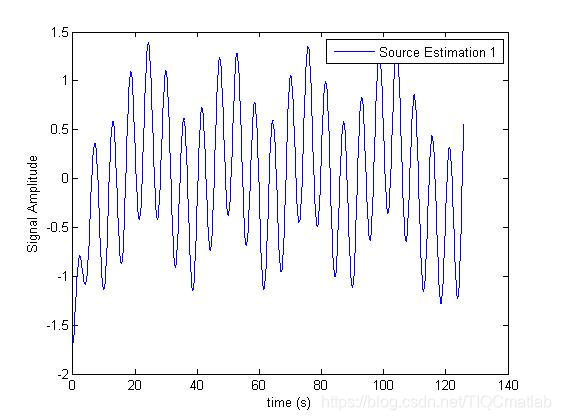
五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118033949
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)